Read "DTC Status" parameter.
The Misfire monitor diagnostic is based on crankshaft rotation velocity variation. The ECM determines crankshaft rotational velocity using the crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sensor. When a cylinder misfires the crankshaft slows down momentarily. By monitoring the crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals, the ECM can calculate when a misfire occurs. For a non-catalyst damaging misfire, the diagnostic will be required to report a misfire present within 1000-3200 engine revolutions. For catalyst damaging misfire, the diagnostic will respond to monitor 200 engine revolutions. Rough roads may cause false misfire detection. The rough road(acceleration)sensor consists of a piezoelectric vibration pick up which detects vertical acceleration of the vehicle. The sensor signal is used by the ECM to determine the degree of vertical movement of the car, for example, on a bumpy road. Since this may also cause uneven engine running, the ECM uses the signal to distinguish the phenomenon from actual misfiring.
The ECM must monitor the engine for misfiring possibly caused by ignition coil defects or injector fails. If misfiring is detected, the ECM will identify the cylinder(s) that has(have) misfired and then calculate misfiring rate for a given duration. The DTC for Misfire (P0301 to 0306) is set as soon as the misfiring rate exceeds the limit which may result in damage to the catalyst or increase emissions. The ECM stores the individual DTC for a cylinder which has more than a 10% total misfire rate.
ITEM | DETECTING CONDITION | POSSIBLE CAUSE | |
DTC Strategy | ●Calculation of engine roughness | ●Faulty spark plugs, hightension lead, or Ignition coil ● Incorrect valve timing ● Uneven compression ● Air leakage ● Improper Fuel pressure or dirty fuel. ● Blocked/Leaking injectors ● Leakage between cooling system and cylinder | |
Enable Conditions | ●After starting ●Mass air flow 〉Approx. 0 ●550< Engine speed(RPM)〈 6500 ●Intake air mass gradient is in predetermined range ●Throttle Angle gradient is in predetermined range ●No injector shut off ●No rough road | ||
Case 1) | Threshold Value | ●Misfire= 6~17 %within 200 rev. | |
Diagnosis Time | ●200 revolution: 3*200 revolution | ||
Case2) | Threshold Value | ●First 1000 rev.: Misfire〉2% ●After first 1000 rev.: Misfire 〉2% | |
Diagnosis Time | ●1000 revolution: 4*1000 revolution | ||
If any codes relating to injectors, HO2S, ECT(Engine Coolant Temperature)Sensor, Throttle Position sensor or Mass Air Flow Sensor are stored, do ALL REPAIRS associated with those codes before proceeding with this troubleshooting tree.
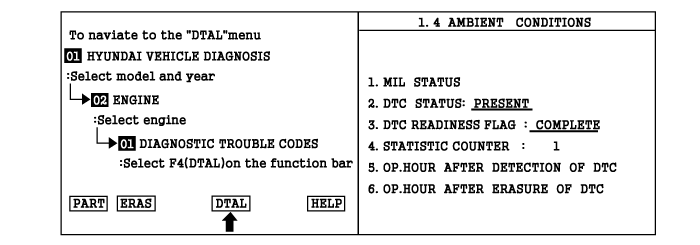
Connect scan tool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode.
Press F4(DTAL) to select DTC information from the DTCs menu.
Confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete". If not, drive the vehicle within conditions noted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions
Read "DTC Status" parameter.

Is parameter displayed "History(Not Present) fault"?
History (Not Present) fault : DTC occurred but has been cleared.
Present fault : DTC is occurring at present time.

