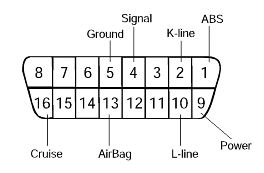
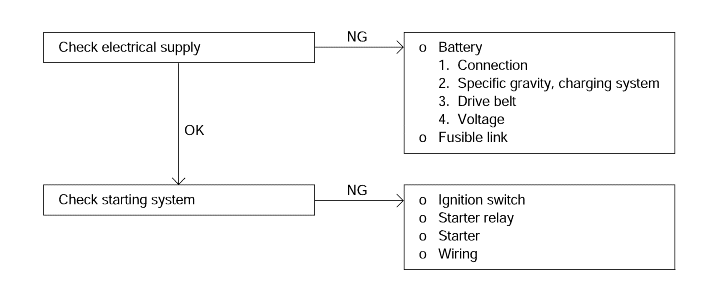
Power supply
Battery
Fusible link
Fuse
Body ground
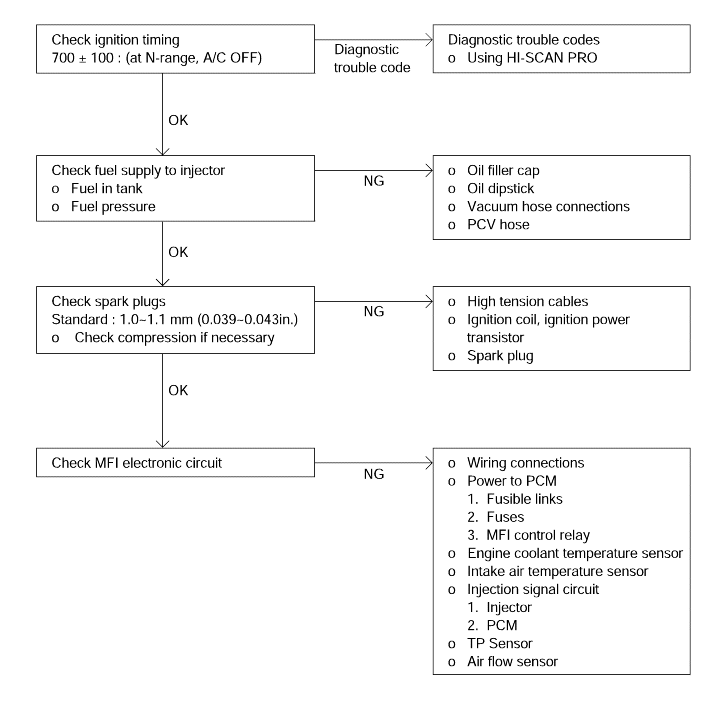
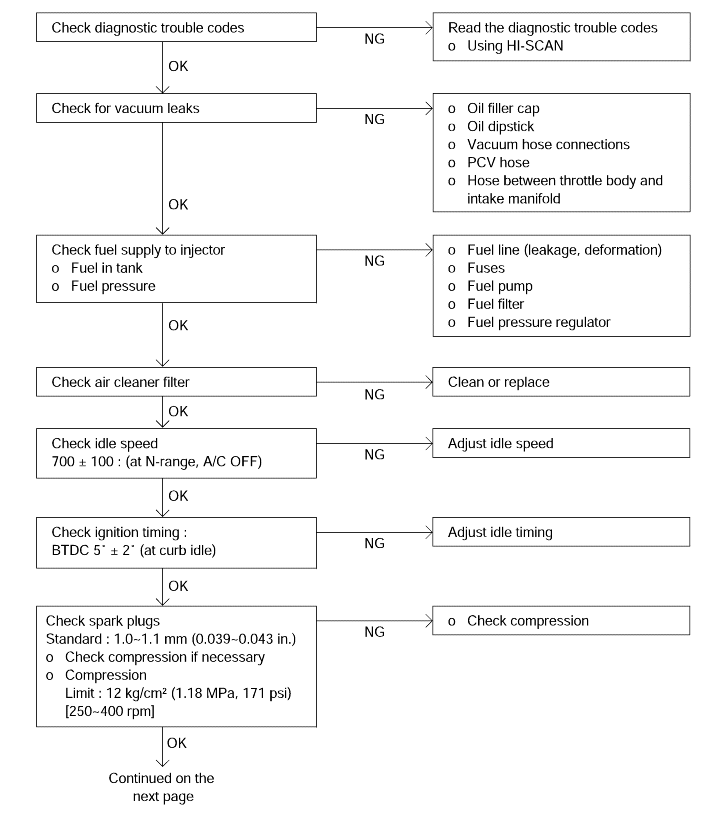
Fuel supply
Fuel line
Fuel filter
Fuel pump
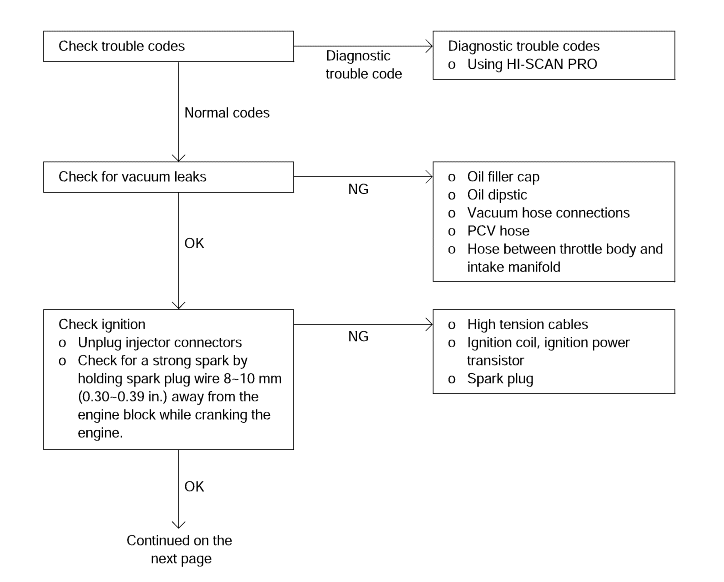
