DTC | Diagnostic item |
P0101 P0102 P0103 | Mass Air Flow Circuit Rang/Performance Problem Mass Air Flow Circuit Low Voltage Mass Air Flow Circuit High Voltage |
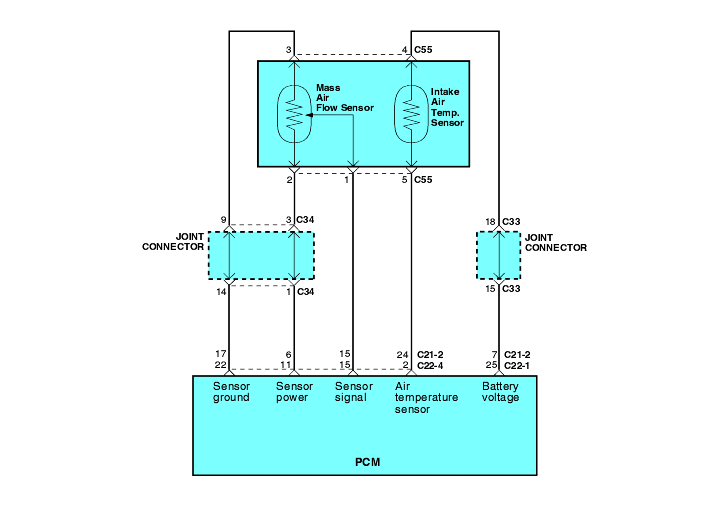
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is located near the air cleaner.
The sensor measures the mass of air passing through the air intake and generates a voltage signal. The Engine Control Module(ECM) receives the voltage generated by the sensor and uses the signal to set fuel injector base pulsewidth and ignition timing.
The voltage of the sensor increases as mass air flow increases.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● While the engine is running, the mass air flow sensor outputs a voltage signal which corresponds to the mass of air flow. ● The engine control module checks whether the voltage of this signal output by the mass air flow sensor while the engine is running at of abovethe set value. Check Area ● At idle rpm ● Or engine speed is 3000 r/min or more Judgment Criteria ● Sensor output voltage has continued to be 0.5V or lower for 4 sec. Check Area ● Throttle position sensor voltage is 12V or lower. ● Engine speed is 2000 r/min or less. Judgment Criteria ● Sensor output voltage has continued to be 4.5V or higher for 4 sec. | ● Mass air flow sensor failed ● Open or shorted mass air flow sensor circuit, or loose connector ● Engine control module failed |
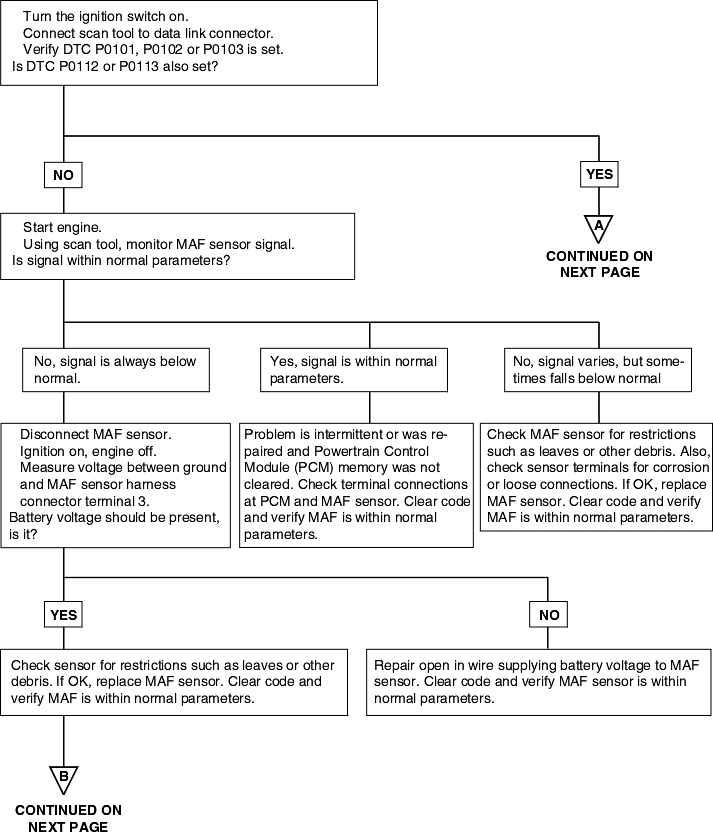
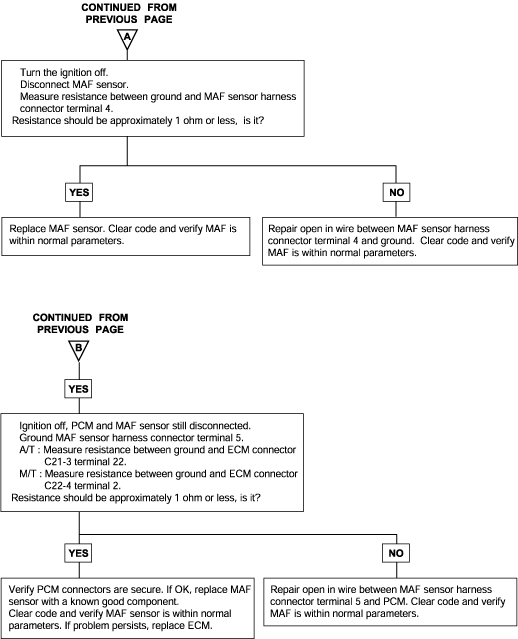
DTC | Diagnostic item |
P0112 P0113 | Intake Air temperature Circuit Low Voltage Intake Air temperature Circuit High Voltage |
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor is in the MAF sensor. The IAT sensor is a variable resistor whose resistance changes as the temperature of the air flowing through the air intake changes. The Engine Control Module (ECM) uses the IAT sensor input to adjust fuel injector pulse width. When the temperature sensed is cold, the ECM enriches fuel mixture by increasing injector pulse width; as the air warms, the injector pulse width time is shortened.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● The intake air temperature sensor converts the intake air temperature to a voltage and outputs it. ● The engine control module checks whether the voltage is within a specified range. Check Area ● Sixty seconds or more have passed since the starting sequence was completed. Judgment Criteria ● Sensor output voltage has continued to be 4.6V or higher [corresponding to an intake air temperature of -45°C (-49°F) or lower] for 4 sec. ● Sensor output voltage has continued to be 0.2V or lower [corresponding to an intake air temperature of 125°C (257°F) or higher] for 4 sec. | ● MAF sensor failed ● Open or shorted mass air flow sensor circuit, or loose connector ● Engine control module failed |

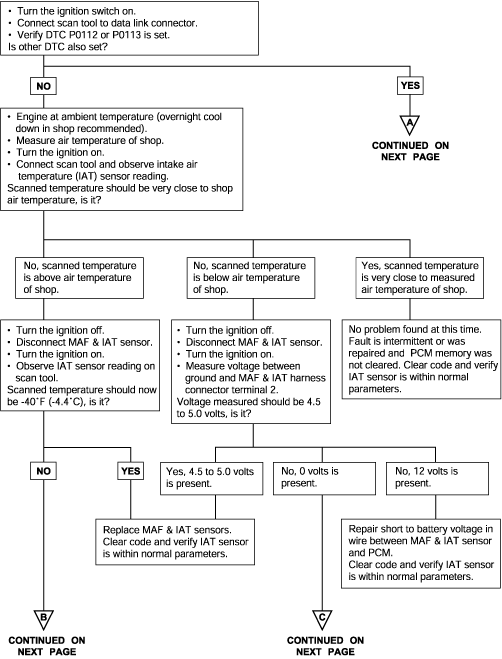
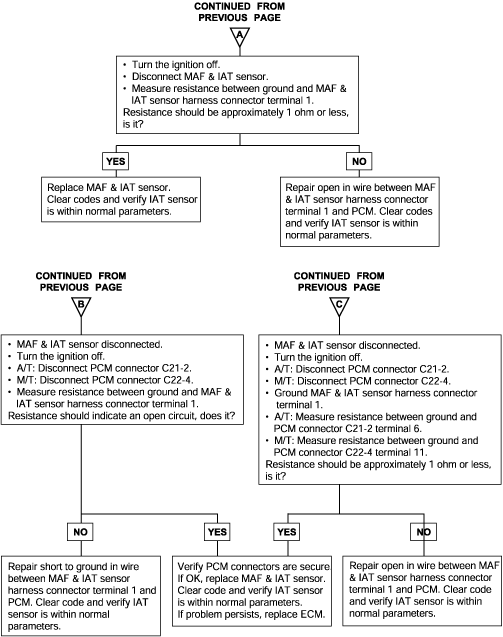
DTC | Diagnostic item |
