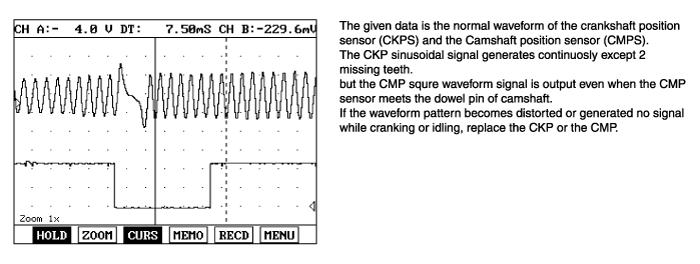
The crankshaft angular sensor detects and counts the teeth on the crankshaft and provides ECM with the information on the current position of crank angle and cylinder. This signal is fed to ECM to be used to determine the engine speed and adjust the fuel injection timing. The camshaft position sensor detects the teeth target wheel and provides ECM with the information on the current position of piston and cylinder.
This signal is fed to ECM to be used to determine the sequence of fuel injection.
In case of the the crankshaft angular sensor or the camshaft position sensor failure, the engine symptoms will occur a running engine stall, starting impossible and rough idle with noise.
If the difference between actual CKP value and calculated CKP value is generated, the ECM judged this as a fault and DTC is set.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause |
DTC Strategy | ● Signal check | ● Open or short to signals(+,-) harness ● Open in ground harness ● Faulty CKP ● Faulty CKP tone wheel ● Faulty ECM |
Enable Conditions | ● Engine run | |
Threshold Value | ● Crank angular with acceleration or deceleration is out of allowed limits (dynamic plausibility) | |
Diagnostic Time | ● 0.09 sec. | |
MIL Fuel Limit Fuel Cut EGR Off | ● No ● No ● Yes ● No |
CKP | |
Resistance | 860 ± 10% Ω at 20°C |