Ignition system
Spark plug
High-tension cable
Ignition coil
Emission control system
PCV system
Vacuum leak
Others
Ignition timing
Idle speed
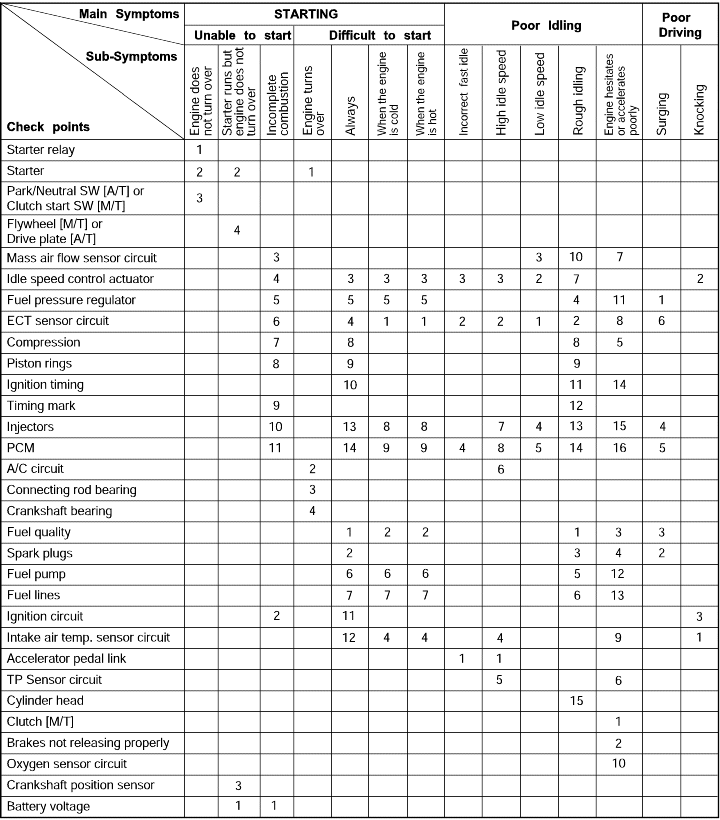
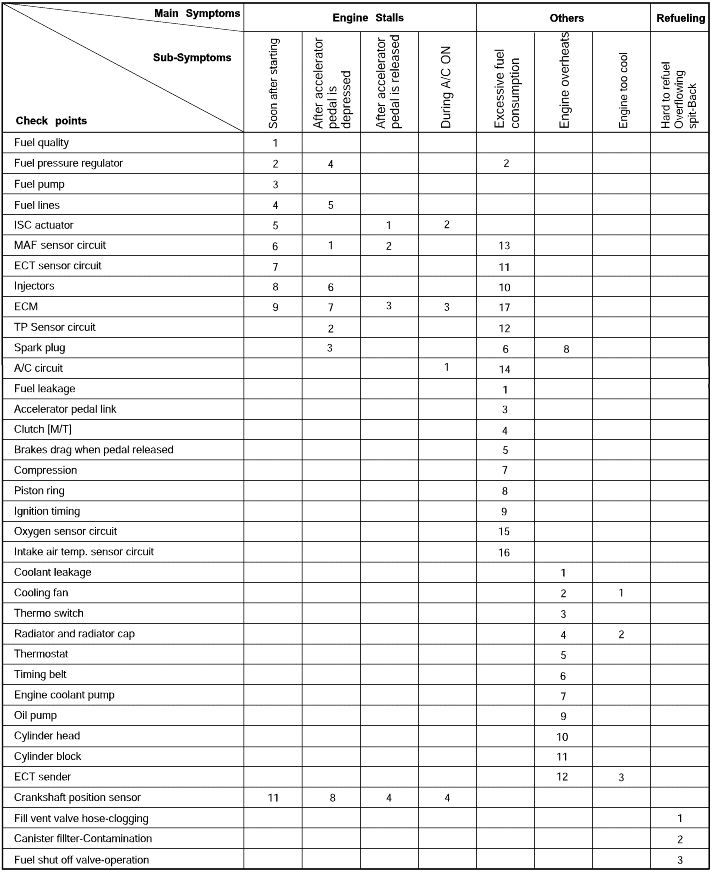
The number herein means the check order.