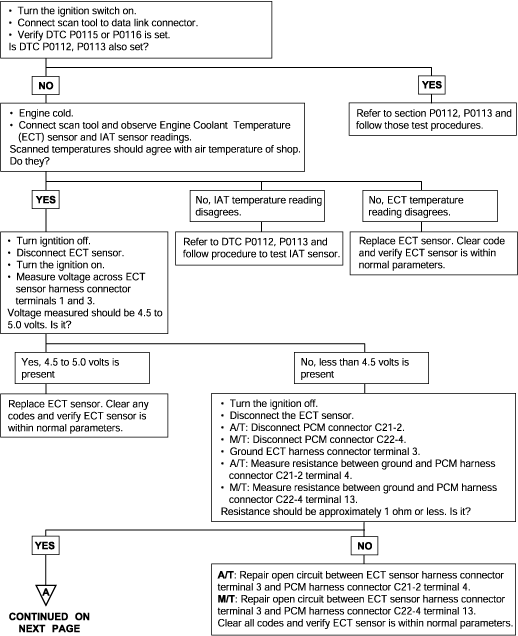
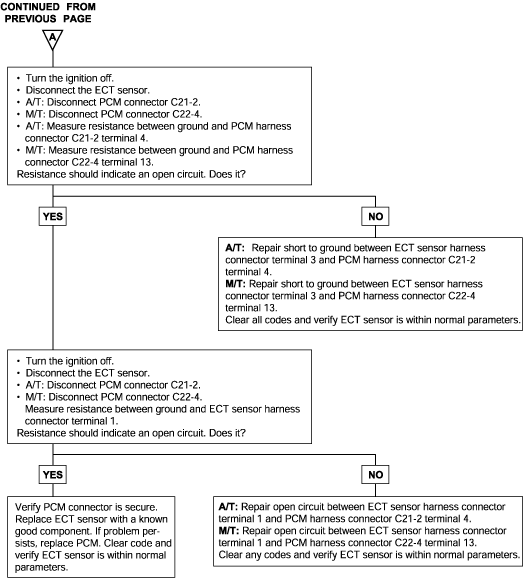
P0115 P0116 | Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Malfunction (Open/Short) Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Drift |
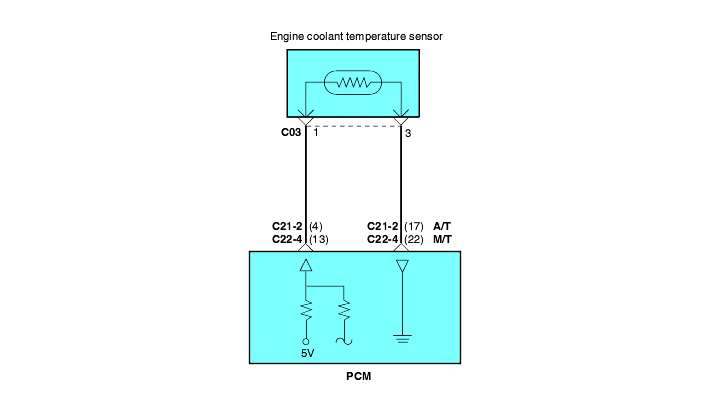
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is located in the coolant passage of the cylinder head. The ECT sensor is a variable resistor whose resistance changes as the temperature of the engine coolant flowing past the sensor changes. When the coolant temperature is low, the sensor resistance is high; when the coolant temperature is high, the sensor resistance is low. The Engine Control Module (ECM) checks ECT voltage fifty times per second and uses the information to adjust the fuel injector pulse width and ignition timing. When the temperature sensed is very cold, the ECM enriches the fuelmixture.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● The engine coolant temperature sensor converts the engine coolant temperature to a voltage and outputs it. ● The Engine Control Module checks whether the voltage is within a specified range. In addition, it checks that the engine coolant temperature (signal)does not drop while the engine is warming up. Check Area, Judgment Criteria ● Sensor output voltage has continued to be 4.6V or higher [corresponding to a coolant temperature of -45°C (-49°F) or lower] for 4 sec. ● Sensor output voltage has continued to be 0.1V or lower [corresponding to a coolant temperature of 140°C (284°F) or higher] for 4 sec. Check Area, Judgment Criteria ● Sensor output voltage increased from a value lower than 1.6V to a value higher than 1.6V [Coolant temperature decreases from a higher than 40°C (104°F) temperature to a lower than 40°C (104°F) temperature.]. ● Then the sensor output voltage has continued to be 1.6V or higher for 5 min. Check Area ● The Engine Coolant Temperature is approx. 40°C (104°F) or less after starting sequence is completed. Judgment Criteria ● Approx. 60 - 300 seconds have passed for the engine coolant temperature to rise to about 40°C (104°F) after starting sequence was completed. | ● Engine Coolant Temperature sensor failed. ● Open or shorted Engine Coolant Temperature sensor circuit, or loose connector. ● Engine Control Module failed. |
DTC | Diagnostic item |
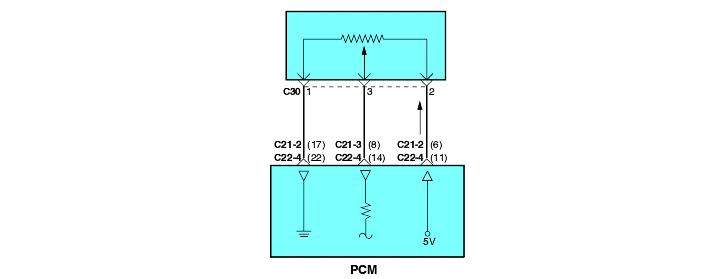
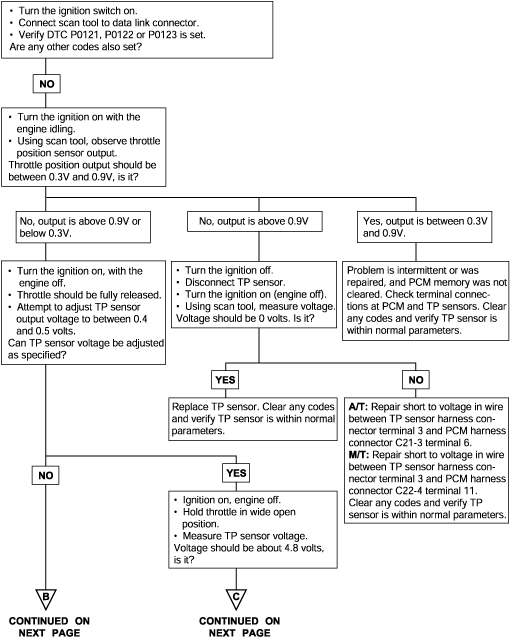
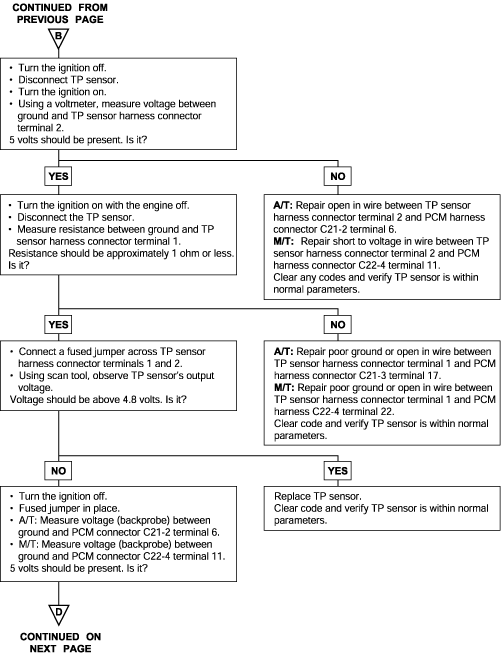
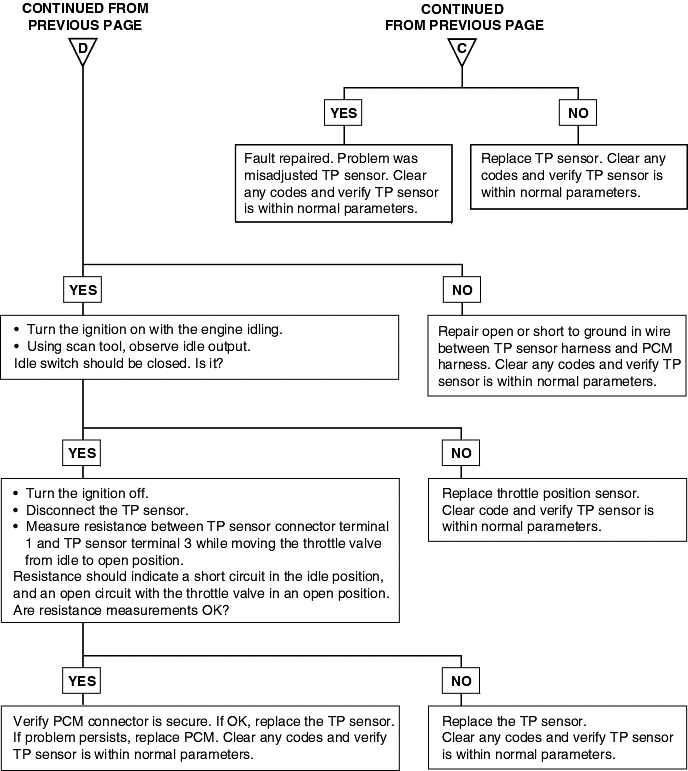
P0121 P0122 P0123 | Throttle Position Circuit Range/Performance Problem Throttle Position Circuit Low Voltage Throttle Position Circuit High Voltage |
