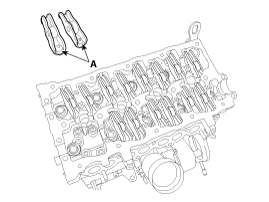
Remove the cam follower (A).
Engine removal is required for this procedure.
To avoid damaging the cylinder head, wait until the engine coolant temperature drops below normal temperature before removing it.
When handling a metal gasket, be careful not to fold the gasket or damage the contacting surface of the gasket.
Turn the crankshaft pulley so that the No. 1 piston is at top dead center.
Remove the engine and transaxle assembly.
(Refer to Engine And Transaxle Assembly - “Engine And Transaxle Assembly”)
Remove the intake manifold.
(Refer to Intake And Exhaust System - "Intake Manifold")
Remove the exhaust manifold.
(Refer to Intake And Exhaust System - "Exhaust Manifold")
Remove the EGR cooler.
(Refer to Intake And Exhaust System - “EGR Cooler”)
Remove the thermostat housing.
(Refer to Cooling System - “Thermostat”)
Remove the glow plug.
(Refer to Engine Electrical System - “Preheating System”)
Remove the common rail.
(Refer to Engine Control/Fuel System - “Common Rail”)
Remove the cylinder head cover.
(Refer to Cylinder Head Assembly - “Cylinder Head Cover”)
Remove the timing chain.
(Refer to Timing System - “Timing Chain”)
Remove the camshaft.
(Refer to Cylinder Head Assembly - “Camshaft”)
Remove the cam follower (A).

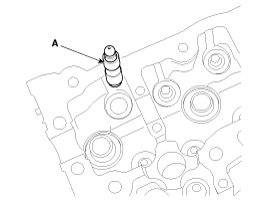
Remove the hydraulic lash adjust (HLA) (A).
Remove the cylinder head bolts, then remove the cylinder head.
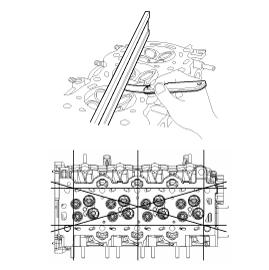
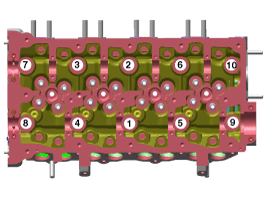
Using bit socket (12PT), uniformly loosen and remove the 10 cylinder head bolts, in several passes, in the sequence shown.
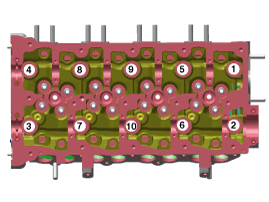
Head warpage or cracking could result from removing bolts in an incorrect order.
Lift the cylinder head (A) from the dowels on the cylinder block and replace the cylinder head on wooden blocks on a bench.
Be careful not to damage the contacting surfaces of the cylinder head and cylinder block.
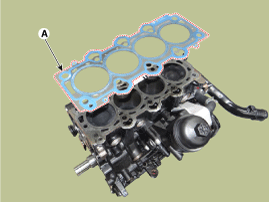
Remove the cylinder head gasket (A).
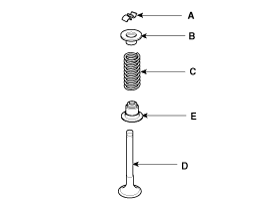
Remove the valves.
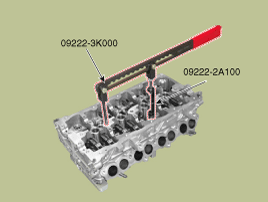
Using the SST (09222-3K000, 09222-2A100), compress the valve spring and remove the retainer lock (A).
Remove the spring retainer (B).
Remove the valve spring (C).
Remove the valve (D).
Using a needle-nose pliers, remove the stem oil seal (E).
Inspect for flatness.
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surface contacting the cylinder block and inspect the manifolds for warpage.
Flatness of cylinder head gasket surface :
Less than 0.05 mm (0.0020 in) for all
Less than 0.03 mm (0.0012 in) for each cylinder
Less than 0.012 mm (0.00047 in) for 50 mm (1.9685 in.) x 50 mm (1.9685 in.)
Flatness of manifold mating surface :
Less than 0.025 mm (0.0010 in) for width
Less than 0.160 mm (0.0063 in) for length
Less than 0.013 mm (0.00051 in) for 50 mm (1.9685 in.) x 50 mm (1.9685 in.)
Inspect for cracks.
Check the intake ports, exhaust ports and cylinder block surface for cracks. If cracked, replace the cylinder head.
Inspect the valve stems and valve guides.
Using a caliper gauge, measure the inner diameter of valve guide.
Valve guide inner diameter :
Intake : 5.500 ~ 5.512 mm (0.2165 ~ 0.2170 in)
Exhaust : 5.500 ~ 5.512 mm (0.2165 ~ 0.2170 in)
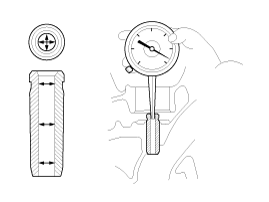
Using a micrometer, measure the outer diameter of valve stem.
Valve stem outer diameter
Intake : 5.455 ~ 5.470 mm (0.2148 ~ 0.2154 in)
Exhaust : 5.435 ~ 5.450 mm (0.2140 ~ 0.2146 in)
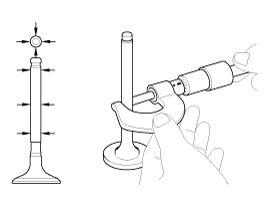
Subtract the valve stem outer diameter measurement from the valve guide inner diameter measurement.
Valve stem- to-guide clearance
Intake : 0.030 ~ 0.057 mm (0.0012 ~ 0.0022 in)
Exhaust : 0.050 ~ 0.077 mm (0.0020 ~ 0.0030 in)
If the clearance is greater than specification, replace the valve and valve guide.
Inspect the valves.
Check that the valve is ground to the correct valve face angle.
Check the surface of valve for wear.
If the valve face is worn, replace the valve.
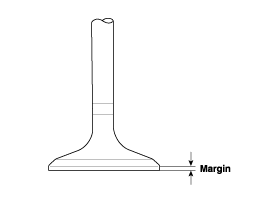
Check the valve head margin thickness. If the margin thickness is less than specification, replace the valve.
Margin
Intake : 1.1 mm (0.0433 in)
Exhaust : 1.2 mm (0.0472 in)
Check the valve length.
Length
Intake : 93.0 mm (3.6614 in)
Exhaust : 93.7 mm (3.6890 in)
Check the surface of valve stem tip for wear.
If the valve stem tip is worn, replace the valve.
Inspect the valve seats.
Check the valve seat for evidence of overheating and improper contact with the valve face. If the valve seat is worn, replace the cylinder head.
Check the valve guide for wear. If the valve guide is worn, replace the cylinder head.
Inspect the valve springs.
Using a steel square, measure the out-of-square of valve spring.
Using a vernier calipers, measure the free length of valve spring.
Valve spring
Standard
Free height : 49.53 mm (1.9500 in)
Load : 16.9 ~ 18.7 kg / 32.0 mm (37.2 ~ 41.2 lb / 1.2598 in)
26.7 ~ 29.0 kg / 23.8 mm (58.9 ~ 63.9 lb / 0.9370 in)
Out of square : Less than 1.5°
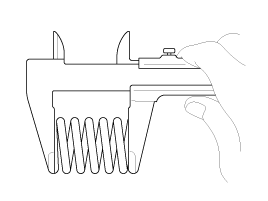
If the load is not as specified, replace the valve spring.
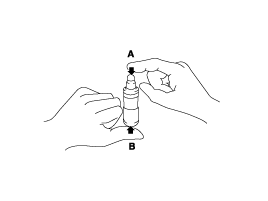
With the HLA filled with engine oil, hold A and press B by hand.
If B moves, replace the HLA.
Problem | Possible cause | Action |
1. Temporary noise during engine cold start | Normal | This noise will disappear after the oil in the engine reaches the normal pressure. |
2. Continuous noise when the engine is started after parking more than 48 hours. | Oil leakage of the high pressure chamber on the HLA, allowing air to get in. | Noise will disappear within 15 minutes when engine runs at 2000-3000 rpm. If it doesn’t disappear, refer to step 7 below. |
3. Continuous noise when the engine is first started after rebuilding cylinder head. | Insufficient oil in cylinder head oil gallery. | |
4. Continuous noise when the engine is started after excessively cranking the engine by the starter motor or band. | Oil leakage of the high-pressure chamber in the HLA, allowing air to get in. Insufficient oil in the HLA. | |
5. Continuous noise when the engine is running after changing the HLA. | note Do not run engine at a speed higher than 3000 rpm, as this may damage the HLA. | |
6. Continuous noise during idle after high engine speed. | Engine oil level too high or too low. | Check oil level. Drain or add oil as necessary. |
Excessive amount of air in the oil at high engine speed. | Check oil supply system. | |
Deteriorated oil. | Check oil quality. If deteriorated, replace with specified type. | |
7. Noise continues for more than 15 minutes. | Low oil pressure. | Check oil pressure and oil supply system of each part of engine. |
Faulty HLA. | Remove the cylinder head cover and press HLA down by hand. If it moves, replace the HLA. |
Thoroughly clean all parts to be assembled.
Before installing the parts, apply fresh engine oil to all sliding and rotating surface.
Replace oil seals with new ones.
Install the valves.
Using the SST (09222-2A110) (A), push in a new stem seal (E).
Do not reuse old valve stem oil seals.
Incorrect installation of the seal could result in oil leakage past the valve guides.
Install the valve (D), valve spring (C) and spring retainer (B).

