Read "DTC Status" parameter.
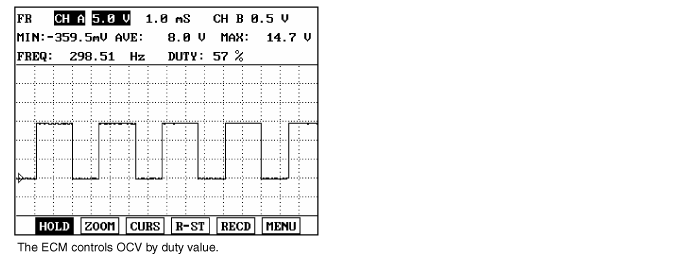
Different from the existing fixed cam phase angle type, CVVT(Continuously Variable Valve Timing) is the device which varies cam phase angle continuously to be optimum. And with engine oil pressure, it operates. CVVT consists of OCV(Oil Control Valve) and cam phaser. OCV, mounted on cylinder head, controlls the amount and direction of oil delivered to cam phaser by oil valve which is connected to a solenoid. Cam phaser, rotating cam phaser rotor with pressure and amount of oil produced by OCV, rotates cam shaft forcefully for or against the rotating direction and finally, cam shaft phase changes. With the appliance of CVVT, engine power,fuel efficiency and the quality of exhause gas are improved.
If there is a delay between the target angle and the real angle over 10 times, PCM sets DTC P0011.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause |
DTC Strategy | ● Slow response check | ● Poor connection ● Contamination of Oil / Clog of Oil path ● OCV ● CVVT |
Enable Conditions | ● Time after engine start > 10~60s ● Coolant temperature : 60~110℃ ● Engine oil temperature : 60~110℃ ● Reference position adaption completed ● CVVT control condition activated | |
Threshold Value | ● arget following delay > 10 times | |
Diagnostic Time | ||
MIL ON Condition | ● 2 driving cycle |
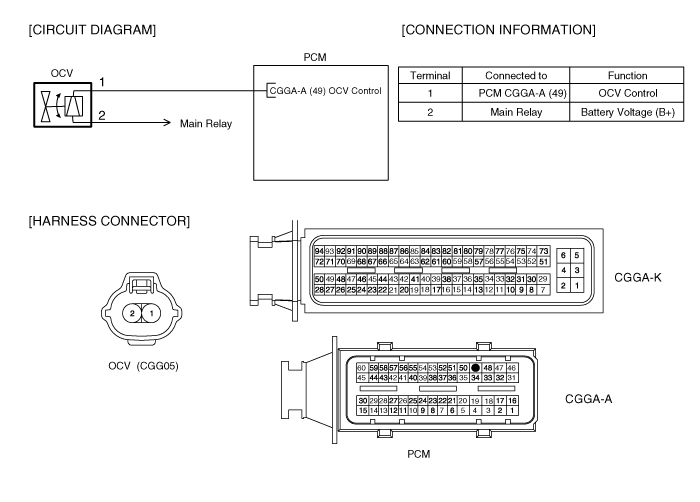
ITEM | SPECIFICATION |
Coil Resistance (Ω) | 6.9 ~ 7.9Ω at 20℃ (68℉) |
Connect scantool to Data Link Connector(DLC).
IG "ON".
Select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode, and then Press F4(DTAL) to check DTC'sinformation from the DTCs menu
Confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete". If not, drive the vehicle within conditionsnoted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions noted in the DTC detecting condition.
Read "DTC Status" parameter.

Is parameter displayed "History(Not Present) fault"?
History fault : DTC occurred but has been cleared.
Present fault : DTC is occurring at present time.

▶ Fault is intermittent caused by poor contact in the sensor's and/or ECM's connector or wasrepaired and ECM memory was not cleared. Thoroughly check connectors for looseness,poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage.Repair or replace as necessary and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

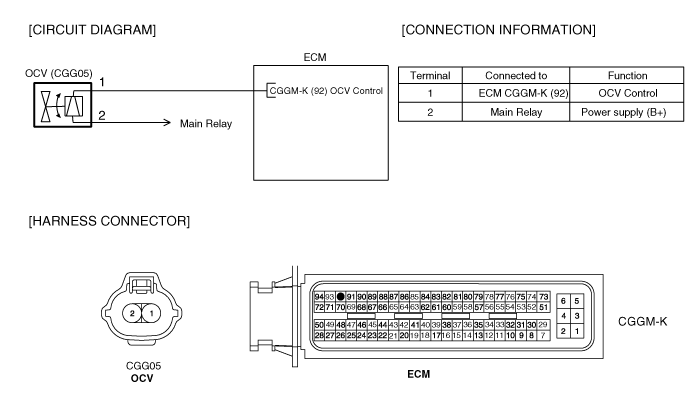
▶ Go to "Terminal & Connector Inspection" procedure
Many malfunctions in the electrical system are caused by poor harness and terminals. Faults can also be caused by interference from other electrical systems, and mechanical or chemical damage.
Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage.
Has a problem been found?

▶ Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Go to "System inspection" procedure.
Visual check.
Check engine oil gauge.
Check contamination of engine oil.
Check contamination of OCV filter.
Check clog of oil path.
Is there any problem?

▶ Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Go to "Component inspection" procedure.
Check OCV
Connect scantool to Data Link Connector(DLC).
Key "ON".
Perform "Actuation Test" for OCV.

Does the OCV work normally? (Check cliking sound)

▶ Substitute with a known-good CVVT and check for proper operation. If the problem is corrected, replace CVVT and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.

▶ Substitute with a known-good OCV and check for proper operation. If the problem is corrected, replace OCV and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
After a repair, it is essential to verify that the fault has been corrected.
Connect scan tool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes(DTCs)" mode.
Press F4(DTAL) and confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete".
If not, drive the vehicle within conditions noted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions.
Read "DTC Status" parameter.
Is parameter displayed "History(Not Present) fault"?

▶ System performing to specification at this time. Clear the DTC.

▶ Go to the applicable troubleshooting procedure.