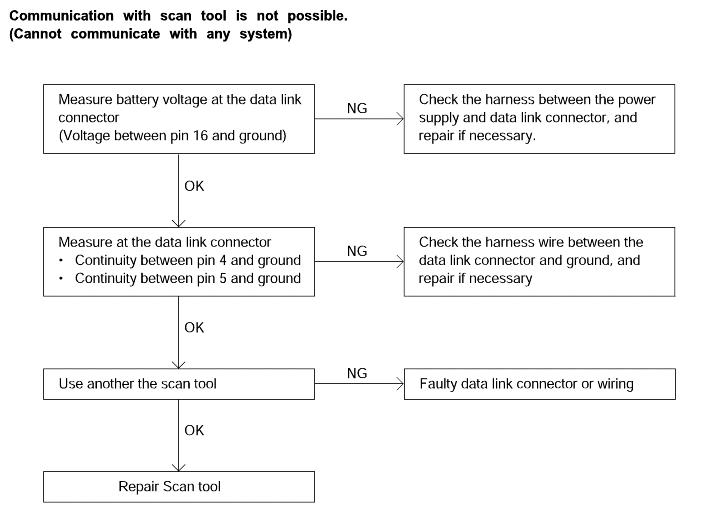
Comment | Probable cause |
One of the following causes may be suspected ● No power supply to PCM ● Defective ground circuit of PCM ● Defective PCM ● Improper communication line between PCM and scan tool | ● Malfunction of PCM power supply circuit. ● Malfunction of the PCM. ● Open circuit between PCM and DLC. |
Trouble symptom | Probable cause | Remedy |
Engine will not crank. | Battery charge low | Charge or replace battery |
Battery cables loose, corroded or worn | Repair or replace cables | |
Transaxle range switch faulty (Vehicle with automatic transaxle only) | Adjust or replace switch | |
Fusible link blown | Replace fusible link | |
Starter motor faulty | Repair starter motor | |
Ignition switch faulty | Replace ignition switch | |
Engine cranks slowly | Battery charge low | Charge or replace battery |
Battery cables loose, corroded or worn | Repair or replace cables | |
Starter motor faulty | Repair starter motor | |
Starter keeps running | Starter motor faulty | Repair starter motor |
Ignition switch faulty | Replace ignition switch | |
Starter spins but engine will not crank | Pinion gear teeth broken or starter motor faulty | Repair starter motor |
Ring gear teeth broken | Replace flywheel ring gear or torque converter |
Trouble symptom | Probable cause | Remedy |
Engine malfunctions due to insufficient fuel supply | Bent or kinked fuel pipe or hose | Repair or replace |
Clogged fuel pipe or hose | Clean or replace. | |
Clogged fuel filter of in-tank fuel filter | Replace | |
Water in fuel filter | Replace the fuel filter or clean the fuel tank and fuel lines | |
Dirty or rusted fuel tank interior | Clean or replace | |
Malfunctioning fuel pump (clogged filter in the pump) | Replace | |
Evaporative emission system malfunction (when fuel filler cap is removed, pressure is released) | Incorrect routing of a vapor line | Correct |
Disconnected vapor line | Correct | |
Folded, bent, cracked or clogged vapor line | Replace | |
Faulty fuel tank cap | Replace | |
Malfunctioning overfill limiter (two-way valve) | Replace |
Fuel Pump Control :
Turns the fuel pump relay ON so that current is supplied to the fuel pump while the engine is cranking or running.
