Read "DTC Status" parameter.

The CVVT (Continuously Variable Valve Timing) system is installed to the chain sprocket of the exhaust camshaft. There is no variation in valve timing of the exhaust cam because the exhaust camshaft is driven by the timing belt. The timing of the intake cam is varied by the relative operation the CVVT vane to the housing. The CVVT controller regulates the intake camshaft angle using oil pressure through the OCV(Oil Control Valve). As result, the relative position between the camshaft and the crankshaft becomes optimal, and the engine torque improves, fuel economy improves, exhaust emissions decrease by changing the valve open/close timing of the intake camshaft.
The deviation of the camshaft position from the target point is evaluated during stable driving condition. The ECM accumulates this deviation for a certain period and sets DTC P0011 when the accumulated deviation is too high. The target camshaft position is predetermined value depending on engine speed and throttle angle in the ECM.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause |
DTC Strategy | ● Monitor deviation between camshaft position setpoint and actual value | ● Faulty Oil leak ● Faulty Oil pump ● Faulty Intake valve control solenoid |
Enable Conditions | ● No relevant failure ● 11V < Battery voltage < 16V ● CVVT control : enabled ● Camshaft setpoint moved more than 5 times for this Driving Cycle ● Stable camshaft set-point moving by more than 1.125°CRK moving ● Camshaft position setpoint-actual > 5°CRK ● 600 ~ 1700rpm < Engine speed < 5000rpm ● 20℃(68℉) < Engine oil temperature < 100℃(212℉) | |
Threshold Value | ● Integral of Camshaft position setpoint - Camshaft position actual value > 150°CRK/sec. | |
Diagnostic Time | ● Approx. 38~300 seconds depending on CAM deviation | |
Mil On Condition | ● 2 Driving Cycles |
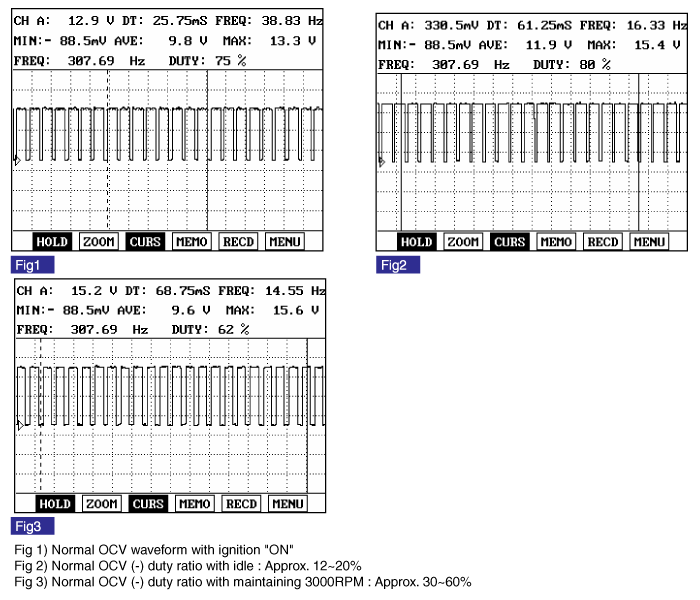
Intake OCV | Normal Parameter |
Insulation Resistance (Ω) | Above 50 ㏁ |
Temp.(℃) | Temp.(℉) | Resistance(Ω) |
0 | 32 | 6.2 ~ 7.4 |
10 | 50 | 6.5 ~ 7.7 |
20 | 68 | 6.9 ~ 7.9 |
30 | 86 | 7.1 ~ 8.3 |
40 | 104 | 7.4 ~ 8.6 |
50 | 122 | 7.7 ~ 8.9 |
60 | 140 | 8.0 ~ 9.2 |
70 | 158 | 8.3 ~ 9.5 |
80 | 176 | 8.6 ~ 9.8 |
90 | 194 | 8.9 ~ 10.1 |
100 | 212 | 9.2 ~ 10.4 |
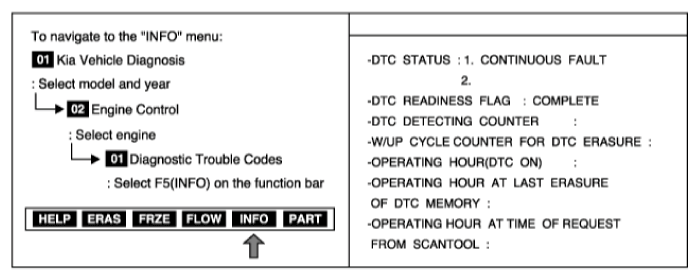
Connect scan tool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode.
Press F4(DTAL) to select DTC information from the DTCs menu.
Confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete". If not, drive the vehicle within conditions noted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions.
Read "DTC Status" parameter.

