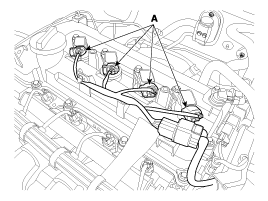
Disconnect the ignition coil connectors (A).
If there is lack of power, excessive oil consumption or poor fuel economy, measure te compression pressure.
Start the engine and allow to warm up to operating temperature. (about five minutes)
Stop the engine.
Remove the air cleaner assembly.
(Refer to Intake And Exhaust System - "Air Cleaner")
Disconnect the ignition coil connectors (A).

Remove the ignition coils (A).
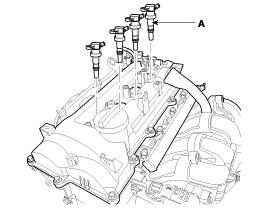
Disconnect the injector connectors (A).
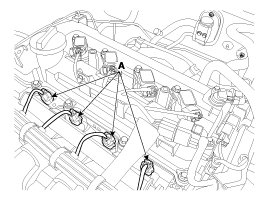
Remove the four spark plugs (A) using a 16mm sparkplug wrench.
Check the cylinder compression pressure.
Insert a compression gauge into the spark plug hole.
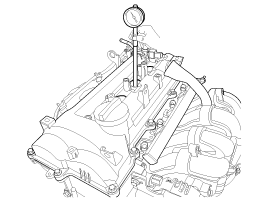
Fully open throttle.
While cranking the engine, measure the compression pressure.
Always use a fully charged battery to obtain engine speed of 250rpm or more.
Repeat step (1) through (3) for each cylinder.
This measurement must be done in as short atime as possible
Compression pressure :
1,373 kPa (14.0 kg/cm², 199.0 psi)
Minimum pressure :
1,226 kPa (12.5 kg/cm², 178.0 psi)
Difference between each cylinder :
98 kPa (1.0 kg/cm², 14 psi) or less
If the cylinder compression in 1 or more cylinders is low, pour a small amount of engine oil into the cylinder through the spark plug hole and repeat step (1) through (3) for cylinders with low compression.
If adding oil helps the compression, it is likely that the piston rings and/or cylinder bore are worn or damaged.
If pressure stays low, a valve may be sticking or seating is improper, or there may be leakage past the gasket.
Reinstall the spark plugs.
Tightening torque :
14.7 ~ 24.5 N.m (1.5 ~ 2.5 kgf.m, 10.8 ~ 18.1 lb-ft)
Connect the injector connectors.
Install the ignition coil.
Tightening torque :
9.8 ~ 11.8 N.m (1.0 ~ 1.2 kgf.m, 7.2 ~ 8.7 lb-ft)
Connect the ignition coil connectors.
Some DTC's may exist after the inspection test and may need to be manually cleard with GDS.