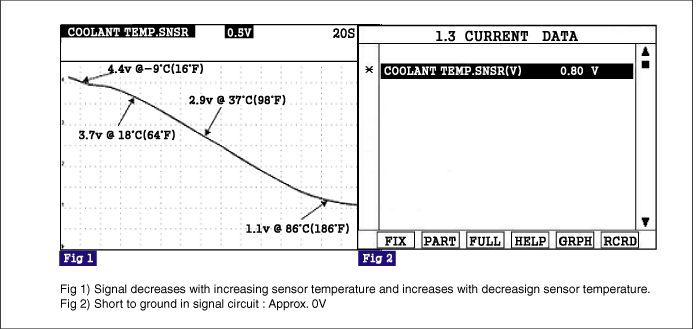
The Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS) is located in the engine coolant passage of the cylinder head for detecting the engine coolant temperature. The ECTS uses a thermistor whose resistance changes with the temperature. The electrical resistance of the ECTS decreases as the temperature increases, and increases as the temperature decreases. The reference 5 V in the PCM is supplied to the ECTS via a resistor in the PCM. That is, the resistor in the PCM and the thermistor in the ECTS are connected in series. When the resistance value of the thermistor in the ECTS changes according to the engine coolant temperature, the output voltage also changes.During cold engine operation the PCM increases the fuel injection duration and controls the ignition timing using the information of engine coolant temperature to avoid engine stalling and improve drivability.
PCM sets DTC P0117 if the PCM detects signal voltage lower than the possible range of a properly operating ECTS.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause |
DTC Strategy | ● Voltage range check | ● Short to ground in signal harness ● Contact resistance in connections. ● Faulty ECT sensor |
Enable Conditions | ● 6 < Battery voltage < 16V ● After 60 seconds from engine start in case of short circuit to B+ or open circuit | |
Threshold value | ● Measured coolant temperature > 138℃(280℉). | |
Diagonostic Time | ● 5 sec. | |
Fall Safe | ● The limp-home value of ECTS depends on intake air temperature. |
Temp.(°C) | Temp.(°F) | Resistance(kΩ) | Temp.(°C) | Temp.(°F) | Resistance(kΩ) |
-20 | -4 | 14.13~16.83 | 40 | 104 | 1.15 |
0 | 32 | 5.79 | 60 | 140 | 0.59 |
20 | 68 | 2.31~2.59 | 80 | 176 | 0.32 |