Normally functioning refrigeration system.
Gauge reading : Low pressure side : 0.15~0.25 MPa (21.8~36.3 psi, 1.5~2.5 kgf/cm²) High pressure side : 1.37~1.57 MPa (199~228 psi, 14~16 kgf/cm²) |
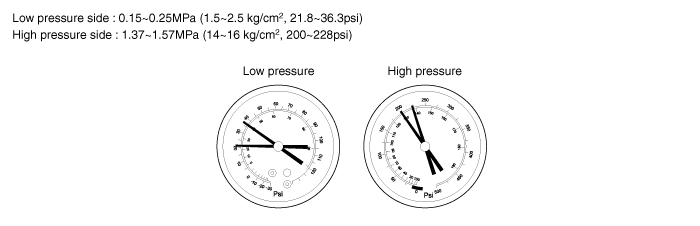
This is a method in which the trouble is located by using a gauge set. Read the gauge pressure when these conditions are established.
Temperature at the air inlet with the switch set at RECIRC is 30~35°C (86~95°F)
Engine running at 1,500rpm
Blower speed control knob on "4" position
Temperature control knob on "COOL" position
It should be noted that the gauge indications may vary slightly due to ambient temperature conditions
Normally functioning refrigeration system.
Gauge reading : Low pressure side : 0.15~0.25 MPa (21.8~36.3 psi, 1.5~2.5 kgf/cm²) High pressure side : 1.37~1.57 MPa (199~228 psi, 14~16 kgf/cm²) |

Moisture present in refrigeration system.
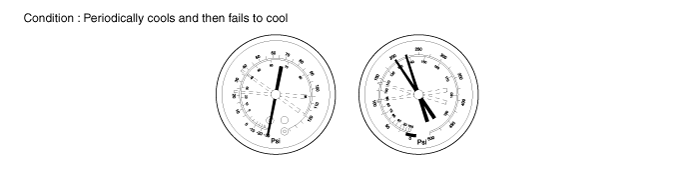
Symptom seen in refrigeration system | Probable cause | Diagnosis | Remedy |
During operation, pressure on low pressure side sometimes become a vacuum and sometime normal | Moisture entered in refrigeration system freezes at expansion valve orifice and temporarily stops cycle, but normal state is restored after a time when the ice melts | ● Drier in oversaturated state ● Moisture in refrigeration system freezes at expansion valve orifice and block circulation of refrigerant | - Raplace drier - Remove moisture in cycle through repeatedly evacuating air - Evacuate the system and charge new refrigerant to specified amount. |
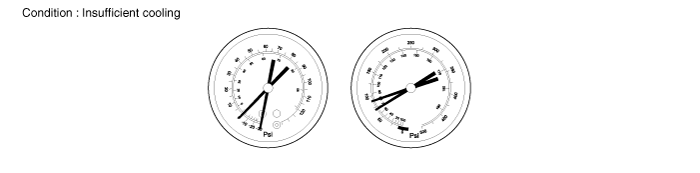
Insufficient cooling
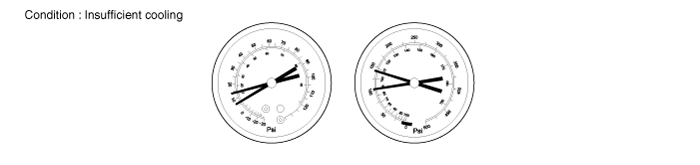
Symptom seen in refrigeration system | Probable cause | Diagnosis | Remedy |
● Pressure low on both low and high pressure sides ● Insufficient cooling performance | Gas leakage at some place in refrigeration system | ● Insufficient refrigerant in system ● Refrigerant leaking | - Check for gas leakage with gas leak detector and repair if necessary - Charge proper amount of refrigerant - If indicated pressure value is near 0 when connected to gauge, create the vacuum after inspecting and repairing the location of the leak |
Poor circulation of refrigerant
Symptom seen in refrigeration system | Probable cause | Diagnosis | Remedy |
● Pressure low in both low and high pressure sides ● Frost on tube from receiver to unit | Refrigerant flow obstructed by dirt in drier | Condenser clogged | Replace drier |
Refrigerant does not circulate
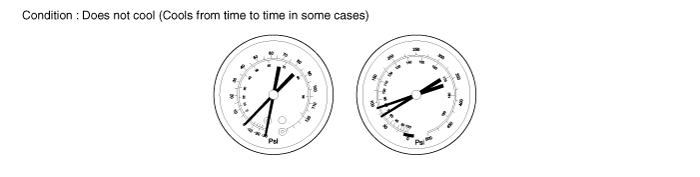
Symptom seen in refrigeration system | Probable cause | Diagnosis | Remedy |
● Vacuum indicated on low pressure side, very low pressure indicated on high pressure side ● Frost or dew seen on piping before and after receiver/drier or expansion valve | ● Refrigerant flow obstructed by moisture or dirt in refrigeration system ● Refrigerant flow obstructed by gas leakage from expansion valve | Refrigerant does not circulate | - Check expansion valve - Clean out dirt in expansion valve by blowing with air - Replace drier - Evacuate the system and charge new refrigerant to specified amount. - For gas leakage from expansion valve, replace expansion valve |
Refrigerant overcharged or insufficient cooling of condenser
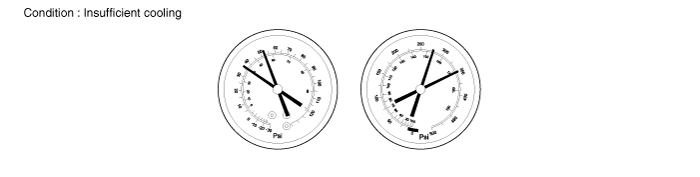
Symptom seen in refrigeration system | Probable cause | Diagnosis | Remedy |
Pressure too high on both low and high pressure sides | ● Unable to develop sufficient performance due to excessive ● Insufficient cooling of condenser | ● Excessive refrigerant in cycle → refrigerant overcharged ● Condenser cooling → condenser fins clogged or condenser fan faulty | - (1) Clean condenser - (2) Check cooling fan with fluid coupling operation. - (3) If (1) and (2) are in normal state, check amount of refrigerant. Evacuate the system and charge new refrigerant to specified amount. |
Air present in refrigeration system
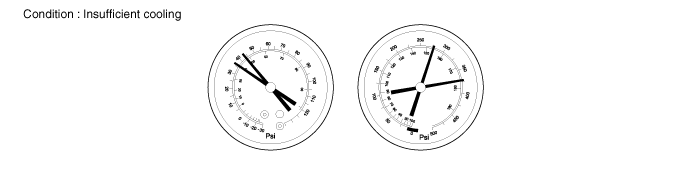
Symptom seen in refrigeration system | Probable cause | Diagnosis | Remedy |
● Pressure too high on both low and high pressure sides ● The low pressure piping hot to the touch | Air entered in refrigeration system | ● Air present in refrigeration system ● Insufficient vacuum purging | - Check compressor oil to see if it is see if it is dirty or insufficient - Evacuate the system and charge new refrigerant to specified amount. |
Expansion valve improperly

