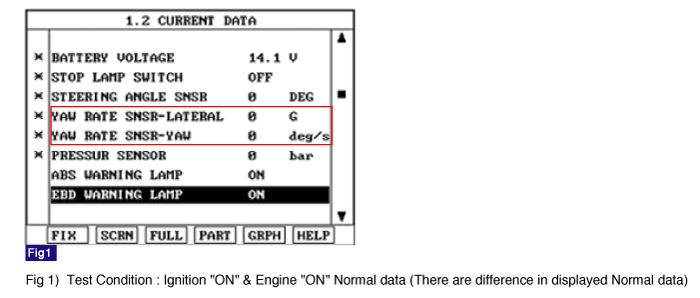
Monitor the "Yaw rate sensor-lateral & Yaw rate sensor-yaw" parameter on the Scantool.
Specification : Lateral G sensor : ± 0 G, YAW rate Sensor : ± 0 deg/s

Both the yaw-rate sensor and later G sensor is installed in lower floor. The yaw-rate sensor detecting the rotation angular velocity calculates a difference with a target amount of turing, the lateral G sensor detecting slip of the vehicle compensates a target amount of turning. Direction and magnitude of lateral G loaded to vehicle can be known with electrostatic capacity changing according to lateral G. The output voltage of the lateral G sensor is 2.5 V when the vehicle is at a standstill.
A lateral acceleration reference signal is calculated from the wheel speeds, the steering angle and the yaw rate signals to observe the lateral acceleration sensor signal. The difference between the reference signal and the sensor signal is evaluated for failure detection. A yaw rate reference signal is calculated from the wheel speeds, the steering angle and the lateral acceleration signals to observe the yaw rate sensor signal. The difference between the reference signal and the sensor signal, and the gradient of the measured sensor signal is evaluated for the failure detection. If the difference between estimated value and measured value of the sensor is larger than predefined value for predefined time, the failure is recognized. Also impossible signal according to sensor characteristic is detected the failure is recognized.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible cause | |
DTC Strategy | ● Signal Monitoring | ● Faulty Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor ● Open or short of Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor ● Faulty HECU | |
Case 1 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (during stable driving) | |
Enable Conditions | ● By building a reference lateral G from the yaw-rate sensor, wheel speed sensor and the SAS it is possible to test the later G Signal on plausibility. If during stable vehicle behavior an later G Failure larger than approximately 2.5 m/s2 occurs, the ESP controller will disregard the later G sensor information so that a false ESP intervention is prevented. A fault is recognized after 1.6 s during model validity. ● The measured and offset compensated yaw rate signal is compared to the reference yaw rate signal calculated from yaw rate sensor, later G sensor, SAS and wheel speed sensor. If the measured yaw rate deviates more than 2.5 °/s plus a dynamic threshold from the reference yaw rate during model validity, a failure is recognized after 1.6 s. The dynamic threshold is between 2.5°/s and more than 5°/s. A typical value is 3°/s. - During the possibility to observe the recognition time depends on the amount of failure. | ||
Case 2 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (during driving) | |
Enable Conditions | ● During normal driving conditions the long time filtered driving direction is straight ahead. The long time filtered later G value is equivalent to the offset. If the offset value exceeds a threshold of approximately 2.25 m/s² an later G fault is determined.Failure detection time depends on the driving distance, vehicle speed and on the amount of failed later G signal. Within 30 km of symmetrical driving the calculated offset corresponds to the sensor offset. | ||
Case 3 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (If no under voltage is detected) | |
Enable Conditions | ● A fault is detected If the lateral G is higher than 15 m/s² for more than 800 ms. | ||
Case 4 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (during standstill) | |
Enable Conditions | ● If the filtered value of |lateral G| is larger than 7 m/s² for more than 400 m/s a fault is set. | ||
Case 5 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (dependent on driving situation) | |
Enable Conditions | ● Standstill compensation : - The offset corresponds to the measured and filtered input value. Failure threshold 5.25 °/s. ● Fast compensation (during driving if no standstill compensation could be completed): - The offset corresponds to the slightly filtered deviation between measured yaw rate and the reference yaw rate calculated from SAS, later G sensor and wheel speed sensor. Failure threshold is 7.5 °/s. ● Long-term ("normal") compensation (during driving after succeeded standstill or fast offset compensation): - The offset corresponds to the strong filtered deviation between measured yaw rate and the reference yaw rate calculated from SAS, later G sensor and wheel speed sensor. Failure threshold is 7.5 °/s | ||
Case 6 | Monitoring Period | ● After every standstill. | |
Enable Conditions | ● The measured yaw rate and the model yaw rates, calculated from the wheel speed sensor and SAS are compared. If the signals doesn.t fit and forward driving is recognized, a fault is determined. | ||
Case 7 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (after initialization of the YRS and if no under voltage is detected) | |
Enable Conditions | ● The yaw rate sensor BITE logic evaluates the BITE-signal by extraction of the measured yaw rate of the vehicle. The allowed range for the BITE-signal is 25 °/s ± 7 °/s. If the BITE-signal is not in the allowed range, a suspected failure bit is set after 200 ms. A failure is set within 400 ms. | ||
Case 8 | Monitoring Period | ● After YRS-initialization, no under voltage | |
Enable Conditions | ● Depending on the driving conditions a signal gradient higher than 10 ~ 23 °/s / 40 ms sets a suspected failure bit after 280 ms, unless a single signal peak is recognized by a peakfilter. A failure is set, if the good check is not settled successfully after 10 s. | ||
Case 9 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (except spinning, use of handbrake, unsteady driving conditions or a detected under voltage) | |
Enable Conditions | ● During standstill - The allowed range of the yaw rate sensor signal is ±30 °/s. Leaving this range for 5 s sets a fault. In case of driving off after the failure was present for longer than 500 ms during standstill, the fault is detected immediately. ● While driving - The allowed range of the yaw rate sensor signal is ±94.75 °/s and a suspected failure bit is set, if the signal is out of this range for 500 ms. A fault is set after 1 s. | ||
Fail Safe | ● Reduced controller function. ● Inhibit the ESP control and allow the ABS/EBD control. ● The ESP warning lamps are activated. | ||
Connect scantool to Data Link Connector(DLC).
Ignition "ON".
Monitor the "Yaw rate sensor-lateral & Yaw rate sensor-yaw" parameter on the Scantool.
Specification : Lateral G sensor : ± 0 G, YAW rate Sensor : ± 0 deg/s