The throttle position (TP) sensor mounts on the side of the throttle body and is connected to the throttle blade shaft. The TP sensor is a variable resistor (potentiometer) whose resistance changes according to the throttle blade shaft position. During acceleration, the TP sensor resistance decreases; during deceleration, the TP sensor resistance increases. The TP sensor also includes an idle position switch. The switch is closed in the idle position. The Engine Control Module (ECM) applies a reference voltage to the TP sensor and then measures the voltage that is present on the TP sensor signal circuit. The ECM uses the TP sensor signal to adjust the timing and injector pulse width. The TP sensor signal along with the MAP sensor signal is used by theECM to calculate the engine load.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● The Throttle Position sensor outputs a voltage which is proportional to the throttle valve opening angle. ● The Engine Control Module checks whether the voltage output by the throttle position sensor is within a specified range. In addition, it checks that the voltage output does not become too large while the engine is idling. Check Area, Judgment Criteria ● With the close Throttle Position switch se to ON, the sensor output voltage has continued to be 2V or higher for 4 sec. ● Sensor output voltage has continued to be 0.2V or lower for 4 sec. Check Area ● Engine speed is between 500 and 3,000 r/min. ● Engine load is lower than 30%. Judgment Criteria ● Sensor output voltage has continued to be 4.6V or higher for 4 sec. | ● Throttle Position sensor failed or maladjusted. ● Open or shorted Throttle Position sensor circuit, or loose connector. ● Closed Throttle Position switch ON malfunction. ● Closed Throttle Position switch signal wire shorted. ● Engine control module failed. |
DTC | Diagnostic item |
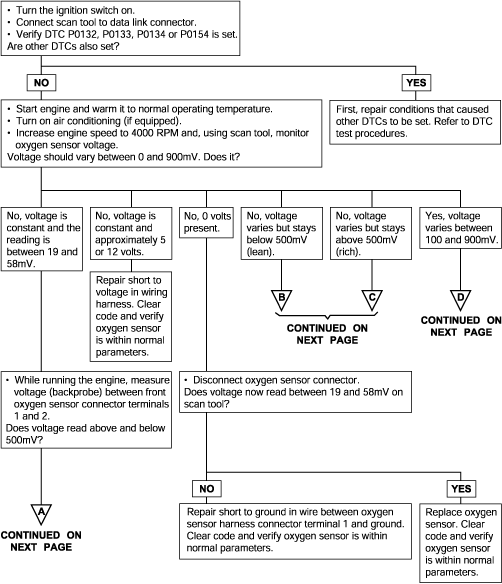
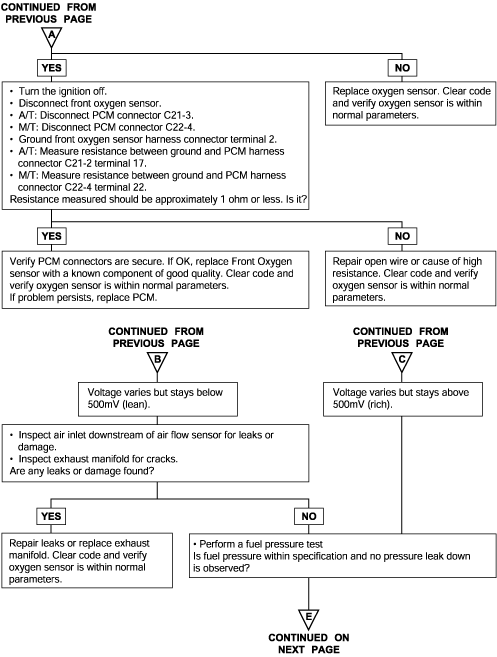
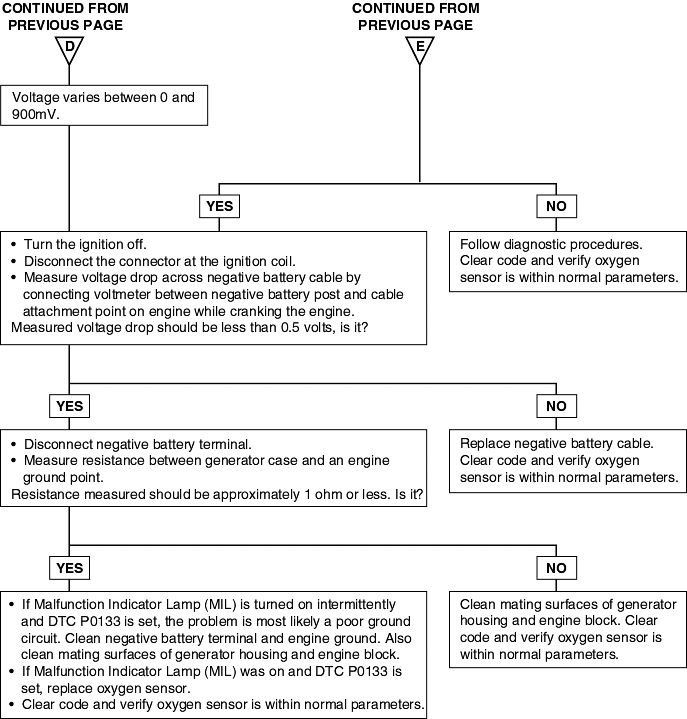
P0132 P0133 P0134 | Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Open) Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (No Activity) |
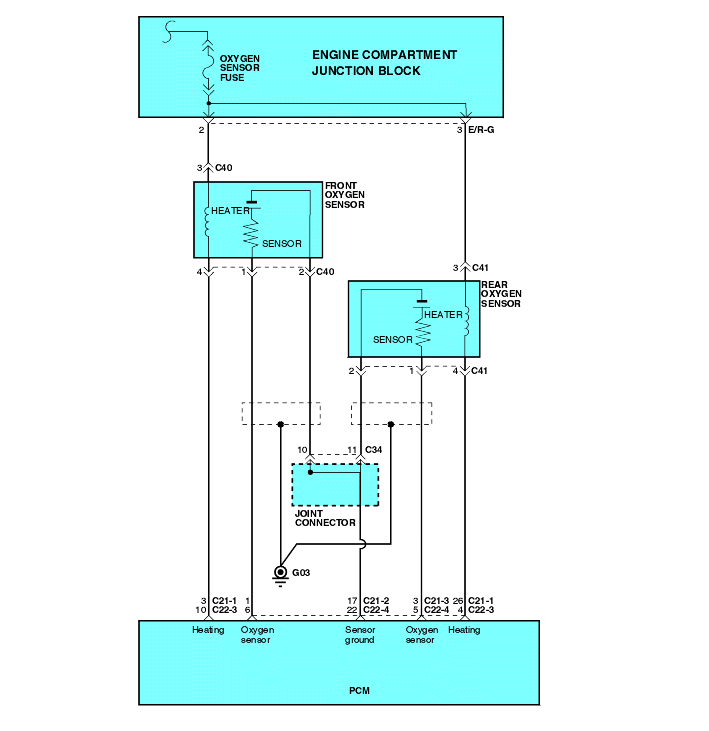
To obtain a high purification rate for the CO, HC and NOx components of the exhaust gas, a three way catalytic converter is used, but for the most efficient use of the three-way catalytic inverter, the ratio of the air must be precisely controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. The oxygen sensor has the characteristic whereby its output voltage changes suddenly in the vicinity of the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. This characteristic is used to detect the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas and provide feedback to the computer for control of the air-fuel ratio. When the air-fuel ratio becomes LEAN, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust increases and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the LEAN condition (small electromotive force: 0V). When the air-fuel ratio is RICHER than the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas is reduced and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the RICH condition (large electromotive force: 1V).
