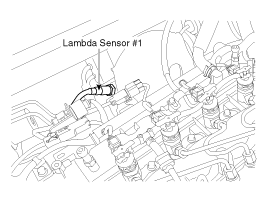
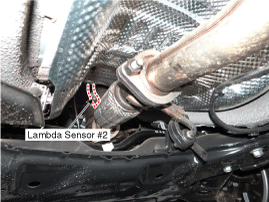
Rich air fuel ratio (0.9 < λ < 1.0): ECM takes away pumping current from lambda sensor (- pumping current) to deactivate the sensor to satisfy λ=1.0 (pumping current = 0). ECM detects the oxygen density in exhaust gas by using the amount of pumping current supplied to lambda sensor. This performance is the most active and fast at normal operating temperature (450℃ - 600℃), thus, in order to reach and maintain normal operating temperature, a heater (heating coil) is integrated with lambda sensor, which is controlled by ECM as Pulse With Modulator (PWM). The resistance of heater coil is low when coil is cold thus, current through it increases while resistance is high when coil is hot thus, current decreases. With this principle, temperature of lambda sensor is measured and lambda sensor heater operation varies based on the data.