
With exhaust-gas recirculation (EGR) a portion of the exhaust gas is led into the engine's intake tract. Up to a certain degree, an increasing portion of the residual exhaust gas content has a positive effect upon energy conversion and therefore upon the exhaust-gas emissions. Depending upon the engine's operating point, the air/gas mass drawn into the cylinders can be composed of up to 40% exhaust gas.
For ECM control, the actual drawn-in fresh-air mass is measured and compared at each operating point with the air-mass setpoint value. Using the signal generated by the control circuit, the EGR valve opens so that exhaust gas can flow into the intake tract.
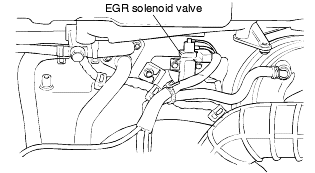
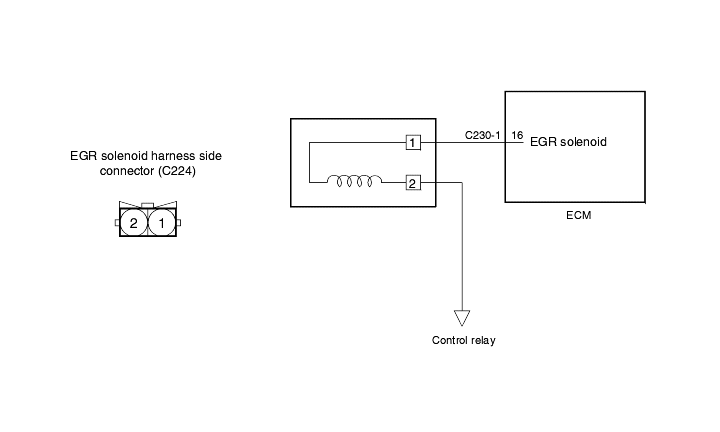


Check item | Check condition | Engine condition | Standard value |
EGR solenoid valve | Solenoid valve OFF → ON | Ignition switch : ON | Check the sound for proper operation |
Check item | Specified value |
EGR solenoid valve resistance | 14 ~ 17 Ω |