The ECM determined by the electromotive force from the oxygen sensor whether the air-fuel ratio is RICH or LEAN and controls the injection time accordingly. However, if malfunction of the oxygen sensor causes output of abnormal electromotive force, the ECM is unable to perform an accurate air-fuel ratio control. The heated oxygen sensors include a heater which heats the Zirconia element. The heater is controlled by the ECM. When the intake air volume is low (the temperature of the exhaust gas is low), current flows to the heater to heat the sensor for accurate oxygen concentration detection.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● When the heated oxygen sensor begins to deteriorate, the oxygen sensor signal response becomes poor. ● The Engine Control Module forcibly varies the air/fuel mixture to make it leaner and richer and checks the response speed of the heated oxygen sensor. In addition, the Engine Control Module also checks for an open circuit in the heated oxygen sensor output line. Check Area ● Coolant temperature sensor: Normal. ● Heated oxygen sensor signal voltage has continued to be 0.1V or lower for 3 min. or more after the staring sequence was completed. ● Engine Coolant Temperature is higher than 80°C (176°F). ● Engine speed is higher than 1,200 r/min. ● Engine load is 25% or more. Judgment Criteria ● Input voltage supplied to the engine control module interface circuit is 4.5V or more when 5V is applied to the heated oxygen sensor output linevia a resistor. Check Area ● Coolant temperature sensor: Normal. ● Engine Coolant Temperature is 50°C (122°F) or more. ● Engine speed is between 1,500 and 3,000 r/min or 1,100 and 3,000 r/min. ● Engine load is 25 - 60%. ● Intake air temperature is -10°C (14°F) or more. ● Under the closed loop air-fuel control. ● Monitoring Time: 8sec. Judgment Criteria ● When the air-fuel ratio is focibly changed (lean to rich and rich to lean), the heated oxygen sensor signal doesn't provide response within 1.28sec. ● Monitored only once per trip. | ● Heated oxygen sensor deteriorated ● Open circuit in heated oxygen sensor output line ● Engine control module failed |
DTC | Diagnostic item |
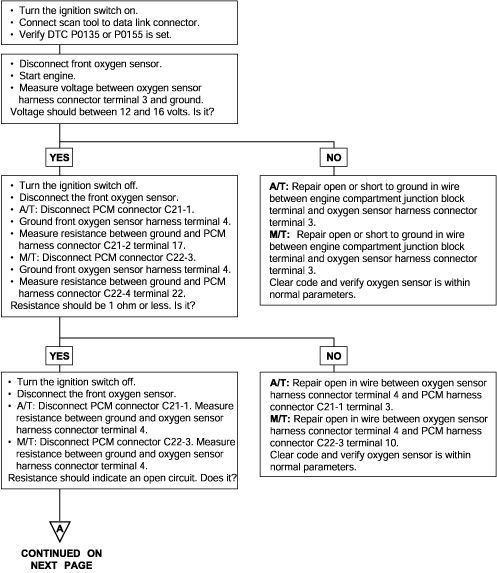
P0135 | Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) |
To obtain a high purification rate for the CO, HC and NOx components of the exhaust gas, a three way catalytic converter is used, but for the most efficient use of the three-way catalytic inverter, the ratio of the air must be precisely controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. The oxygen sensor has the characteristic whereby its output voltage changes suddenly in the vicinity of the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. This characteristic is used to detect the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas and provide feedback to the computer for control of the air-fuel ratio. When the air-fuel ratio becomes LEAN, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust increases and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the LEAN condition (small electromotive force: 0V). When the air-fuel ratio is RICHER than the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas is reduced and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the RICH condition (large electromotive force: 1V).
The ECM determined by the electromotive force from the oxygen sensor whether the air-fuel ratio is RICH or LEAN and controls the injection time accordingly. However, if malfunction of the oxygen sensor causes output of abnormal electromotive force, the ECM is unable to perform an accurate air-fuel ratio control. The heated oxygen sensors include a heater which heats the Zirconia element. The heater is controlled by the ECM. When the intake air volume is low (the temperature of the exhaust gas is low), current flows to the heater to heat the sensor for accurate oxygen concentration detection.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● The Engine Control Module checks whether the heater current is within a specified range when the heater is energized. Check Area ● Battery voltage is between 12 and 16V. Judgment Criteria ● Heater current of the front heated oxygen sensor heater (Bank 1 Sensor 1) has continued to be 0.2 A or less, or 3.5 A or higher for 6 sec. ● Monitored only once per trip. | ● Open or shorted oxygen sensor heater circuit ● Open circuit in oxygen sensor heater ● Engine control module failed |

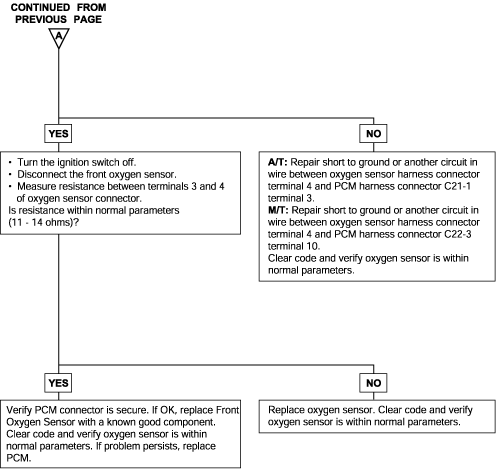
DTC | Diagnostic item |
P0136 | Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 2) |
To obtain a high purification rate for the CO, HC and NOx components of the exhaust gas, a three way catalytic converter is used, but for the most efficient use of the three-way catalytic inverter, the ratio of the air must be precisely controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. The oxygen sensor has the characteristic whereby its output voltage changes suddenly in the vicinity of the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. This characteristic is used to detect the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas and provide feedback to the computer for control of the air-fuel ratio. When the air-fuel ratio becomes LEAN, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust increases and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the LEAN condition (small electromotive force: 0V). When the air-fuel ratio is RICHER than the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas is reduced and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the RICH condition (large electromotive force: 1V).
