Special injectors with hydraulic servo-system and electrical triggering element (solenoid valve) are used with the common rail system in order to achieve efficient start of injection and precise injected fuel quantity.
Metering and spray preparation of the diesel fuel, as needed by the engine according to the engine map, Realization of pilot and main injection and post injection if required.
Pilot injection is used to reduce the engine noise and vibration and post injection is used to reduce the NO and N0X in the exhaust gas.
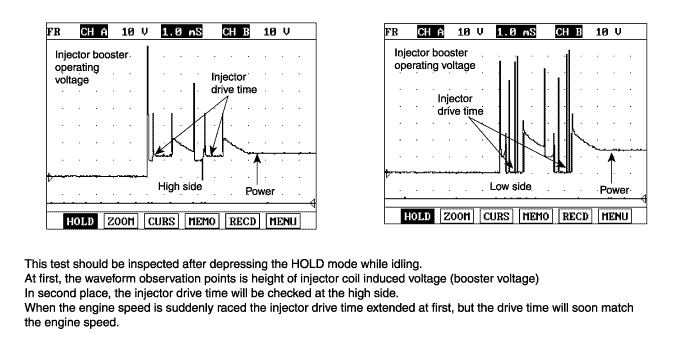
Control of injected quantity and injection timing based on the system pressure and enerizing time as actuated by the ECM. The injected fuel quantity is now defined by the injector opening time and rail pressure.
Injection is terminated when the solenoid valve is no longer triggered and closes as a result.
In case of more than 2 injectors failure, the engine symptoms will occur the running engine stall and the starting impossible.
If the signal exceeds threshold value, the ECM judged this as a fault and DTC is set.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause |
DTC Strategy | ● Circuit continuity check | ● Short to battery in power circuit ● Faulty injector ● Faulty ECM |
Enable Conditions | ● Engine run | |
Threshold Value | ● Overcurrent high side connection : injector current increases the maximum value of 28 A ~ 36 A | |
Diagnostic Time | ● 0.3 sec. | |
MIL Fuel Limit Fuel Cut EGR Off | ● Yes ● Yes ● No ● No |
Injector | |
Resistance | 0.365 ± 0.055 Ω at 20°C |