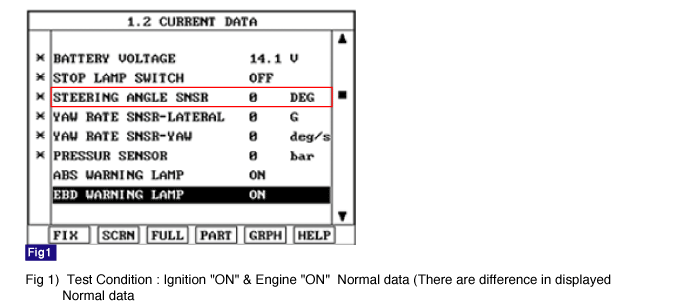
Monitor the "steering sensor" parameters on the Scantool.
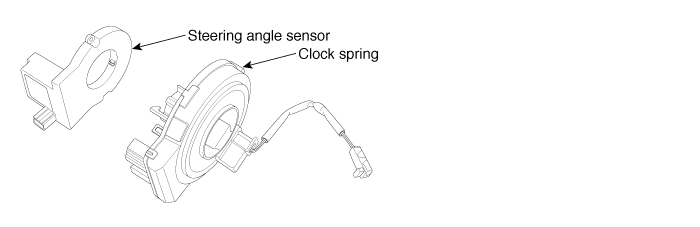
The Steering angle sensor(SAS) is composed of main gear, serve gear1 and serve gear2 to determine the turning direction. The SAS is a CAN communication type sensor. If main gear is rotated according to the rotation of steering wheel serve gear1 and serve gear2, which is contact with main gear, will be rotated. The HECU detects the absolute angle by using magnetic MR effect and the difference gear ratio of each serve gear and then send to the CAN comunication line. The HECU detects the steering wheel's operating speed and operating angle by using absolute angle, and this signal is used in a input signal of anti-roll control.
If the SAS signal is different from calculated value by yaw-rate sensor and wheel speed sensor, mechanically impossible SAS signal is detected, there is a difference between SAS signal and driving condition of the vehicle calculated from yaw-rate sensor and later G sensor, a failure is detected.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible cause | |
DTC Strategy | ● Voltage Monitoring | ● Open or short of steering angle sensor circuit ● Faulty steering angle sensor ● Faulty HECU | |
Case 1 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous | |
Enable Conditions | ● During normal driving conditions the long time filtered driving direction is straight ahead. The long time filtered SAS-value is equivalent to the offset. If the offset value exceeds a threshold of approximately 15 deg a SAS-fault is determined. Failure detection time depends on the driving distance, vehicle speed and on the amount of failed SAS signal. Within 30 km of symmetrical driving the calculated offset corresponds to the sensor offset. | ||
Case 2 | Monitoring Period | ● Continous (If the following conditions are satisfied)
| |
Enable Conditions | ● A SAS-gradient-failure is set, if
| ||
Case 3 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (After initialization and no under voltage detected) | |
Enable Conditions | ● If value is higher than 665° + 90° tolerance for more than 300 ms a fault is determined. | ||
Case 4 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (during driving) | |
Enable Conditions | ● Based on a vehicle model a reference SAS signal is build. The difference between measured SAS signal and SAS signal calculated from yaw-rate sensor signal is evaluated for fault detection. Dependent on the driving conditions failures in size of [10 + 60 m/s / vehicle reference speed] deg at steering angle are recognized within 400 ~ 4800 ms through three possible recognition paths:
| ||
Case 5 | Monitoring Period | ● Initialization once in every ignition cycle. ● The monitoring is active until a reset by a change in the SAS signal or until a right and left cornering can be recognized. | |
Enable Conditions | ● If there is no change in the signal, but a right and left cornering has been recognized, a fault is determined. (lateral G > 2 m/s² in combination with a yaw rate > 6 °/s in both directions). - At a minimum change of e.g. 5° in the signal, the monitoring is reset. | ||
Case 6 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (during driving) | |
Enable Conditions | ● The measured yaw rate and the yaw rates, calculated from the wheel speed sensor and SAS are compared. If the signals don’t fit and forwards driving is detected, a fault is determined. | ||
Case 7 | Monitoring Period | ● Continuous (during driving) | |
Enable Conditions | ● Under normal conditions, two SAS messages are sent in one 20 ms cycle, which is shown by an increase of the message counter by 2. If the message counter shows an increase higher than 3 or lower than 1 in one 20 ms-cyle, a fault is stored after 160 ms. | ||
Fail Safe | ● Reduced controller function caused by faulty SAS signal. Allow the ABS/EBD control. ● The ESP warning lamp is activated. | ||
Connect scantool to Data Link Connector(DLC).
Ignition "ON" & Engine "ON".
Turn the steering wheel to the left or right.
Monitor the "steering sensor" parameters on the Scantool.

Whenever steering wheel is turned, is the steering sensor's scantool data changed?

▶ Fault is intermittent caused by poor connection in steering sensor harness and/or HECU's connector or was repaired and HECU memory was not cleared. Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage. Repair or replace as necessary and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Go to "Component Inspection" procedure.
Ignition "OFF".
Engine "ON".
Does warning lamp remain On?

▶ Substitute with a known-good steering angle sensor and check for proper operation. If problem is corrected, replace sensor and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
▶ Substitute with a known-good HECU and check for proper operation. If problem is corrected, replace HECU and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Fault is intermittent caused by caused by open or short of steering angle sensor harness, faulty steering angle sensor.Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage. Repair or replace as necessary and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
After a repair, it is essential to verify that the fault has been corrected.
Connect scantool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode
Using a scantool, Clear DTC.
Operate the vehicle within DTC Detecting Condition in General Information.
Are any DTCs present ?

▶ Go to the applicable troubleshooting procedure.

▶ System performing to specification at this time.