The ECM determined by the electromotive force from the oxygen sensor whether the air-fuel ratio is RICH or LEAN and controls the injection time accordingly. However, if malfunction of the oxygen sensor causes output of abnormal electromotive force, the ECM is unable to perform an accurate air-fuel ratio control. The heated oxygen sensors include a heater which heats the Zirconia element. The heater is controlled by the ECM. When the intake air volume is low (the temperature of the exhaust gas is low), current flows to the heater to heat the sensor for accurate oxygen concentration detection.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● The Engine Control Module checks for an open circuit in the heated oxygen sensor output line. Check Area ● Coolant temperature sensor: Normal. ● Heated oxygen sensor signal voltage has continued to be 0.1V or lower for 3 min. or more after the staring sequence was completed. ● Engine coolant temperature is 80°C (176°F) or more. ● Engine speed is higher than 1,200 r/min. ● Engine load is 25% or more. ● Monitoring Time: 7 - 10 sec. Judgment Criteria ● Input voltage supplied to the engine control module interface circuit is 4.5V or more when 5V is applied to the heated oxygen sensor output linevia a resistor. ● Making the air-fuel ratio 15% richer doesn't result in raising the heated oxygen sensor output voltage beyond 0.1V. | ● Heated oxygen sensor failed ● Open circuit in heated oxygen sensor output line ● Engine control module failed |

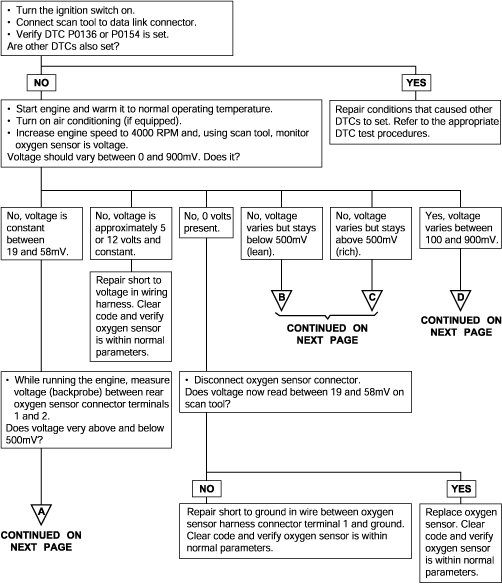
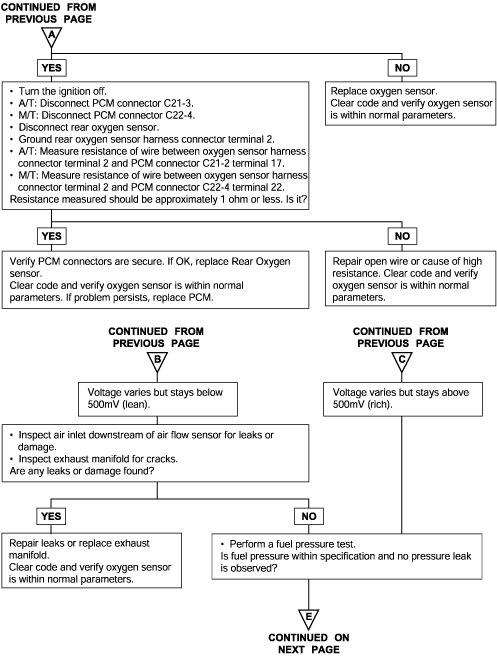
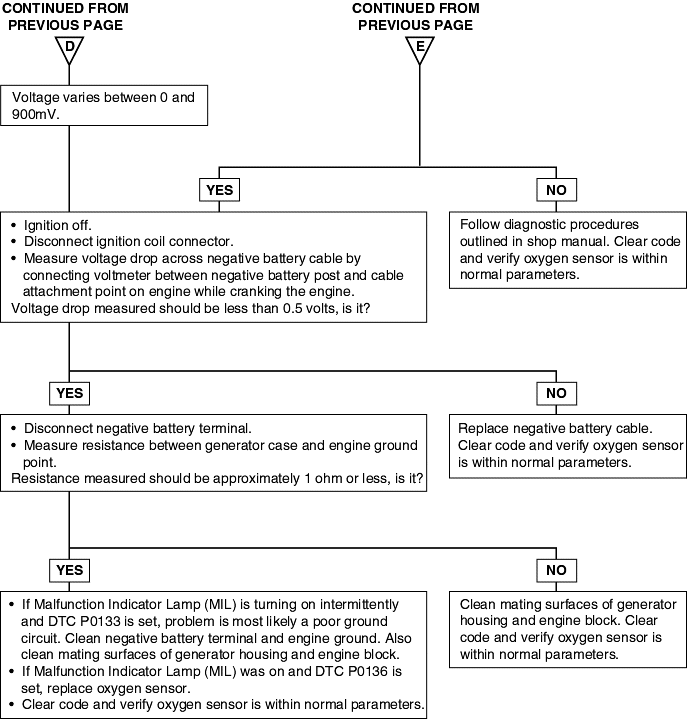
DTC | Diagnostic item |
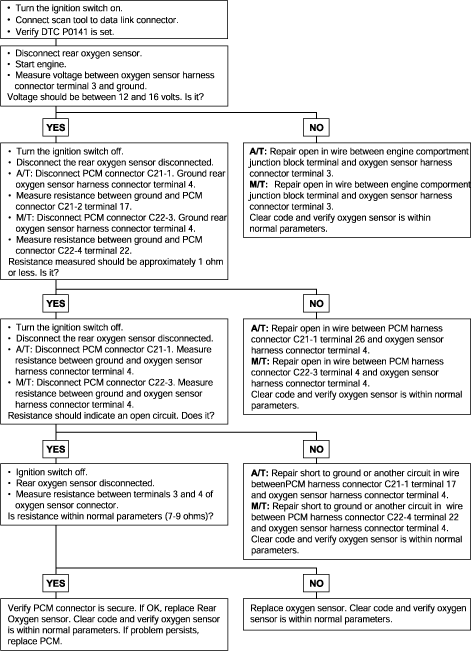
P0141 | Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 2) |
To obtain a high purification rate for the CO, HC and NOx components of the exhaust gas, a three way catalytic converter is used, but for the most efficient use of the three-way catalytic inverter, the ratio of the air must be precisely controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. The oxygen sensor has the characteristic whereby its output voltage changes suddenly in the vicinity of the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. This characteristic is used to detect the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas and provide feedback to the computer for control of the air-fuel ratio. When the air-fuel ratio becomes LEAN, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust increases and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the LEAN condition (small electromotive force: 0V). When the air-fuel ratio is RICHER than the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas is reduced and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the RICH condition (large electromotive force: 1V).
The ECM determined by the electromotive force from the oxygen sensor whether the air-fuel ratio is RICH or LEAN and controls the injection time accordingly. However, if malfunction of the oxygen sensor causes output of abnormal electromotive force, the ECM is unable to perform an accurate air-fuel ratio control. The heated oxygen sensors include a heater which heats the Zirconia element. The heater is controlled by the ECM. When the intake air volume is low (the temperature of the exhaust gas is low), current flows to the heater to heat the sensor for accurate oxygen concentration detection.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● The Engine Control Module checks whether the heater current is within a specified range when the heater is energized. Check Area ● Battery voltage is between 12 and 16V. Judgment Criteria ● Heater current of the front heated oxygen sensor heater (Bank 1 Sensor 2) has continued to be 0.2 A or less, or 3.5 A or more for 6 sec. ● Monitored only once per trip. | ● Open or shorted oxygen sensor heater circuit ● Open circuit in oxygen sensor heater ● Engine control module failed |

DTC | Diagnostic item |
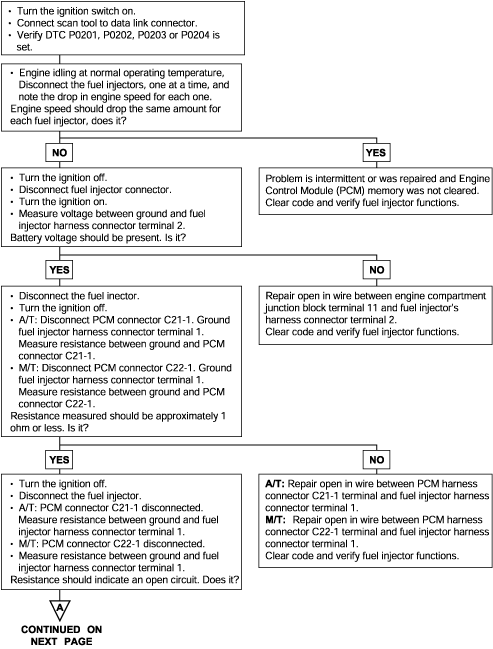
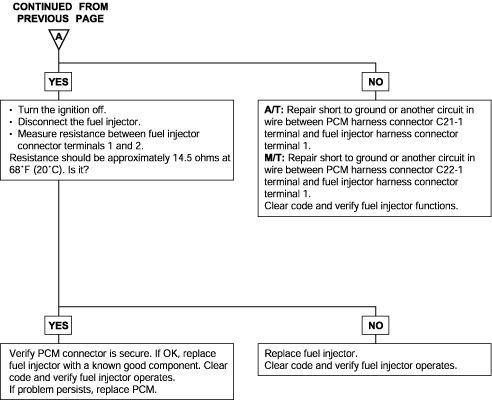
P0201, P0202 P0203, P0204 | Injector Circuit Malfunction (Cylinder-1, Cylinder-2, Cylinder-3, Cylinder-4) |
The fuel injectors are solenoid operated valves that are normally closed. When a fuel injector solenoid is energized (pulsed) the injector needle valve moves, allowing pressurized fuel to pass through the injector and mix with the air entering the engine. Each fuel injector (there is one for each engine cylinder) is mounted in the intake manifold and is positioned to spray fuelinto a cylinder head intake port.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls injector timing and pulse width (how long the fuel injectors are turned on). The ECM pulses the fuel injectors based on information provided by its network of engine sensors. The ECM uses the crankshaft position sensor to determine when to pulse the injectors. Engine coolant temperature, intake air temperature, air flow and throttle positiondata are all used by the ECM to calculate injector pulse width.
The ECM also uses its network of sensors to determine whether all injectors should be pulsed at the same time (simultaneous injection) or each injector should be pulsed individually (sequential injection). Sequential injection is almost always used during normal engine operation and simultaneous injectionmay be used when the engine is being cranked.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● A surge voltage is generated when the injectors are driven and the current flowing to the injector coil, is shut off. ● The engine control module checks this surge voltage. Check Area ● Engine speed is between 50 and 1,000 r/min ● Throttle position sensor output voltage is 1.16V or less. ● Monitoring Time: 4 sec. Judgment Criteria ● Injector coil surge voltage (system voltage +2V) has not been detected for 4 sec. | ● Injector failed ● Open or shorted injector circuit, or loose connector ● Engine control module failed |
DTC | Diagnostic item |
P0300 | Random Misfire Detected |
With the ignition switch ON or START, voltage is applied to the ignition coil. The ignition coil consists of two coils. High tension leads go to each cylinder from the ignition coil. The ignition coil fires two spark plugs every power stroke (the cylinder under compression and the cylinder on the exhaust stroke). Coil number one fires cylinders 1 and 4. Coil number two fires cylinders2 and 3.
