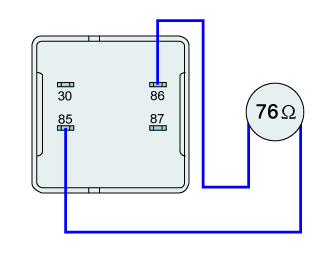
Measure the resistance between terminal "85" and terminal "86".
■ Specification : 76Ω ± 10 % (20℃)
First of all check damage of harness and terminals : Check terminals for contact resistance, corrosion and deformation.
When battery power is not supplied to starter although start relay circuit is normal, Inspect the start relay.
IG KEY "OFF", ENGINE "OFF"
Remove the start relay.
Before measuring resistance, you must calibrate(0Ω) the tester.
Refer to "Multimeter calibration" of detail inspections (Equipment settings).
Measure the resistance between terminal "85" and terminal "86".
■ Specification : 76Ω ± 10 % (20℃)

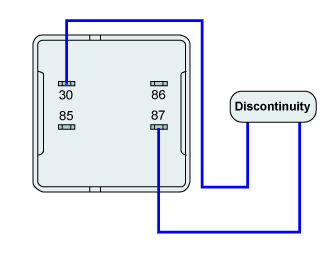
Measure the resistance between terminal "30" and terminal "87".
■ Specification : Discontinuity (Infinite Ω)
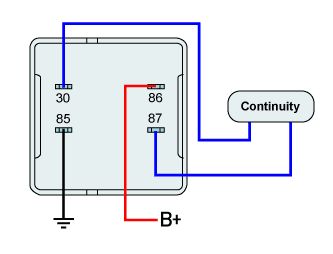
Actuate the relay by suppling battery power and chassis ground at terminal "85", "86".
☞ Inspect operating sound in the main relay when power is supplied.
Measure the resistance between terminal "30" and terminal "87" when relay is actuated.
■ Specification : Continuity (below 1.0 Ω)
※ If trouble symptom occurs intermittently although relay is operated well as above, Inspect the inside of the relay.
☞ Make sure of damage of the relay cover.
- Contact : Inspect contact connection and carbon deposit by spark.
- Coil : Inspect partial damage by coil short and enamel coating damage.
Symptom | Inspection procedure | |
Case1 | ● Relay coil resistance is high. (Open) | ● Engine cranking is impossible because battery power is NOT supplied to starter. ● Replace the start relay. |
Case2 | ● Relay coil resistance is low. (Short) | ● Fuse is blown because of relay coil short (Over current). ● Engine cranking is impossible because battery power is NOT supplied to starter. ● Replace the start relay. |
Case3 | ● Relay coil is normal. (Intermittent poor contact connection) | ● Engine cranking is impossible intermittently because battery power is NOT supplied to starter intermittently. ● Replace the start relay. |