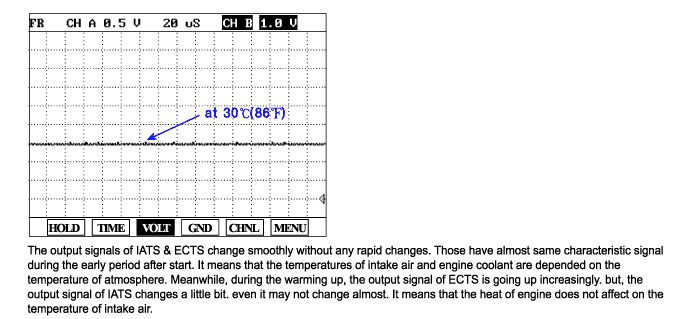
The Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS) is located in the engine coolant passage of the cylinder head for detecting the engine coolant temperature. The ECTS uses a thermistor whose resistance changes with the temperature. The electrical resistance of the ECTS decreases as the temperature increases, and increases as the temperature decreases. The reference 5 V in the PCM is supplied to the ECTS via a resistor in the PCM. That is, the resistor in the PCM and the thermistor in the ECTS are connected in series. When the resistance value of the thermistor in the ECTS changes according to the engine coolant temperature, the output voltage also changes. During cold engine operation the PCM increases the fuel injection duration and controls the ignition timing using the information of engine coolant temperature to avoid engine stalling and improve drivability.
PCM calculates the difference between the startup and current coolant temperatures and compares against the threshold. So if the difference is less than 3℃ over certain period of time PCM determines that a fault exists and a DTC is stored. MIL(Malfunction Indication Lamp) turns on when the malfunction lasts till consecutive 2 driving cycle.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible cause |
DTC Strategy | ● Rationality check | ● Poor connection ● Low level of Engine Coolant ● Improperly installed ECTS ● Open or short in circuit ● ECTS ● PCM |
Enable Conditions | ● Engine Run state ● Time from IG "OFF" to IG "ON" >360min ● No Disabling Faults Present | |
Threshold Value | ● Diffence between startup and current ECT < 3 °C(5.4°F) | |
Diagnosis Time | ● Continuous (More than 120 seconds failure within 150 second test) | |
MIL On Condition | ● 2 Driving Cycles |
Temp. (°C/°F) | Resistance (kΩ) | Temp. (°C/°F) | Resistance (kΩ) |
-40(-40) | 48.14 | 40(104) | 1.15 |
-20(-4) | 14.13 ~ 16.83 | 60(140) | 0.59 |
0(32) | 5.79 | 80(176) | 0.32 |
20(68) | 2.31 ~ 2.59 |