The ignition power transistor, controlled by the Engine Control Module (ECM), provides a switching circuit to ground for energizing the primary ignition coils. When a primary ignition coil is energized and deenergized, the secondary coil produces a high voltage spike across the attached spark plugs. At the same time, the tach interface (part of the ignition power transistor) providesthe ECM and Transaxle Control Module (TCM) with an RPM signal.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● If a misfiring occurs while the engine is running, the engine speed suddenly changes. ● The Engine Control Module checks for changes in the engine speed. Check Area ● Five seconds or more have passed after the engine was started. ● Engine speed is between 500 and 6,000 r/min. ● Engine Coolant Temperature is higher than -10°C(14°F). ● Intake air temperature is higher than -10°C (14°F). ● Running free from sudden accelerations/decelerations such as shift change. Judgment Criteria (change in the angular acceleration of the crankshaft is used for misfire detection.) ● Misfire has occurred more frequently than allowed during the last 200 revolutions [when the catalyst temperature is higher than 950°C (1,742°F)]. ● Misfire has occurred more frequently than the allowed number of times (2%) during 1,000 motor revolutions. | ● Ignition system related part(s) failed ● Poor crankshaft position sensor signal ● Incorrect air/fuel ratio ● Low compression pressure ● Engine coolant temperature sensor failed ● Timing belt missing teeth ● Injector failed ● Engine control module failed |
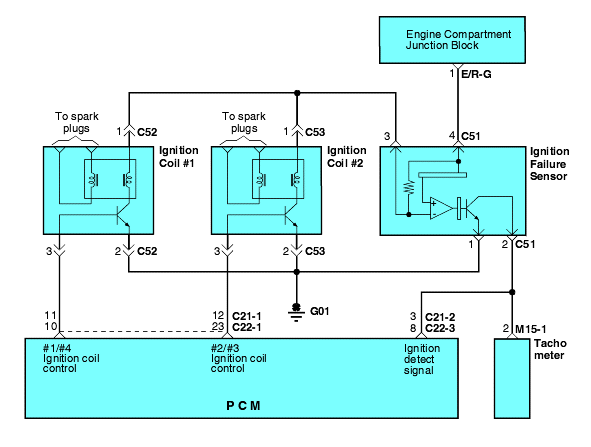
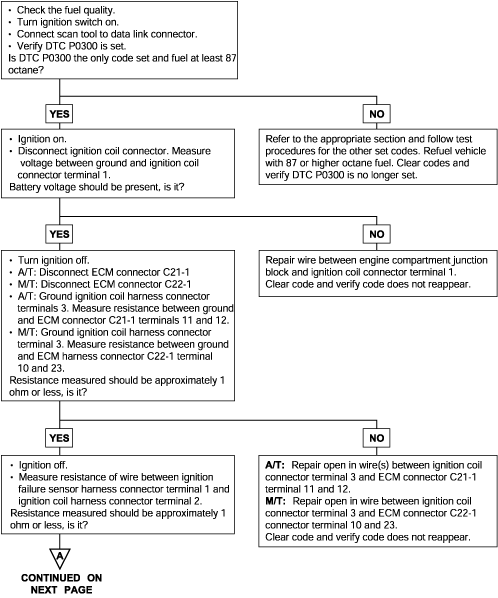
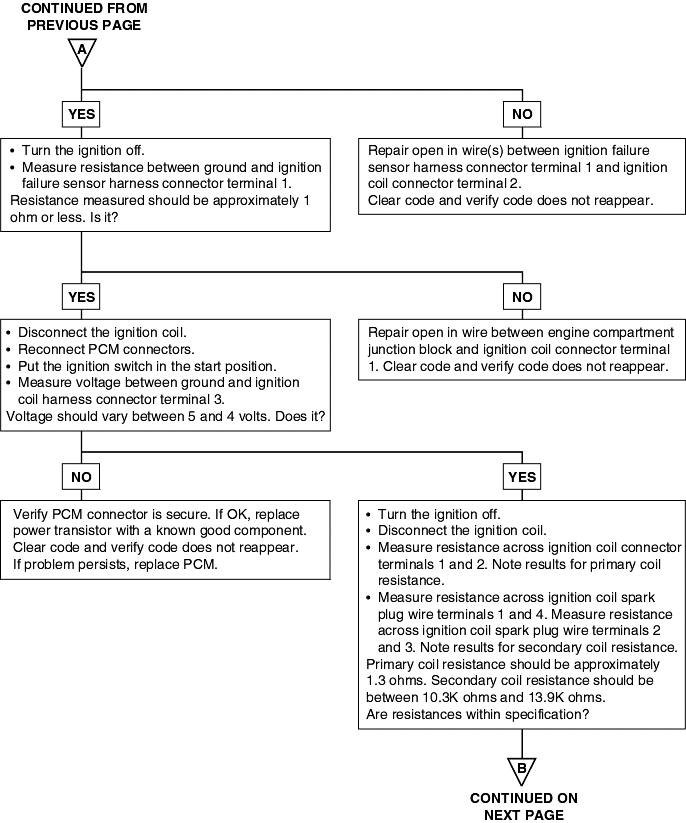
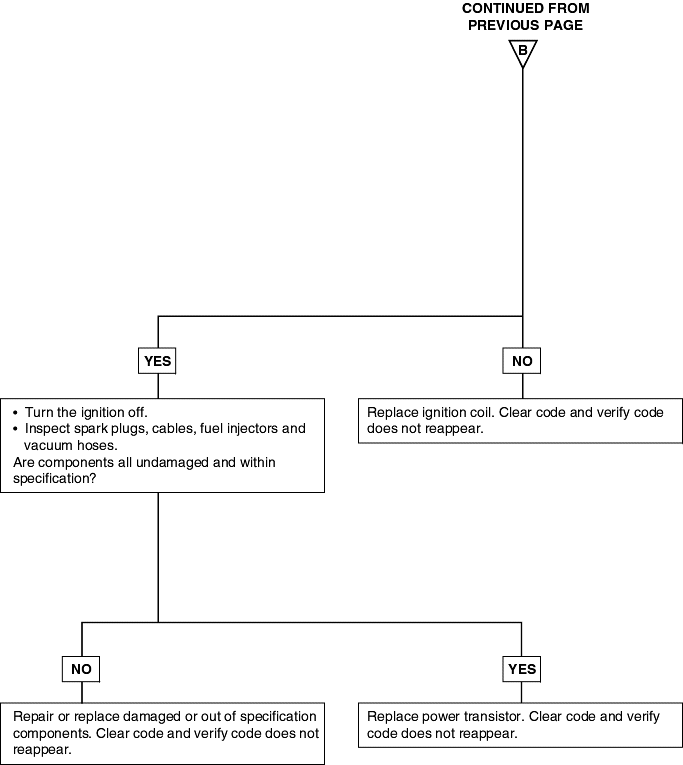
DTC | Diagnostic item |
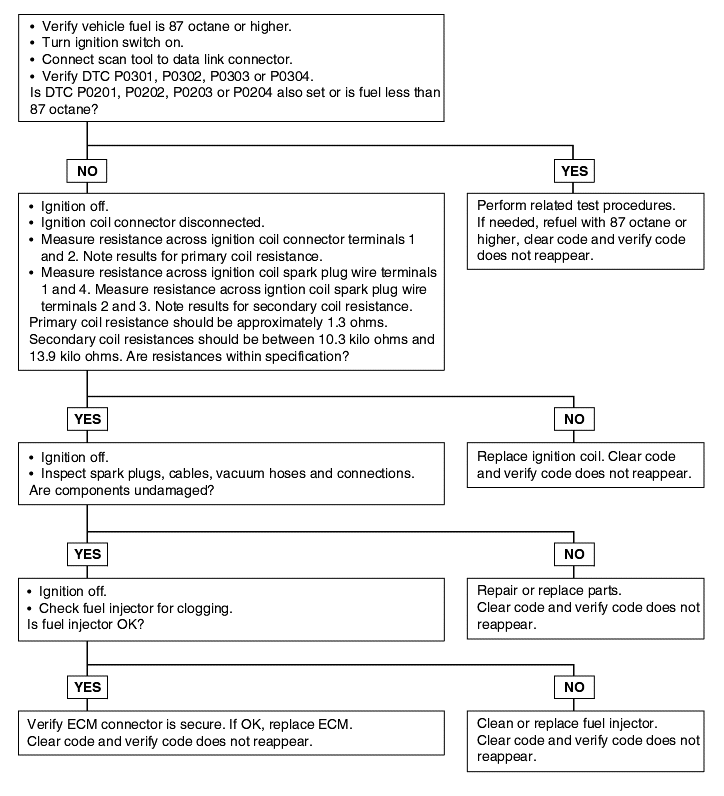
P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, | Misfire detected (Cylinder-1, Cylinder-2, Cylinder-3, Cylinder-4) |
Refer to Random Misfire Detected (P0300).
