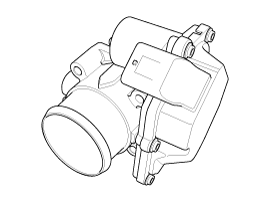
The air control valve is mounted on throttle body of diesel engine and controls air control valve according to PWM (Pulse With Modulation) signal from ECM.
It consists of;
a DC motor which actuates the air control valve,
a 2-step gear (transmission ratio = 1:40) which is located in between the DC motor and the air control valve and increases torque of the DC motor,
a position sensor which is a hall-effect sensor and detects status of the air control valve,
an electric control unit which is a micro-controller and drives the DC motor by the PWM (Pulse With Modulation) signal from the ECM,
and a reset spring which resets the de-energized air control valve to its open position.
Its function is described below:
Anti-judder function: When engine is shut off, the ECM can prevent intake air from entering to intake manifold by fully closing the air control valve for 1.5 seconds (95% < Duty < 97%) to reduce engine vibration.
Intake air control for EGR: When exhaust gas pressure is equal to or lower than intake air pressure (for example, when low engine speed), the exhaust gas would not enter to the intake manifold. At this time, the ECM partially closes the air control valve (5% < Duty < 94%) to reduce the intake air quantity. The intake air pressure thus is lower than the exhaust gas pressure.
Exhaust gas temperature control for DPF regeneration: When the Catalyzed Particulate Filter (DPF) is need to regenerate, the ECM partially closes the air control valve (5% < Duty < 94%) to reduce the intake air quantity. At this time, the air-fuel ratio would become rich and the exhaust gas temperature would be high enough to burn the soot inside the DPF.