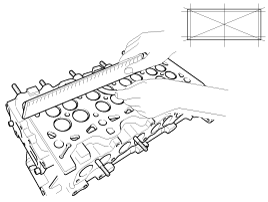
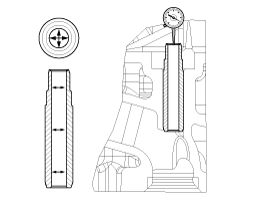
Inspect for flatness.
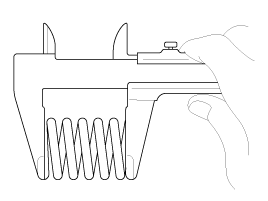
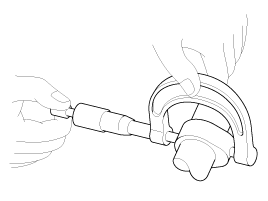
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surface the contacting the cylinder block and the manifolds for warpage.
Flatness of cylinder head gasket surface :
Less than 0.03mm (0.0012in) for width
Less than 0.09mm (0.0035in) for length
Less than 0.012mm/50X50mm (0.0005in/1.9685X1.9685in)
Flatness of manifold mating surface :
Less than 0.025mm (0.0010in) for width
Less than 0.160mm (0.0063in) for length