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● If a misfiring occurs while the engine is running, the engine speed suddenly changes. ● The Engine Control Module checks for changes in the engine speed. Check Area ● Five seconds or more have passed after the engine was started. ● Engine speed is between 500 and 6,000 r/min. ● Engine Coolant Temperature is higher than -10°C (14°F). ● Intake air temperature is higher than -10°C (14°F). ● Running free from sudden accelerations/decelerations such as shift change. Judgment Criteria (change in the angular acceleration of the crankshaft is used for misfire detection.) ● Misfire has occurred more frequently than allowed for during the last 200 revolutions [when the catalyst temperature is higher than 950°C (1,742°F)]. ● Misfire has occurred more frequently than the allowed number of times (2%) during 1,000 motor revolutions. | ● Ignition system related part(s) failed ● Poor crankshaft position sensor signal ● Incorrect air/fuel ratio ● Low compression pressure ● Engine coolant temperature sensor failed ● Timing belt missing teeth ● Injector failed ● EGR valve failed ● Engine control module failed |

DTC | Diagnostic item |
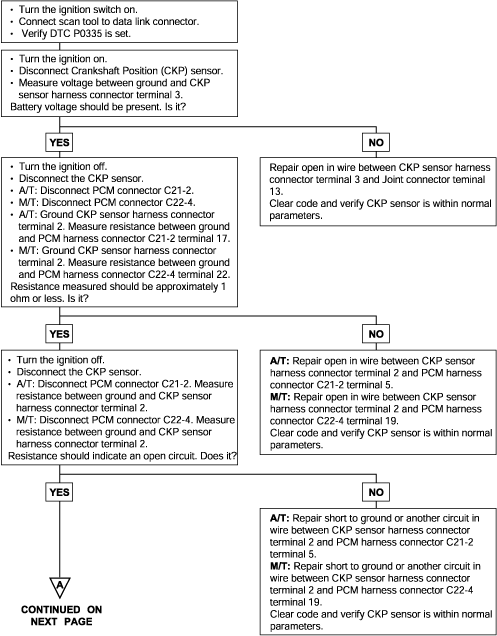
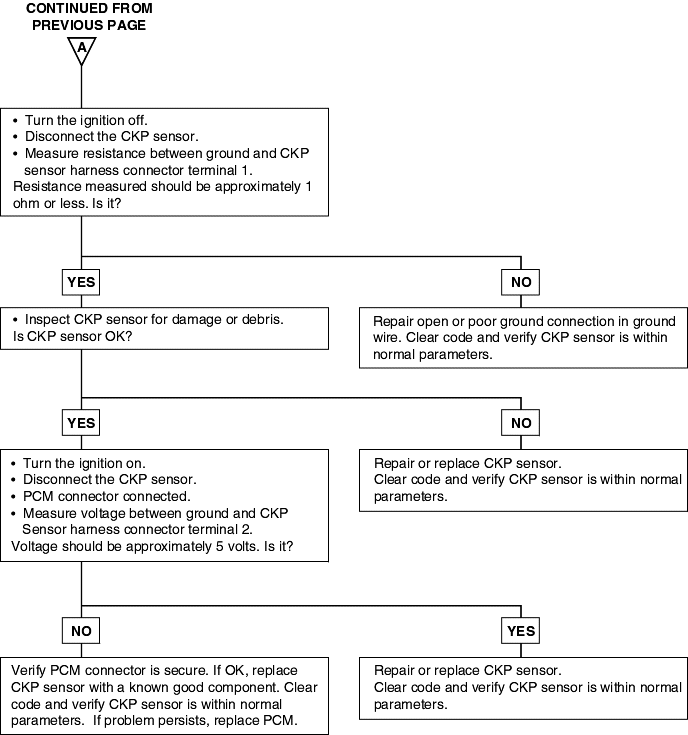
P0335 | Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction |
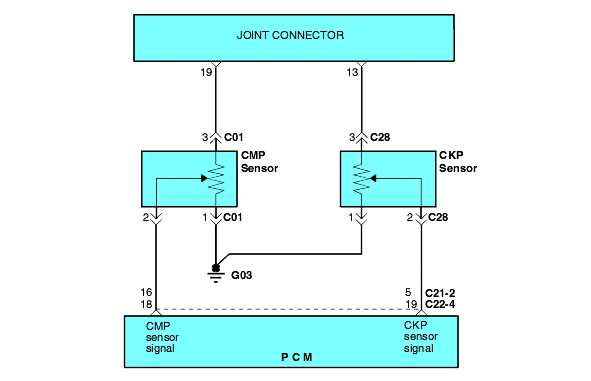
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor consists of a magnet and coil located next to the flywheel. The voltage signal from the CKP sensor allows the Engine Control Module (ECM) to determine the engine of the RPM and Crankshaft Position.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● When the engine is running, the Crankshaft Position sensor outputs a pulse signal. ● The Engine Control Module checks whether the pulse signal is input while the engine is cranking. Check Area ● Engine is being cranked. Judgment Criteria ● Sensor output voltage has not changed (no pulse signal is input) for 4 sec. Check Area, Judgment ● Normal signal pattern has not been input for cylinder identification from the crankshaft position sensor signal and camshaft position sensor signalfor 4 sec. | ● Crankshaft position sensor failed ● Open or shorted crankshaft position sensor circuit ● Engine control module failed |
DTC | Diagnostic item |
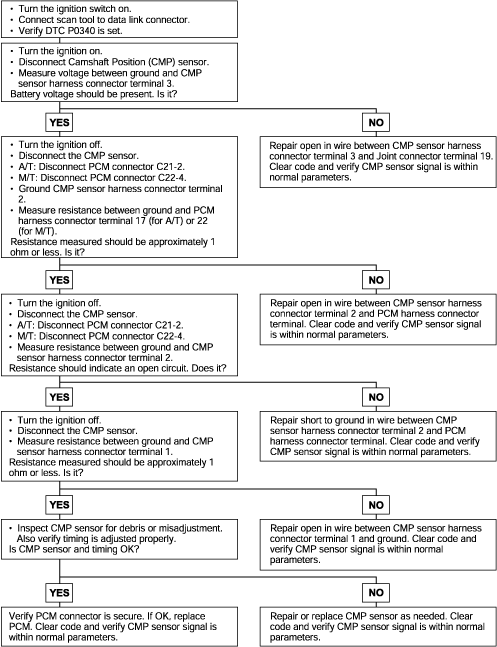
P0340 | Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction |
The Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor senses the Top Dead Center (TDC) point of the #1 cylinder in the compression stroke. The CMP sensor signalallows the ECM to determine the fuel injector sequence starting point.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● When the engine is running, the Camshaft Position sensor outputs a pulse signal. ● The Engine Control Module checks whether the pulse signal is input. Check Area, Judgement Criteria ● Sensor output voltage has not changed (no pulse signal is input) for 4 sec. Check Area, Judgement Criteria ● Normal signal pattern has not been input for cylinder identification from the camshaft position sensor signal for 4 sec. | ● Camshaft Position sensor malfunction ● Open or shorted camshaft position sensor circuit or loose connector ● Engine control module failed |

DTC | Diagnostic item |
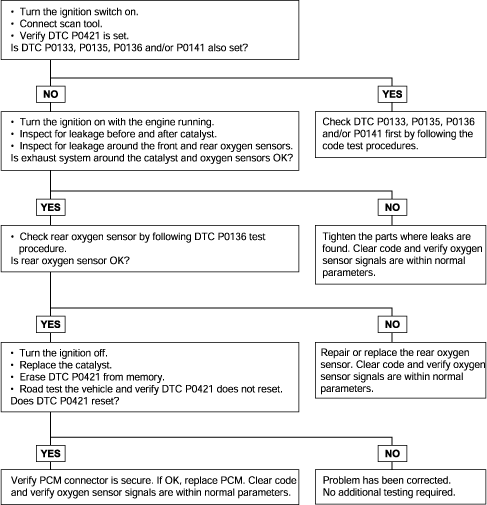
P0421 | Warm Up Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) |
The ECM compares the waveform of the oxygen sensor located in front of the catalyst with the waveform of the oxygen sensor located after the catalyst to determine whether or not catalyst performance has deteriorated. Air-fuel ratio feedback compensation keeps the waveform of the oxygen sensor in frontof the catalyst repeatedly changing back and forth from rich to lean.
