
DTC | P0401 | Exhaust gas recirculation flow insufficient detected |
P0402 | Exhaust gas recirculation flow excessive detected | |
P0405 | Exhaust gas recirculation flow A circuit low | |
P0406 | Exhaust gas recirculation flow A circuit high |
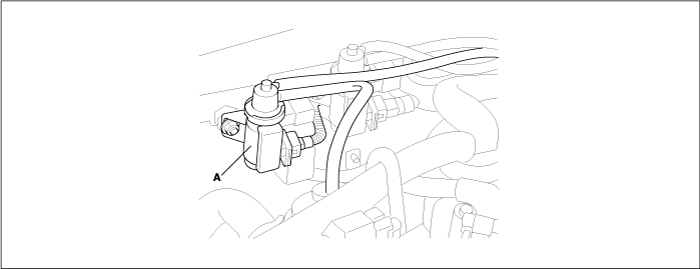
The exhaust-gas recirculation (EGR) system is designed to introduce exhaust gas into the engine’s intake manifold. Up to a certain degree, this system enables to reduce the formation of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) by cooling the combustion process. EGR solenoid valve(A) will not open under all driving conditions. For it to cycle, the engine must be at normal operating temperature and not under heavy load. The amount and timing of exhaust gas introduced into the combustion cycle varies by such factors as engine vacuum, exhaust system back pressure, coolant temperature and accel position. Depending upon the engine’s operating point, the air/gas mass drawn into the cylinders can be composed of up to 40% exhaust gas. Using the signal generated by the ECM control circuit, the EGR valve opens so that exhaust gas can flow into the intake manifold. If the EGR valve begins to clog or only partially opens, its flow will be reduced and emissions will increase.
DTC No | Detecting Condition & Limp Home | Suspected area |
P0401 P0402 P0405 P0406 | Detecting Condition P0406 : Short circuit to power supply line. P0405 : Breaking of wire. P0402 : ( *Qt - *Qm) ≥ 320mg/stroke P0401 : ( *Qt - *Qm) ≤ -220mg/stroke *Qt : the target intake air quantity *Qm : the measured intake air quantity Enable Condition Engine state : running Limp Home None | - Open or short in EGR solenoid valve circuit - EGR solenoid valve - Vacuum leakage - MAFS - ECM |
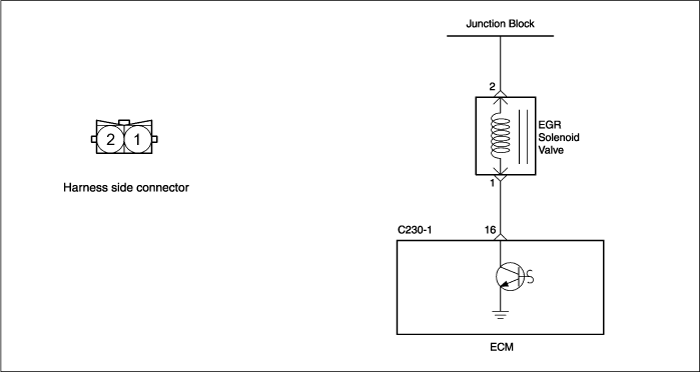
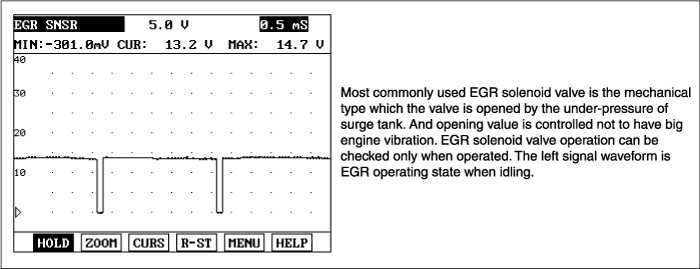


















Proceed with ECM problem procedure. |