The gear changing mechanism utilizes three multi-disc clutches. The retainers of these clutches are fabricated from high-precision sheet metal for lightness and ease of production. Also, more responsive gear shifts at high engine speeds are achieved by a pressure-balanced piston mechanism that cancels out centrifugal hydraulic pressure. This mechanism replaces the conventionalball check valve.
The underdrive clutch operates in 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gears and transmits driving force from the input shaft to the underdrive sun gear.
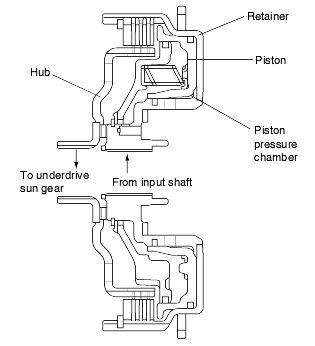
The components comprising the underdrive clutch are as illustrated on the below.
Hydraulic pressure acts in the piston pressure chamber (between the piston and retainer) and thus pushes the piston. In turn, the piston depresses the clutch discs and thereby transmits driving force from the retainer tothe hub side.
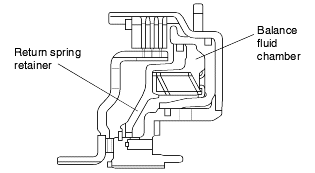
At high speeds, fluid remaining in the piston pressure chamber is subjected to centrifugal force and attempts to push the piston.
However, fluid in the balance fluid chamber (the space between the piston and return spring retainer) is also subjected to centrifugal force.
Thus, the hydraulic pressure on one side of the piston cancels out the hydraulic pressure on the other side, and the piston does not move.
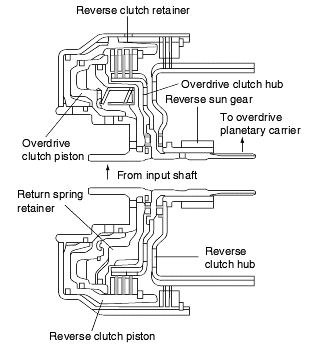
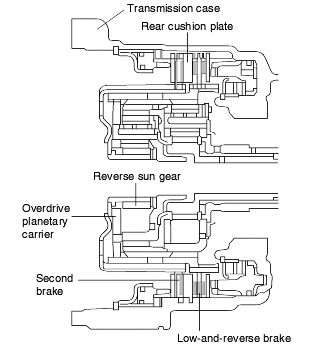
The reverse clutch operates when the reverse gear is selected and transmits driving force from the input shaft to the reverse sun gear.
The overdrive clutch operates in 3rd and 4th gears and transmits driving force from the input shaft to the overdrive planetary carrier and low-reverseannulus gear.
The gear changing mechanism utilizes two multi-disc brakes.
The low-reverse brake operates in 1st and reverse gears, when the vehicle is parked, and during manual operation.
It locks the low-reverse annulus gear and overdrive planetary carrier to the case.
The second brake operates in 2nd and 4th gears and locks the reverse sun gear to the case.
The components comprising the low-reverse brake and second brake are as illustrated on the below.
As shown, the discs and plates of the two brakes are arranged on either side of the rear cushion plate, which is itself secured to the case by a snapring.
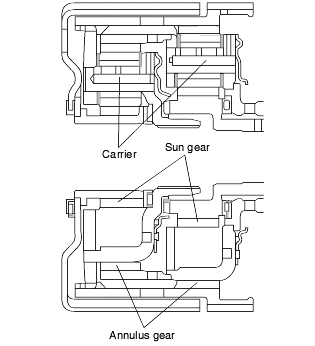
The planetary gear sets have two planetary gears each.
The carrier of one gear set is connected mechanically to the annulus gear of the other.
This arrangement allows the gear ratio to be varied by connecting or locking the carriers and sun gears.
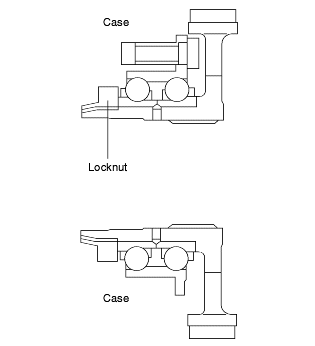
With the transfer drive gear, increased tooth height and a higher contact ratio have reduced gear noise.
Also, the bearing that supports the drive gear is a pre-loaded type that eliminates rattle, and the rigidity of the gear mounting has been increasedby bolting the bearing directly onto the case.
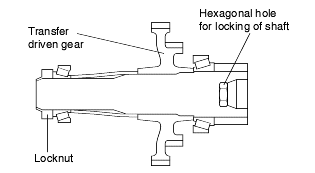
As shown in the illustration on the below, the transfer driven gear is press-fitted onto the output shaft, and the output shaft is secured bya locknut and supported by bearings.
The locknut has a left-handed thread, and a hexagonal hole in the other end of the shaft enables the shaft to be held in position for locknut removal.
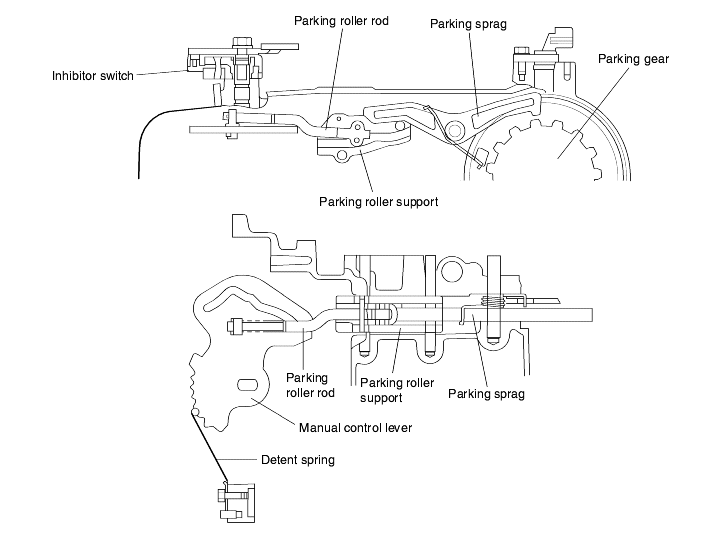
The manual control lever is fitted to the top of the valve body and is linked to the parking roller rod and manual control valve pin.
A detent mechanism is provided to improve the gear shift feeling during manual selection.
When the manual control lever is moved to the parking position, the parking roller rod moves along the parking roller support and pushes up theparking sprag.
As a result, the parking sprag meshes with the transfer driven gear (parking gear), thereby locking the output shaft. To minimize the operatingforce required, a roller is fitted to the end of the rod.