After warming-up, check following items.

The CVVT (Continuously Variable Valve Timing) system built on the camshaft helps the engine decrease the exhaust gas and increase engine power and fuel economy by changing the valve open/close timing of the camshaft continuously. The valve control solenoid, the main control part of the CVVT, changes the direction of the oil path through the CVVT by the duty control of the PCM and changes the open and close timing of the intake and exhaust valves.
PCM sets DTC P0077 if the PCM detects that the OCV control circuit is open or shorted to battery.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause |
DTC Strategy |
•
Electrical Check | 1. Open or short to battery in control circuit 2. Poor connection or damaged harness 3. Faulty Intake Valve Control Solenoid |
Enable Conditions |
•
10V < Battery voltage < 16V | |
Threshold Value |
•
Short circuit to battery | |
Diagnostic Time |
•
2 sec. | |
Mil On Condition |
•
2 Driving Cycles |
Oil Control Valve | Normal Parameter At 20℃ (68℉) |
Insulation Resistance | 9.9±0.5Ω |
Connect GDS and select Data Analysis.
After warming-up, check following items.

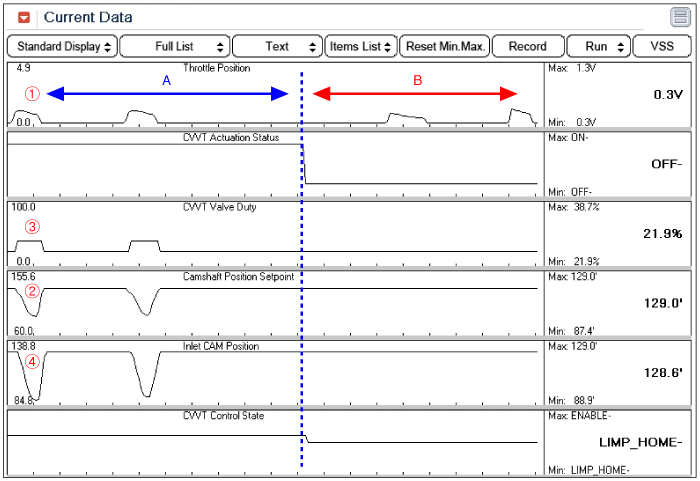
Data analysis
▶ A Sector : CVVT works
▶ B Sector : Limp Home Mode (CVVT doesn't work.)
▶ CVVT Control Flow (A Sector)
: Acceleration pedal(①) shift → Engine RPM change → Camshaft Position Setpoint (②) change → CVVT Valve Duty(③) change → Inlet CAM Position(④) change