Is parameter displayed within specifications?

▶ Fault is intermittent caused by poor connection in Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor harness and/or HECU’s connector or was repaired and HECU memory was not cleared. Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination.

▶ Go to "W/Harness Inspection" procedure.
Many malfunctions in the electrical system are caused by poor harness(es) and terminals. Faults can also be caused by interference from other electrical systems, and mechanical or chemical damage.
Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage.
Has a problem been found?

▶ Repair as necessary and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Go to "Power Circuit Inspection" procedure.
Ignition "ON" & Engine "OFF".
Measure voltage between terminal "3, 5, 6" of the Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor harness connector and chassis ground.
Specification : Approx. 2.5V ( Voltage between terminal "5,6" of the Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor harness connector and chassis ground.)
Specification : Approx. above 2.1V and below 2.9V ( Voltage between terminal "3" of the Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor harness connector and chassis ground.)

Is the measured resistance within specifications?

▶ Go to "Self Test Circuit Inspection" procedure.

▶ Check for open or short in the Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor harness between terminal "3, 5, 6" of the Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor harness connector and terminal "16, 18, 20" of thechassis ground. Repair as necessary and then go to "Verification of vehicle Repair" procedure.
▶ If OK, Substitute with a known-good Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor and check for proper operation. If problem is corrected, replace sensor and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Ignition "OFF".
Engine "ON".
Does warning lamp remain On?

▶ Substitute with a known-good HECU and check for proper operation. If problem is corrected, replace HECU and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Fault is intermittent caused by poor connection in Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor circuit and/or faulty Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor or was repaired and HECU memory was not cleared. Go to the applicable troubleshooting procedure.
After a repair, it is essential to verify that the fault has been corrected.
Connect scantool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode
Using a scantool, Clear DTC.
Operate the vehicle within DTC Detecting Condition in General Information.
Are any DTCs present ?

▶ Go to the applicable troubleshooting procedure.

▶ System performing to specification at this time.