Is parameter displayed "History(Not Present) fault"?
History (Not Present) fault : DTC occurred but has been cleared.
Present fault : DTC is occurring at present time.

▶ Fault is intermittent caused by poor contact in the sensor's and/or ECM's connector or was repaired and ECM memory was not cleared. Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage. Repair or replace as necessary and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Go to next step as below.
Many malfunctions in the electrical system are caused by poor harness(es) and terminals. Faults can also be caused by interference from other electrical systems, and mechanical or chemical damage.
Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage.
Has a problem been found?

▶ Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Check valve timing. Refer to "P0016: Crankshaft Position-Camshaft Position Correlation(Bank1)" procedure. Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure
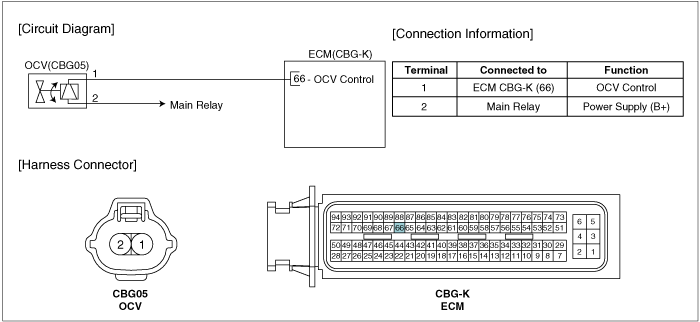
Check resistance of OCV.
Ignition "OFF"
Disconnect intake OCV connector.
Measure resistance between terminals 1 and 2 of the intake OCV connector.(Component side)
Specification : Approx. 6.9~7.9Ω at 20℃(68℉)
Is resistance within the specification?

▶ Go to next step as below.

▶ Replace OCV and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Check operation of OCV
Start the engine and let it idle.
With OCV connector still disconnected, connect 12V and a ground to 2 and 1 of the OCV(Component side).
Test Condition | Disconnect OCV connector | Apply battery voltage |
Normal Value | Normal engine speed | Rough idle or engine stall |
Has a problem been found?

▶ Go to next step as below.

▶ Go to "Check CVVT(Continuously Variable Valve Timing) Assembly" procedure.
Check OCV and Filter.
Ignition"OFF"
Check OCV filter for sticking or contamination.
Remove the OCV and visually check the spool column of OCV for contamination.
Has a problem been found?

▶ Clean or replace as necessary and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Go to next step as below.
Apply 12V and a ground to 2 and 1 terminals of the OCV(Component side).
Verify that a "clicking" sound is heard when applying the battery voltage.
Repeat this procedure 4 or 5 times to ensure intake OCV reliability.
Is OCV working properly?

▶ Go to next step as below.

▶ Check OCV for contamination, deterioration, or damage. Substitute with a known-good OCV and check for proper operation. If the problem is corrected, replace OCV and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
Remove the CVVT assembly. Refer to "Removal Procedure" in Workshop Manual.
Check that the CVVT assembly is locked.
The one of the 2 holes on the cam journal is for advances(upper) and the rest is for retards(lower). Apply masking tape to all oil path holes except the one advance hole("B") indicated by the arrow as shown in the figure.
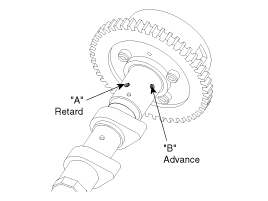
To release the CVVT lock pin, wrap some tape around the tip of an air pressure adapter and apply low air pressure of approx. 150kPa(1.5kg/㎠, 21 psi) to the exposed camshaft port. Wrap a shop towel or rag around the CVVT because residual oil may leak out of the unit when applying air pressure.
With low air pressure applied, turn the CVVT to the ADVANCE direction as indicated in the figure.
If too much air leaks when applying the low air pressure, the CVVT lock pin may not release and the CVVT may not turn.
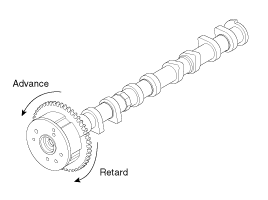
Allow the CVVT assembly to move in the ADVANCE and DELAY directions to ensure there is no binding and that it moves freely.(Movable smoothly in the range about 20˚)
Turn the CVVT by hand and make sure it locks in the maximum delay angle position.
Is CVVT assembly working properly?

▶ Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure

▶ Replace the CVVT assembly and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure
After a repair, it is essential to verify that the fault has been corrected.
Connect scan tool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode.
Press F4(DTAL) and confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete". If not, drive the vehicle within conditions noted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions.
Read "DTC Status" parameter.
Is parameter displayed "History(Not Present) fault"?

▶ System performing to specification at this time. Clear the DTC

▶ Go to the applicable troubleshooting procedure.