Read "DTC Status" parameter.
In order to provide the best possible combination of drivability, fuel economy and emission control, the ECM uses a closed loop air/fuel metering system. The ECM monitors the HO2S signal voltage and adjusts fuel delivery based it in closed loop fuel control. Changes in fuel delivery will be indicated by the long-term and the short-term fuel trim values. The ideal fuel trim value is around 0%. The ECM will add fuel when the HO2S signal is indicating a lean condition. Additional fuel is indicated by fuel trim values that are above 0%. The ECM will reduce fuel when the HO2S signal is indicating a rich condition. Reduction in fuel is indicated by fuel trim values that are below 0%. The DTC relevant to fuel trim will be set when the amount reaches excessive levels because of a lean or rich condition.
Breaking lambda adaptation and lambda controller limits for a an extended period, which initially may have been caused by failures in the fuel or intake system, will involve emission rise, and therefore shall be diagnosed by fuel system monitoring.
If same error code is set in the next driving cycle, the ECM illuminates the MIL. The lambda controller deviations, including adaptive terms, are used for fuel system monitoring. The time counter is increased if lambda controller deviations exceed a specific threshold and the ECM will then set DTC P0171 or P0172 respectively depending on the direction of the deviation. P0171 is set with positive deviation and P0172 is set with negative deviation.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause |
DTC Strategy | ● Monitoring deviation of lambda fuel control | ● Restricted intake or exhaust system ● Dirty engine oil or oil level too high ● Front HO2S or MAFS contamination ● Over purging of the EVAP system ● High fuel pressure ● Faulty sensor signals |
Enable Conditions | ● Estimated canister loading 〉-11% ● Estimated altitude 〈 8000ft ● Coolant temp.〉60℃ (140℉) ● Fueling adaptation 〉14.5% | |
Threshold Value | ● Lambda controller + Trim value 〈-27%(Rich A/F ratio) ● Rich A/F ratio: 300sec. | |
Diagnostic Time | ● 900 sec. |
If any codes relating to fuel system, injectors, HO2S, ECT(Engine Coolant Temperature)Sensor, Throttle Position sensor or Mass Air Flow Sensor are stored, do ALL REPAIRS associated with those codes before proceeding with this troubleshooting tree.
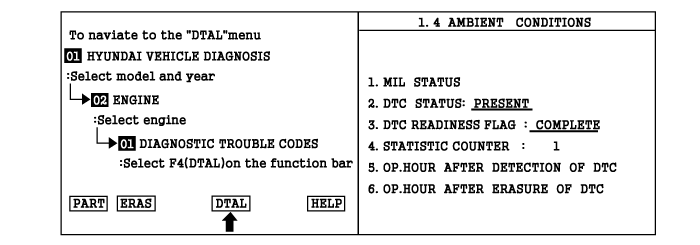
Connect scan tool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode.
Press F4(DTAL) to select DTC information from the DTCs menu.
Confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete". If not, drive the vehicle within conditions noted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions.
Read "DTC Status" parameter.

Is parameter displayed "History(Not Present) fault"?
History (Not Present) fault : DTC occurred but has been cleared.
Present fault : DTC is occurring at present time.

▶ Fault is intermittent caused by poor contact in the sensor's and/or ECM's connector or was repaired and ECM memory was not cleared. Thoroughly check connectors for loose or poor connections, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage. Repair or replace as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Go to "Monitor Actuation Test" procedure.
The main purpose of this test is to identify potential engine mechanical condition problems and fuel and ignition systems problems that are not common to all cylinders. For best results, perform this test while maintaining as steady an rpm reading as possible.
Before beginning tests; set the parking brake, place gear selector in P or N and block drive wheels for safety.
Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature and let it idle.
Using a Scan Tool and select "INJECTOR #1" parameter on the Actuation Test mode shown in the figure.
Monitor engine rpm and shut off the injector #1 by pressing "STRT(F1)" key.
Repeat procedure on all injectors and record the engine rpm.
Specification : All cylinders should show an even RPM drop.
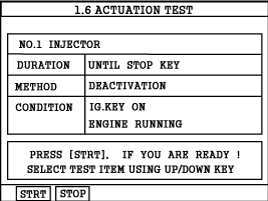
Was each cylinder's rpm drop within the same value?