Symptom seen in refrigeration system | Probable cause | Diagnosis | Remedy |
● Pressure too high on both low and high pressure sides ● Frost or large amount of dew on piping on low pressure side | Trouble in expansion valve | ● Excessive refrigerant in low pressure piping ● Expansion valve opened too wide | - Check expansion valve - Replace if defective |
Defective compression compressor
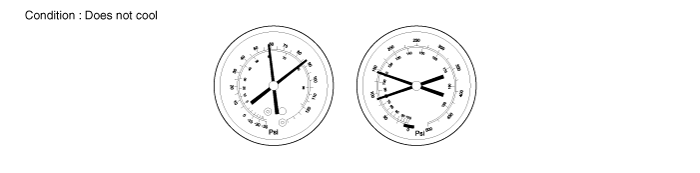
Symptom seen in refrigeration system | Probable cause | Diagnosis | Remedy |
● Pressure too high on low and high pressure sides ● Pressure too low to on high pressure side | Internal leak in compressor | ● Compression defective ● Valve leaking or broken sliding parts | Repair or replace compressor |
Always conduct a leak test with an electronic leak detector whenever leakage or refrigerant is suspected and when conducting service operations which are accompanied by disassembly or loosening or connection fittings.
In order to use the leak detector properly, read the manual supplied by the manufacturer.
Check the torque on the connection fittings and, if too loose, tighten to the proper torque. Check for gas leakage with a leak detector.
If leakage continues even after the fitting has been tightened, discharge the refrigerant from the system, disconnect the fittings, and check their seating faces for damage. Always replace, even if the damage is slight.
Check the compressor oil and add oil if required.
Charge the system and recheck for gas leaks. If no leaks are found, evacuate and charge the system again.
Air conditioning refrigerant or lubricant vapor can irritate your eyes, nose, or throat.
Be careful when connecting service equipment.
Do not breathe refrigerant or vapor.
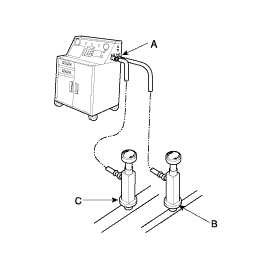
Connect a R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging station (A) to the high-pressure service port (B) and the low-pressure service port (C), as shown, following the equipment manufacturer's instruction.
Measure the amount of refrigerant oil removed from the A/C system after the recovery process is completed. Be sure to put the same amount of new refrigerant oil back into the A/C system before charging.
Air conditioning refrigerant or lubricant vapor can irritate your eyes, nose, or throat.
Be careful when connecting service equipment.
Do not breathe refrigerant or vapor.
When an A/C System has been opened to the atmosphere, such as during installation or repair, it must be evacuated using a R-134a refrigerant recover/recycling/charging station (If the system has been open for several days, the receiver/dryer should be replaced, and the system should be evacuated for several hours.)
Connect a R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging station(A) to the high-pressure service port(B) and the low-pressure service port(C), as shown, following the equipment manufacturer's instruction. Evacuate the system.

If the low-pressure does not reach more than 93.3 kPa(700 mmHg, 27.6 in.Hg) in 15 minutes, there is probably a leak in the system. Partially charge the system (see page HA-24), and check for leaks (see page HA-22).
Air conditioning refrigerant or lubricant vapor can irritate your eyes, nose, or throat.
Be careful when connecting service equipment.
Do not breathe refrigerant or vapor.
Connect a R-134a refrigerant recover/recycling/charging station (A) to the high-pressure service port (B) and the low-pressure service port (C), as shown, following the equipment manufacture's instructions.

Add the same amount of new refrigerant oil to the system that was removed during recovery. Use only ND-OIL8 refrigerant oil.
Charge the system with the specified amount of R-134a refrigerant. Do not overcharge the system; the compressor will be damaged.
Refrigerant capacity : 510 ± 25g