

A Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS) is a magnetic type sensor that generates voltage using a sensor and a target wheel mounted on the crankshaft; there are 58 slots in the target wheel where one is longer than the others. When the slot in the wheel aligns with the sensor, the sensor voltage outputs low. When the metal (tooth) in the wheel aligns with the sensor, the sensor voltage outputs high. During one crankshaft rotation there are 58 rectangular signals and one longer signal. The PCM calculates engine RPM by using the sensor’ s signal and controls the injection duration and the ignition timing. Using the signal differences caused by the longer slot, the PCM identifies which cylinder is at top dead center.
The PCM sets DTC P0336 when the crankshaft signal is missing while camshaft signal is detected.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause | |
DTC Strategy |
•
Signal plausibility check | 1. Open or short in signal, ground or power supply circuit 2. Poor connection or damaged harness 3. Damage to the connecting flange/flywheel 4. Misadjust crankshaft and camshaft pulley position 5. Faulty CKP sensor | |
Enable Conditions |
•
Engine synchronized
•
Engine speed > 512rpm | ||
Threshold Value | Case 1) |
•
Tooth number check(Number of missing/additional teeth > 1) | |
Case 2) |
•
Tooth number check(Number of missing/additional teeth > 2) | ||
Diagnostic Time | Case 1) |
•
5 rev. | |
Case 2) |
•
3 rev. | ||
MIL On Condition |
•
2 Driving Cycles | ||
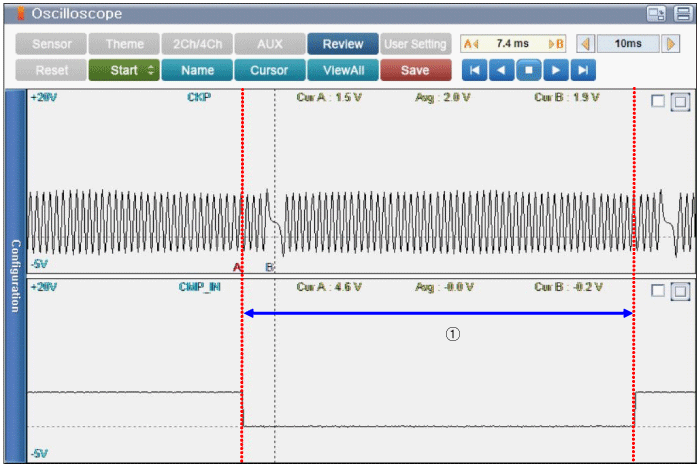
① There are 60 signals of CKPS(Including missing tooth) during the semi-cycle of CMPS #1.
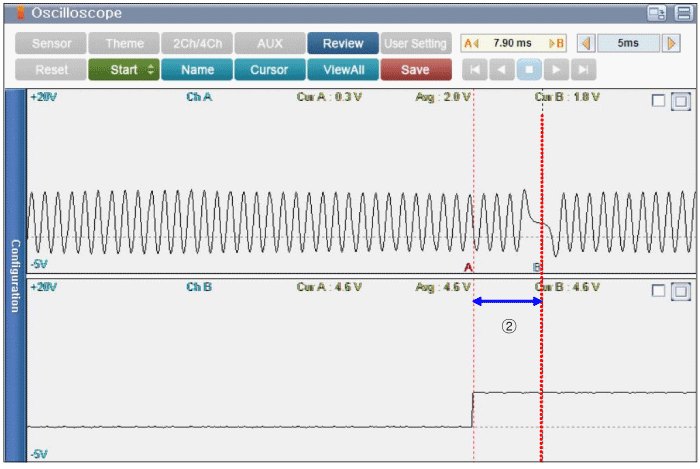
② There are 3~5 signals of CKPS between the switching point of CMPS #1 and the missing tooth of CKPS.