

In order to control emissions of the CO, HC and NOx components of the exhaust gas, heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), mounted on the front side and rear side of catalytic converter, detects the oxygen content in the exhaust gas. The front HO2S signal is used to control air/fuel ratio (closed loop fuel control) and the rear HO2S signal is used to monitor front HO2S and catalyst for proper operation. The HO2S requires a minimum temperature to operate properly and provide a closed loop fuel control system. The HO2S contains the heater element to reduce its warming-up time and ensure its performance during all driving conditions. The oxygen sensor generates a voltage that indicates the difference between the oxygen content of the exhaust stream and the oxygen content of ambient air. When the exhaust stream is “rich,” there is more oxygen in the ambient air than in the exhaust stream, so the voltage will be higher.
Checking output signals from HO2S under detecting condition, if an output signal is above 1.3V for more than predeterminate time, ECM sets P0152.
Item | Detecting Condition | Possible Cause |
DTC Strategy |
•
Signal check, high |
•
Poor connection
•
Short to Power in signal circuit
•
B2S1 |
Enable Conditions |
•
Target lambda = 1
•
Battery voltage > 10.7V
•
Exhaust gas temperature (model) < 900C
•
Upstream O2S Heater control On | |
Threshold value |
•
B1S1 sensor voltage > 1.08V | |
Diagnosis Time |
•
10 sec | |
MIL On Condition |
•
2 Driving Cycles |
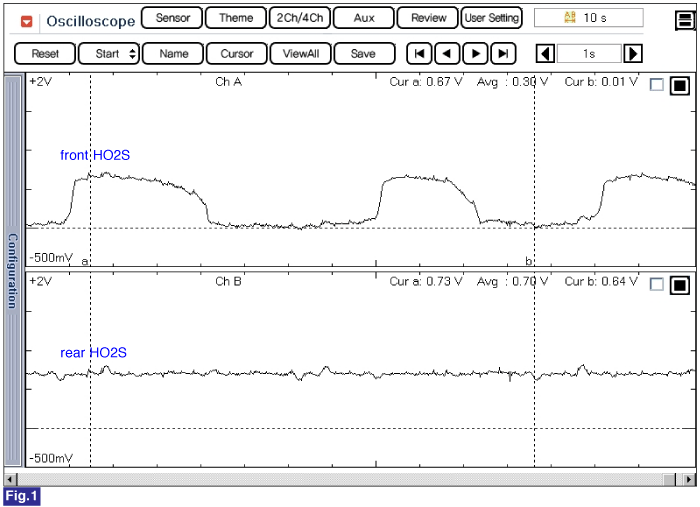
Fig. 1) Normal waveforms of front HO2S(the upper) and rear HO2S(the lower)
After warming-up, if accelerator pedal is released suddenly around 4000rpm, the HO2S signal reading will be lower than 200mV resulting from Fuel cut-off for the moment. Conversely, if suddenly accelerator pedal is depressed, HO2S signal reading will be around 0.6V ~1.0V. At idle, Normally HO2S signal will switch from lean to rich with 3 Hz. And as racing, Its frequency rises.