If the catalyst is functioning normally, the waveform of the oxygen sensor after the catalyst switches back and forth between rich and lean much more slowly than the waveform of the oxygen sensor in front of the catalyst. But when both waveforms change at a similar rate, it indicates that catalystperformance has deteriorated.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● The signal from the heated oxygen sensor which follows the catalytic converter differs from that which precedes the catalytic converter. This is because the catalytic converter purifies exhaust gas. When the catalytic converter has deteriorated, the signal from the heated oxygen sensor which follows the catalytic converter becomes similar to that which precedes the catalytic converter. ● The Engine Control Module checks the outputs of the heated oxygen sensor signals. Check Area ● Engine speed is 3,000 r/min or higher. ● Closed throttle position switch: OFF ● Under the closed loop air-fuel ratio control ● Monitoring Time: 140 sec. Judgment Criteria ● The front or rear heated oxygen sensor signal is abnormal. | ● Catalytic converter deteriorated ● Heated oxygen sensor failed ● Engine control module failed |
DTC | Diagnostic item |
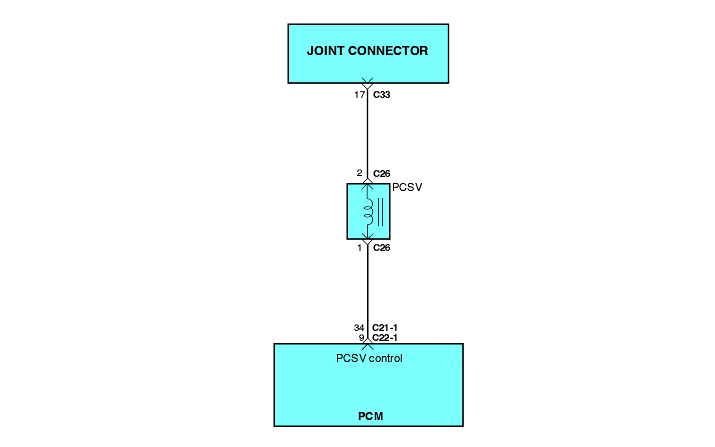
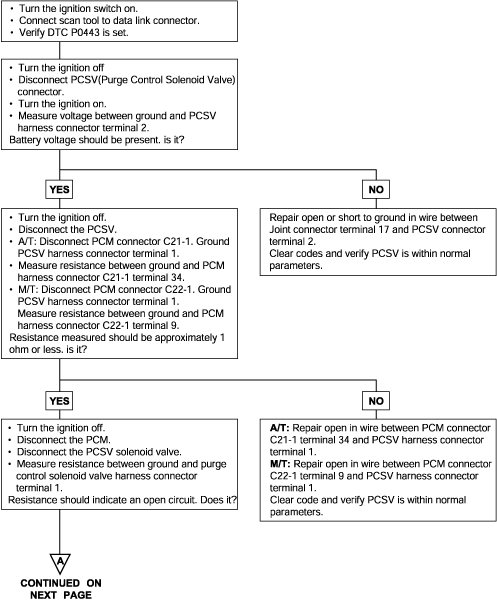
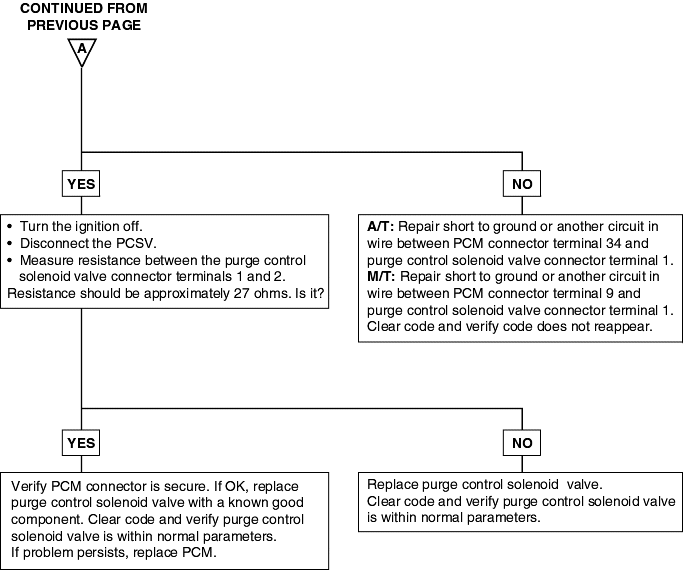
P0443 | Purge Control Solenoid Valve Malfunction |
The evaporative system reduces hydrocarbon emission by trapping fuel tank vapors until they can be burned as part of the incoming fuel charge. Evaporating fuel is stored in a charcoal canister until it can be flushedinto the intake manifold.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● The engine control module checks current flows in the evaporative emission purge solenoid drive circuit when the solenoid is ON and OFF. Check Area ● Battery voltage is 10V or higher. Judgment Criteria ● Solenoid coil surge voltage (system voltage +2V) is not detected when the EVAP emission vent solenoid is turned on/off. | ● Evaporative emission purge solenoid failed ● Open or shorted evaporative emission purge solenoid circuit, or loose connector ● Engine control module failed |
DTC | Diagnostic item |
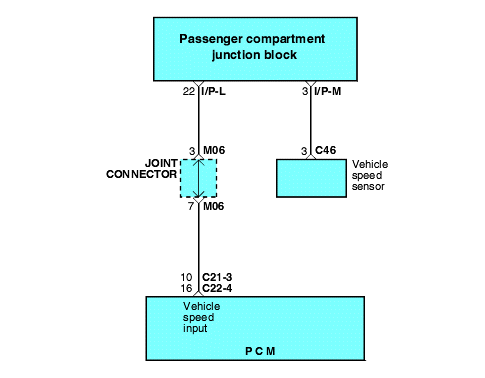
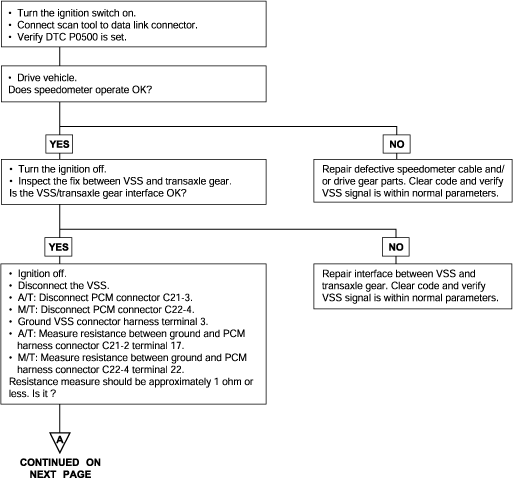
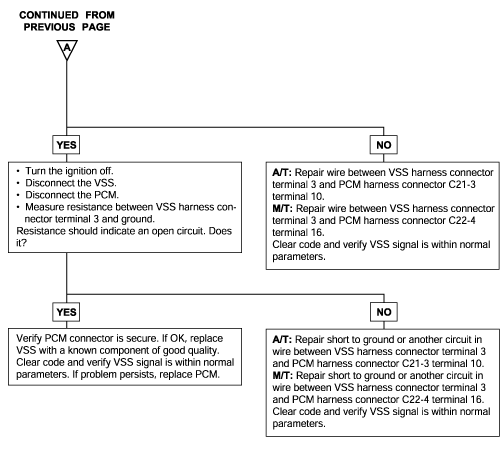
P0500 | Vehicle Speed Sensor Malfunction |
The vehicle speed sensor outputs a pulse signal while the vehicle is driven.
The engine control module checks whether the pulse signal is output.
DTC detection condition | Probable cause |
Background ● The vehicle speed sensor outputs a pulse signal while the vehicle is driven. ● The engine control module checks whether the pulse signal is outputted. Check Area ● Closed throttle position switch: OFF ● Engine speed is 3,000 r/min or more. ● Engine load is 70% or more. Judgment Criteria ● Sensor output voltage has not changed (no pulse signal is input) for 4 sec. | ● Vehicle speed sensor failed ● Open or shorted vehicle-speed sensor circuit, or loose connector ● Engine control module failed |