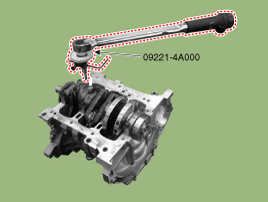
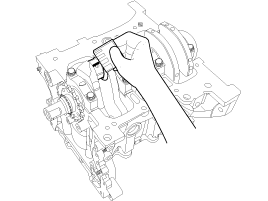
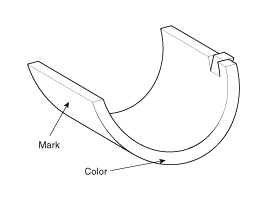
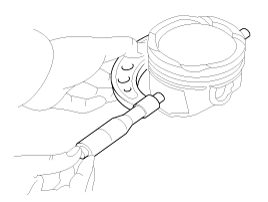
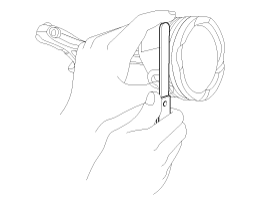
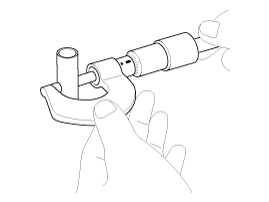
Check the connecting rod end play.
Using a feeler gauge, measure the end play while moving the connecting rod back and forth.
Standard end play :
0.10 ~ 0.25 mm (0.0039 ~ 0.0098 in)
If out-of-tolerance, install a new connecting rod.
If still out-of-tolerance, replace the crankshaft.