▶ Fault is intermittent caused by poor contact in the sensor's and/or ECM's connector or was repaired and ECM memory was not cleared. Thoroughly check connectors for loose or poor connections, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage. Repair or replace as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Go to "Monitor Actuation Test" procedure.
The main purpose of this test is to identify potential engine mechanical condition problems and fuel and ignition systems problems that are not common to all cylinders. For best results, perform this test while maintaining as steady an rpm reading as possible.Caution! Before beginning tests; set the parking brake, place gear selector in P or N and block drive wheels for safety.
Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature and let it idle.
Using a Scan Tool and select "INJECTOR #1" parameter on the Actuation Test mode shown in the figure.
Monitor engine rpm and shut off the injector #1 by pressing "STRT(F1)" key.
Repeat procedure on all injectors and record the engine rpm.
Specification : All cylinders should show an even RPM drop.
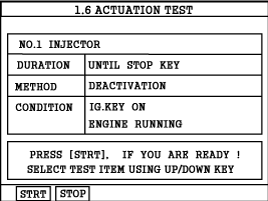
Was each cylinder's rpm drop within the same value?

▶ Go to "Timing Inspection" procedure

▶ Cylinders with the least amount of RPM drop are not contributing their share of power. Go to "Spark plug cable Inspection" procedure.
If the RPM loss between cylinders is quite large(200RPM or more) and engine has high mileage, there is possibility of engine wear. Perform compression test with pressure gauge to check the engine wear.
Remove suspect cylinder's spark plug cable.
Visually/physically inspect the following items:
Damage, crack and flashover
Measure the resistance of the spark plug cable referring to specification.
Specification :
SPARK PLUG INSPECTION | |||||
N0.1 | No.2 | No.3 | No.4 | No.5 | No.6 |
4.39~6.59 | 2.28~3.43 | 3.49~5.24 | 1.9~2.86 | 3.25~4.87 | 1.3~1.95 |
Resistance should not be higher than 10,000Ω per foot of cable. If resistance is higher than specification, replace the cable.
Is resistance within the specification?

▶ Go to "Spark Plug Inspection " procedure.

▶ Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Remove suspect cylinder's spark plugs.
Visually/physically inspect the following items:
Damaged insulation, Worn electrodes, Oil or fuel fouled, Loose terminals and cracks.
Check for plug gap : 1.0 - 1.1 mm (0.039 - 0.043 in.).
Check if the spark plug for the relevant cylinder is lighter in color than the other plugs.
Was a problem found in any of the above areas?

'Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

Go to "Fuel Injector Inspection" procedure.
Check the fuel injectors for clogging or any restrictions.
Test Condition : Ignition "OFF"
Specification : No clogging and restriction
Is the fuel injector OK?

▶ Visually/physically inspect the engine mechanical problem as below:
Bent push rods
Leaky or sticky valves or rings
Excessive valve deposits
Weak valve spring
Leaking head gasket
If NG, repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
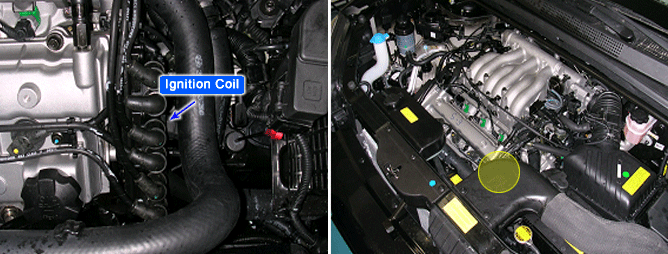
If OK, go to "Ignition Coil Inspection" procedure.

▶ Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Ignition "OFF"
Disconnect ignition coil connector
Visually/physically inspect the following items:
Damage, cracks and flashover.
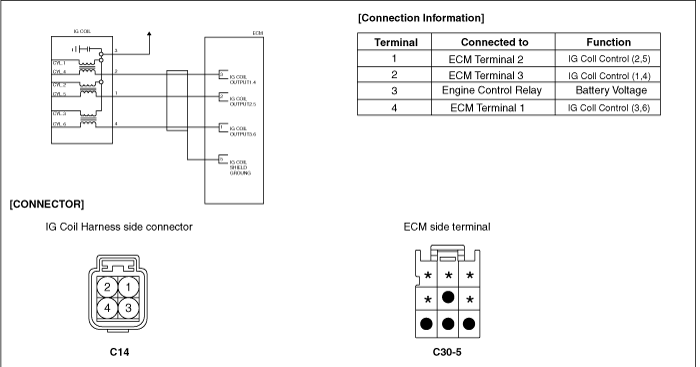
Measure the resistance between terminals 2 and 3 of the primary ignition coil (Component side).
Specification : Approx. 0.96 ± 10%Ω at 20°C(68°C)
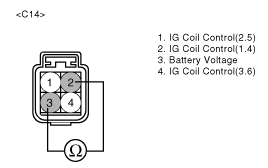
Is resistance within the specification?