▶ Go to " Check intake/exhaust system for restriction or leakage " procedure.

▶ Cylinders with the least amount of RPM drop are not contributing their share of power. Go to "Fuel Injector Inspection" procedure and check the suspect cylindersNote) If the RPM loss between cylinders is quite large(200RPM or more) and engine has high mileage, there is possibility of engine wear. Perform compression test with pressure gauge to check the engine wear.
Visually/physically inspect the following items:
Air cleaner filter element for excessive dirt or for any foreign objects
Throttle body inlet for damage or for any foreign objects
Throttle bore, throttle plate and the ICA passages for chocking and for any foreign objects
Restricted exhaust system
Was a problem found in any of the above areas?

▶ Replace or repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Go to "Engine oil contamination Inspection" procedure.
Check the engine oil level. The oil level should be between the min. and max. marking. Fill to the correct oil level.
Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature.
Connect Scantool and note the "SHORT TERM FUEL-B1" parameter on the Scantool data list.
Disconnect and plug the positive crankcase ventilation
Monitor the "SHORT TERM FUEL-B1" parameter on the Scantool data list once again.
Specification : The value should remain more or less unchanged
Is the displayed value within the specification?

▶ Go to "Sensor Contamination Inspection" procedure.

▶ The engine oil is diluted with fuel. Change the oil and oil filter and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Visually/physically inspect following items:
Remove and inspect the front HO2S for any silicon contamination. This contamination will be indicated by a white powdery coating and this will result in a but false voltage signal.
Check MAFS for contamination, deterioration, or damage.
If contamination is evident on the HO2S or MAFS, replace contaminated sensor and go to next step.
Check the EVAP. EM system for possible over.
Remove the manifold side vacuum hose from the EVAP canister purge valve.
Using a hand vacuum pump apply specified vacuum(Approx. 15 in, Hg) to the manifold side of the valve.
Does the valve hold vacuum?

▶ Go to "Fuel System Inspection" procedure.

▶ Repair air leakage and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Check the fuel for excessive water, alcohol, or other contaminants. Replace contaminated fuel as necessary.
Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure regulator and inspect the hose for the presence of fuel. If any fuel is present in the vacuum hose, replace the fuel pressure regulator. Go to next step.
Install a fuel pressure gage.
Start engine and let it idle. With the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure regulator disconnected, inspect fuel pressure.
Specification : 330~350kPa(3.30~3.50 ㎏/㎠, 47~50 psi)
Is fuel pressure within the specification?

▶ Go to "Fuel Injector Inspection" procedure as below

▶ Repair as necessary refer to inspection note as below and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.(Inspection Note)
Check if fuel line pressure decreases when accelerating quickly.
- If it does, check fuel pump maximum pressure. If pressure is OK, check fuel line and filter for clogging |
If fuel pressure is lower than specification : Check for fuel line pressure while pinching fuel return hose.
- If pressure quickly increases, check pressure regulator - If pressure gradually increases, check for clogging between fuel pump and pressure regulator. If hose is not clogged, check fuel pump maximum pressure. |
If fuel pressure is higher than specification : Is fuel line clogged?
- If it is not, replace pressure regulator. - If it is, replace it. |
Check the fuel injectors for clogging or any restrictions.
Test Condition : Ignition "OFF".
Specification : No clogging and restriction.
Is the fuel injector OK?

▶ Visually/physically inspect the engine mechanical problem. Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Check injector for contamination, deterioration, or damage. Substitute with a known-good injector and check for proper operation. If the problem is corrected, replace injector and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Check the fuel injectors for clogging or any restrictions.
Test Condition : Ignition "OFF".
Specification : No clogging and restriction.
Is the fuel injector OK?

▶ Visually/physically inspect the engine mechanical problem. Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Check injector for contamination, deterioration, or damage. Substitute with a known-good injector and check for proper operation. If the problem is corrected, replace injector and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
After a repair, it is essential to verify that the fault has been corrected.
Connect scan tool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode.
Press F4(DTAL) and confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete". If not, drive the vehicle within conditions noted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions.
Read "DTC Status" parameter.
Is parameter displayed "History(Not Present) fault"?

▶ System performing to specification at this time. Clear the DTC.

▶ Go to the applicable troubleshooting procedure.