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay Control :
Turns the compressor clutch of the A/C ON and OFF.
Fan Relay Control :
The radiator fan and condenser fan speeds are controlled in response to the engine coolant temperature and vehicle speed.
Evaporative Emission Purge Control (Refer to GROUP EC).
When an abnormality is detected in one of the sensors or actuators related to emission control, the CHECK ENGINE/MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP illuminatesas a warning to the driver.
When an abnormality is detected in one of the sensors or actuators, a diagnostic trouble code corresponding to the abnormality is output.
The RAM data inside the PCM that is related to the sensors and actuators can be read by means of the scan tool. In addition, the actuators can be controlledunder certain circumstances.
Most intermittent malfunctions occur under certain conditions. If those conditions can be identified, the cause will be easier to find.
Ask the customer about the malfunction.
Ask what it feels like, what it sounds like, etc. Then ask about driving conditions, weather, frequency of occurrence, and so on.
Determine the conditions from the customer's responses.
Typically, almost all intermittent malfunctions occur from conditions like vibration, temperature and/or moisture change, poor connections. Fromthe customer's replies, it should be deduced which condition exists.
Run a simulation test
In the cases of vibration or poor connections, use the simulation tests below to attempt to duplicate the customer's complaint. Determine the most likely circuit(s) and perform the simulation tests on the connectors and parts of that circuit(s). Be sure to use the inspection procedures provided for diagnostic trouble codes and trouble symptoms. For temperature and/or moisture conditions related intermittent malfunctions, using common sense, try to change the conditions of the suspected circuit components, then use the simulationtests below.
Repair the malfunctioning part and try to duplicate the condition(s) again to verify that the intermittent malfunction has been eliminated.
Shake the connector up-and-down, right-and-left.
Shake the wiring harness up-and-down, right-and-left.
Vibrate the part or sensor.
Remove the fuse and measure the resistance between the load side of the fuse and ground. Set the switches of all circuits which are connected to this fuse to a condition of continuity. If the resistance is almost 0Ω at this time, there is a short somewhere between these switches and the load. If the resistance is not 0Ω, there is no short at the present time, buta momentary short has probably caused the fuse to blow.
Harness being crushed by the vehicle body.
Damage to the outer casing of the harness due to wear or heat.
Water getting into the connector or circuitry.
Human error (mistakenly shorting a circuit, etc.).
Engine is hard to start or does not start at all
Unstable idle
Poor driveability
Diagnostic trouble codes are set as follows:
After the PCM first detects a malfunction, a diagnostic trouble code is recorded when the engine is restarted and the same malfunction is re-detected. (The malfunction is detected in driving cycle). However, for fuel system rich/lean misfiring, a diagnostic trouble code is recorded on the first detection ofthe malfunction.
Erasing diagnostic trouble codes:
After recording the diagnostic trouble code, if the PCM does not re-detect the malfunction for 40 driving cycles, the diagnostic trouble code will be erased from the PCM memory. However, for fuel system rich/lean or misfiring, the diagnostic trouble code will be erased if both of the following conditionsare met:
- When driving conditions (engine speed, engine coolant temperature, etc.) are identical to those when the malfunction was first recorded. - When the PCM does not re-detect the malfunction for 80 driving cycles. |
A "driving cycle" is complete as soon as the vehicle goes into closed-loop operation.
Catalyst
Fuel system
Air flow sensor (MAF sensor)
Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IAT sensor)
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECT sensor)
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
Front Oxygen Sensor
Rear Oxygen Sensor Heater
Rear Oxygen Sensor
Front Oxygen Sensor Heater
Injector
Misfire
Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP sensor)
Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP sensor)
Evaporative Emission Control System
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
Idle Speed Control
PCM
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Idle Switch
EGR System
After turning the ignition key on, check that the light illuminates for 5 seconds without the engine running.
If the light does not illuminate, check for an open circuit in the harness, blown fuse and blown bulb.
When battery voltage is excessively low, diagnostic trouble codes can not be read. Be sure to check the battery for voltage and the chargingsystem before starting the test.
Codes are erased if the battery or the PCM connector is disconnected. Do not disconnect the battery before the diagnostic trouble codes are completelyread and recorded.
Turn OFF the ignition switch.
Connect the scan tool to the data link connector on the lower crash pad.
Turn ON the ignition switch.
Use the Hi-Scan Pro to check the diagnostic trouble code.
Repair the faulty part from the diagnosis chart.
Erase the diagnostic trouble code.
Disconnect the Hi-Scan Pro.