
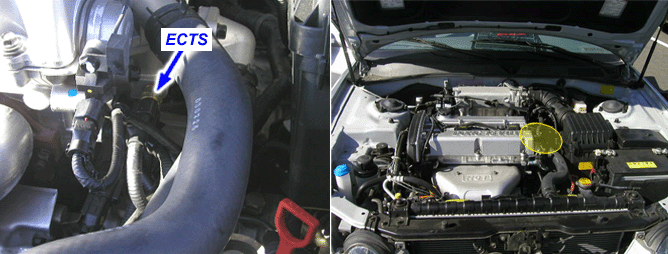
An Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS) monitors the temperature of the coolant. This input is used by the ECM for engine control and as an enabling criteria for same diagnostics.
The air flow coming into the engine is accumulated and used to determine if the engine has been driven within conditions that would allow the engine coolant to heat up normally to the thermostat regulating temperature. If the coolant temperature does not reach regulating temperature of the thermostat, diagnostics that use engine coolant temperature as enabling criteria, may not run when expected.
If there has been excessive time to reach a minimum coolant temperature required for closed loop fuel control, the ECM judged as a fault and DTC is set.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible cause | ||
DTC Strategy | ● Time(Tfbi) from engine starting to the reaching engine coolant temp. of F/B on | ● Poor connection. ● Improper coolant level ● Resistance of wire in ECT sensor circuit ● Defective thermostat ● Defective ECT sensor | ||
Case 1 | Enable Conditions | ● AFS voltage ≥ 1.75V | ||
Threshold value | ● Tfbi > 300sec @-7℃(19.4℉) ● Tfbi > 120sec @10℃(50℉) ● Tfbi > 60sec @80℃(176℉) | |||
Case 2 | Enable Conditions | ● AFS voltage< 1.75V | ||
Threshold value | ● Tfbi > 300sec @10℃(50℉) ● Tfbi > 200sec @20℃(68℉) ● Tfbi > 60sec @80℃(176℉) | |||
Diagnosis Time | ● 300 sec | |||
MIL On Condition | ● 2 driving cycles | |||