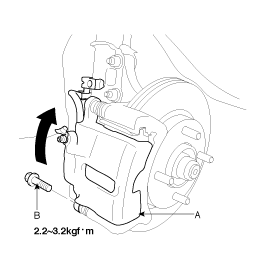
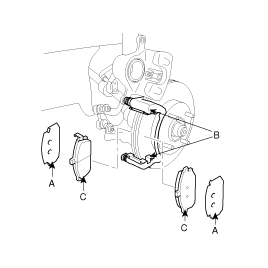
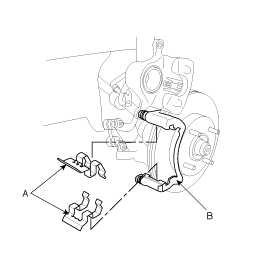
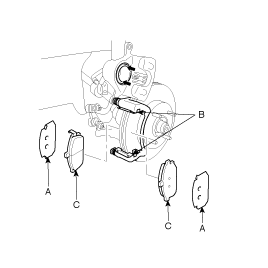
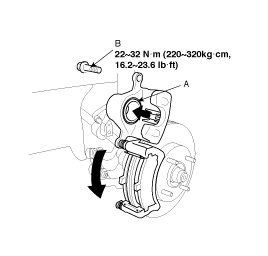
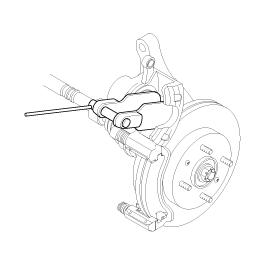
Check the brake pad thickness throgh the caliper body inspection hole
Pad thickness
Standard value : 11.0 mm ( 0.43 in.)
Service limit : 2.0 mm (0.0787 in.)
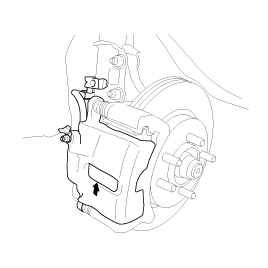
If the pad lining thickness is out of specilfication, left and right pads must be replaced as a complete set.
When the thickness difference between the left pad right pad is large, check the sliding condition of the pistion and the guide rod.