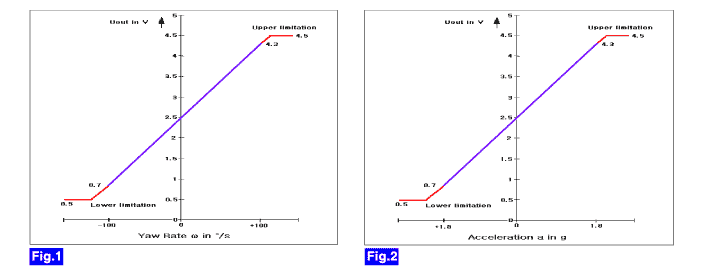
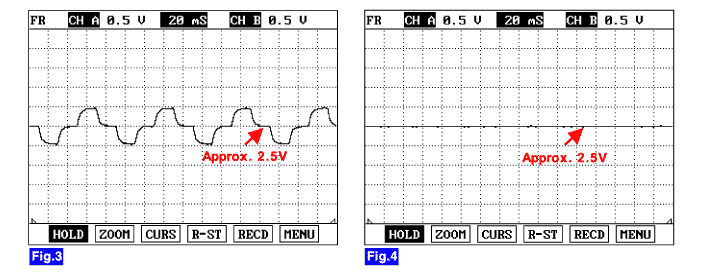
Both the yaw-rate sensor and later G sensor is installed in lower floor. The yaw-rate sensor detecting the rotation angular velocity calculates a difference with a target amount of turing, the lateral G sensor detecting slip of the vehicle compensates a target amount of turning. Direction and magnitude of lateral G loaded to vehicle can be known with electrostatic capacity changing according to lateral G. The output voltage of the lateral G sensor is 2.5V when the vehicle is at a standstill.
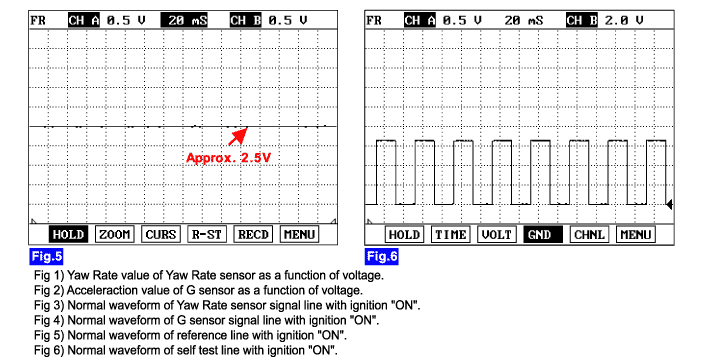
The HECU monitors a signal voltage of either yaw-rate sensor or later G sensor to detect open or short to battery or short to ground. A failure is detected if the lateral acceleration sensor or yaw rate sensor signal voltage stays in the fault range longer than the 100ms or the lateral acceleration sensor or yaw rate sensor reference voltage stays in the fault range longer than the 200ms, or the self test form is against specification during self test.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible cause | |
Case1 | DTC Strategy | ● Voltage Monitoring | ● Faulty Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor ● Open or short of Yaw Rate & Lateral G sensor ● Faulty HECU |
Monitoring Period | ● Continuous | ||
Enable Conditions | ● A line fault is detected if VLG < 0.3V or VLG > 4.7V for a time t >= 100ms. ● A line fault is detected if VYAW < 0.225V OR VYAW > 4.774V for a time t >= 100ms. ● A line fault is detected if VYAW REFERENCE < 2.1V OR VYAW REFERENCE > 2.9V for a time t >= 200ms. | ||
Case2 | DTC Strategy | ● Selftest Monitoring | |
Monitoring Period | ● Once after power up and no low voltage. | ||
Enable Conditions | ● A line fault is detected if 0.2V < VLG < 0.8V isn’t continued for a time t >= 60ms during POS (POS : power on selftest) | ||
Fail Safe | ● Reduced controller function. ● Inhibit the ESP control and allow the ABS/EBD control. ● The ESP warning lamps are activated. |