The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system is used to divert some of the exhaust gas to the engine inlet system in order to reduce an excess of air and the temperature in the combustion chamber.
This device also significantly reduces emissions of the nitric oxide at the exhaust.
The EGR system is composed of a solenoid valve, a proportional pneumatic valve and an air flow meter.
The EGR solenoid valve controls the opening and closing the pneumatic valve using the low pressure from the braking assistance circuit. The low pressure is created by the vaccum pump located at the end of the alternator.
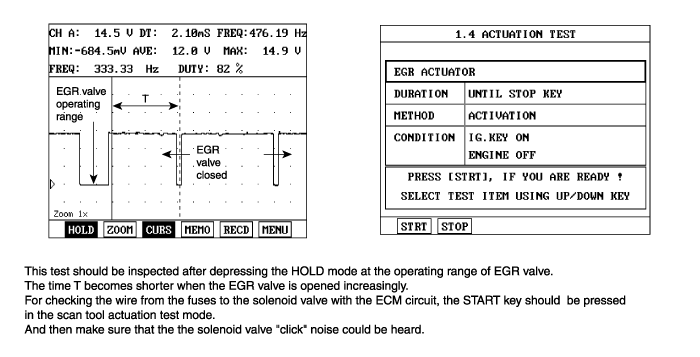
The duty control of the solenoid valve is determined by the injection computer depending on the air flow requested.
In case of EGR solenoid valve failure, the engine performance will be reduced.
If the signal exceeds threshold value, the ECM judged this as a fault and DTC is set.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause |
DTC Strategy | ● Rationality check | ● Fuse blown ● Faulty MAFS ● Faulty EGR system ● Faulty Turbo charger system ● Faulty ECM |
Enable Conditions | ● Engine run | |
Threshold Value | ● 1400 < Engine speed < 2000 rpm and injection quantity < 0.2 mcc. | |
Diagnostic Time | ● 6 sec. | |
MIL Fuel Limit Fuel Cut EGR Off | ● Yes ● Yes ● No ● Yes |
EGR | |
Resistance | Operating Frequency |
14 ~ 17 Ω at 20°C | 300 Hz |