DTC | Diagnostic item |
P0201 P0202 P0203 P0204 P0261 P0262 P0264 P0265 P0267 P0268 P0270 P0271 | Injector Circuit Malfunction - Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit Malfunction - Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit Malfunction - Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit Malfunction - Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit Low Input - Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit High Input - Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit Low Input - Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit High Input - Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit Low Input - Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit High Input - Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit Low Input - Cylinder 4 Injector Circuit High Input - Cylinder 4 |
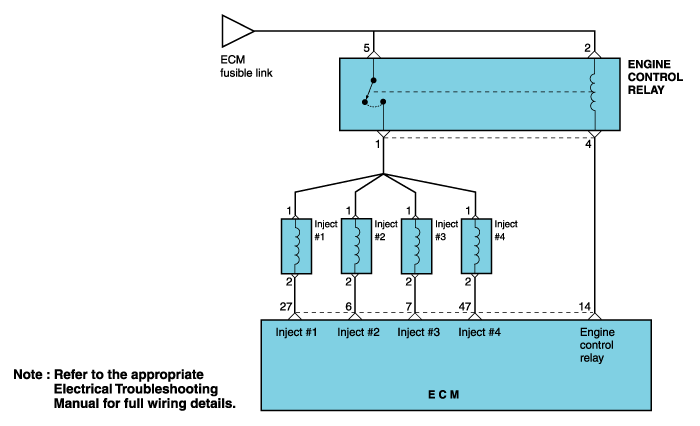
The fuel injectors are solenoid operated valves. When a fuel injector solenoid is energized (pulsed) the injector needle valve opens, allowing pressurized fuel to pass through the injector and mix with air entering the engine.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls injector timing and pulse width. The ECM pulses the fuel injectors based on information provided by its network of engine sensors. The ECM uses the crankshaft position sensor to determine when to pulse the injectors. Engine coolant temperature, intake air temperature, air flow, and throttle position data are all used by the ECM to calculate injector pulse width.
The ECM also uses its network of sensors to determine whether all injectors should be pulsed at the same time (simultaneous injection) or each injector should be pulsed individually (sequential injection). Sequential injection is almost always used during normal engine operation. Simultaneous injection may be used when the engine is being cranked.
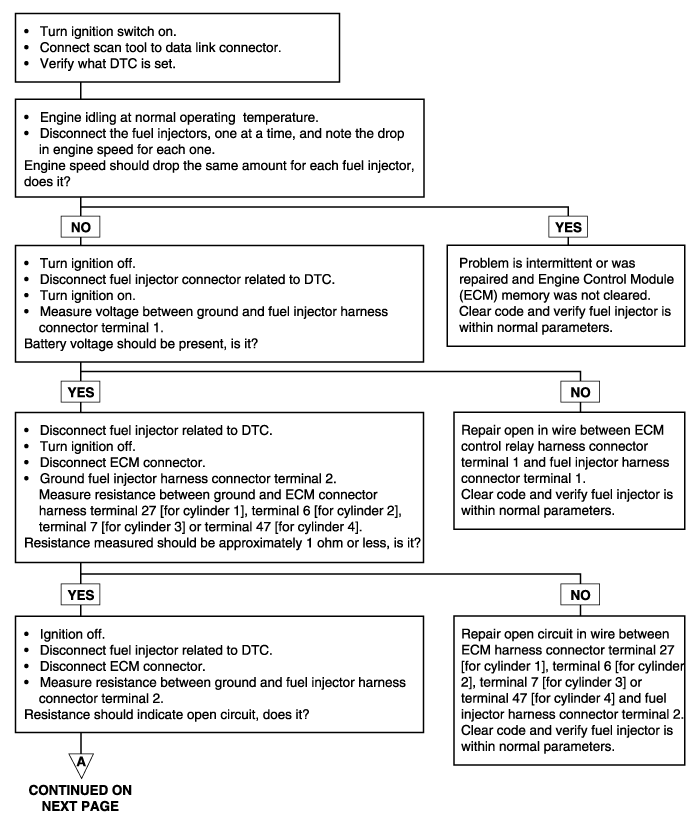
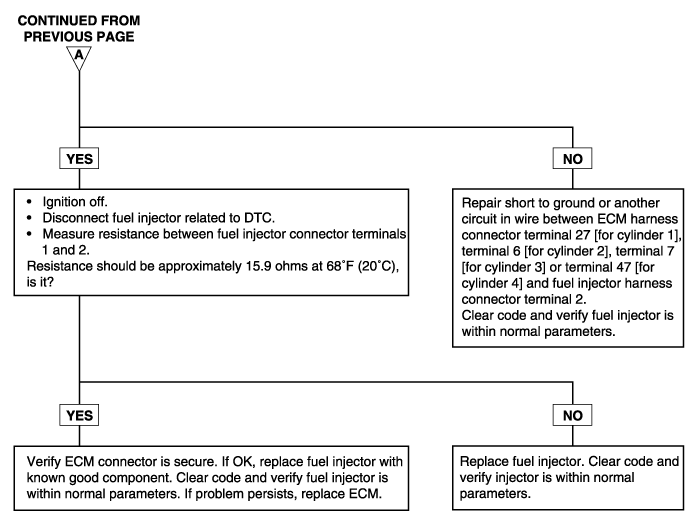
The ECM will set a code and the MIL will turn on if an open circuit or short to ground is detected in the fuel injector circuit during two driving cycles.