
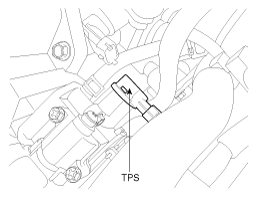
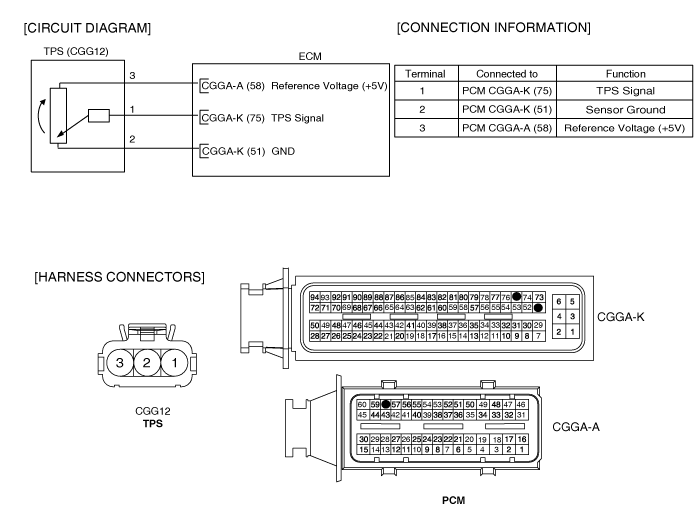
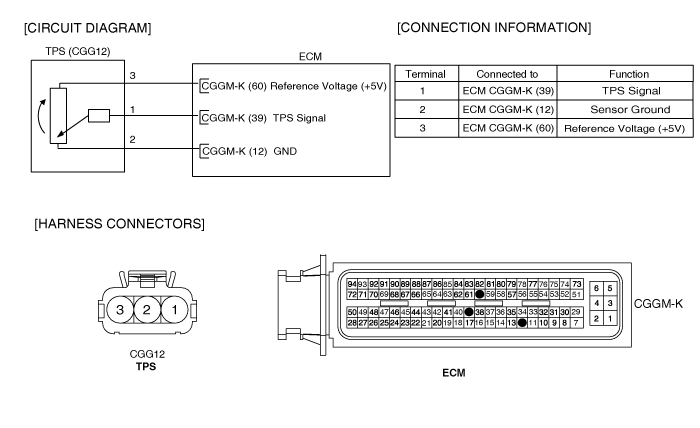
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is mounted on the throttle body and detects the opening angle of the throttle plate. The TPS has a variable resistor (potentiometer) whose characteristic is the resistance changing according to the throttle angle. During acceleration, the TPS resistance between the reference 5V and the signal terminal decreases and output voltage increases; during deceleration, the TPS resistance increases and TPS output voltage decreases. The PCM supplies a reference 5V to the TPS and the output voltage increases directly with the opening of the throttle valve. The TPS output voltage will vary from 0.25~0.9V at closed throttle to minimum 4.0V at wide-open throttle. The PCM determines operating conditions such as idle (closed throttle), part load, acceleration/deceleration, and wide-open throttle from the TPS. Also The PCM uses the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS) signal along with the TPS signal to adjust fuel injection duration and ignition timing.
Throttle Angle | Output Voltage (V) |
C.T | 0.25 ~ 0.9 |
W.O.T | Min. 4.0V |
Items | Specification |
Sensor Resistance (㏀) | 1.6 ~ 2.4 |
Connect a scantool on the Data Link Connector (DLC).
Start engine and check output voltages of TPS at C.T and W.O.T.
Specification: Refer to SPECIFICATION.
Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the scantool from the DLC.
Disconnect TPS connector and measure resistance between TPS terminals 2 and 3
Specification: Refer to SPECIFICATION.