▶ Go to "Timing Inspection" procedure.

▶ Test with a new ignition coil and check for proper operation. If problem is corrected, replace ignition coil and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Start engine and let vehicle idle
Connect scantool and select "Current Data" mode
Monitor "CKP T/WHEELS-LO CMP" & "CKP T/WHEELS-HI CMP" parameters on the Scantool data list.
Specification :
"CKP T/WHEELS-LO CMP" : 38 +/- 4 tooth
"CKP T/WHEELS-HI CMP" : 98 +/- 4 tooth
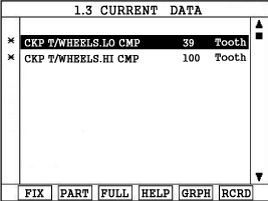
Are "CKP T/WHEELS-LO CMP" & "CKP T/WHEELS-HI CMP" parameters within the specification?

▶ Go to " Air Leakage Inspection " procedure.

▶ Remove Crankshaft Position Sensor(CKPS) and calculate air gap between sensor and flywheel/torque converter. Readjust as necessary and go to next step.
Air gap [0.3~1.7 mm [0.012~0.067 in] = measure distance from hosing to teeth on flywheel/torque converter (measurement "A") and from mounting surface on sensor to sensor tip (measurement "B") subtract "B" from "A"..
If fail to synchronize CKPS with CMPS, check that the crankshaft and camshaft are correctly aligned the matching marks of the pulleys. Repair or readjust as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Visually/physically inspect the air leakage in intake/exhaust system as following items,
If OK, go to next step
If NG, repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks and improper connections.
Throttle body gasket
Gasket between intake manifold and cylinder head
Seals between intake manifold and fuel injectors
Exhaust system between HO2S and Three way catalyst for air leakage
Was a problem found in any of the above areas?

▶ Go to "Fuel System Inspection" procedure

▶ Repair air leakage and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Check the fuel for excessive water, alcohol, or other contaminants. Replace contaminated fuel as necessary.
Install a fuel pressure gage.
Start engine and let it idle. Inspect fuel pressure with vacuum hose disconnected.
Test Condition : Engine "ON" at Idle
Specification : 330~350kPa(3.30~3.50 kg/㎠, 47~50 psi)
Is fuel pressure within the specification?

▶ Check for poor connection between ECM and component: backed out terminal, improper mating, broken locks or poor terminal to wire connection. Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure

▶ Repair as necessary refer to inspection noted as below and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure
Check if fuel line pressure decreases when accelerating quickly.
- If it does, check fuel pump maximum pressure. If pressure is OK, check fuel line and filter for clogging. |
If fuel pressure is lower than specification : Check for fuel line pressure while pinching fuel return hose.
- If pressure quickly increases, check pressure regulator - If pressure gradually increases, check for clogging between fuel pump and pressure regulator. If hose is not clogged, check fuel pump maximum pressure. |
If fuel pressure is higher than specification : Is fuel line clogged?
- If it is not, replace pressure regulator. - If it is, replace it. |
After a repair, it is essential to verify that the fault has been corrected.
Connect scan tool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode.
Press F4(DTAL) and confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete". If not, drive the vehicle within conditions noted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions.
Read "DTC Status" parameter.
Is parameter displayed "History(Not Present) fault"?

▶ System performing to specification at this time. Clear the DTC

▶ Go to the applicable troubleshooting procedure.