Place the valve springs so that the side coated with enamel faces toward the valve spring retainer and then install the retainer.
Using the SST(09222-2A100, 09222-3K000), compress the spring and install the retainer locks (A).
After installing the valves, ensure that the retainer locks are correctly in place before releasing the valve spring compressor.

Lightly tap the end of each valve stem two or three times with the wooden handle of a hammer to ensure proper seating of the valve and retainer lock.
Thoroughly clean all parts to be assembled.
Always use a new cylinder head and manifold gasket.
Always use new cylinder head bolts. Cylinder head bolts are torque-to-yield bolts designed to be permanently elongated beyond the state of elasticity when torqued, so if the bolts are removed and reused, it may cause the bolts to break or fail to maintain clamping force.
The cylinder head gasket is a metal gasket. Be careful not to bend it.
Rotate the crankshaft, and set the No.1 piston at TDC.
Cylinder head dowel pins must be aligned.
Select the cylinder head gasket.
Measure the piston protrusion from the upper cylinder block face (I) on 8 places (A ~ H) at T.D.C.
Measure on the crankshaft center line considering the piston migration.
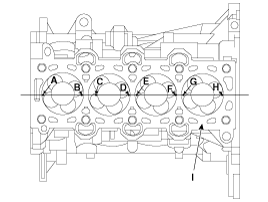
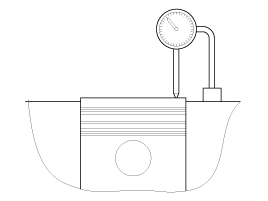
Select the gasket in the table below using the average value of piston protrusions. If the measured value of any of the points exceeds the limit of certain rank, use the gasket of the next higher rank.
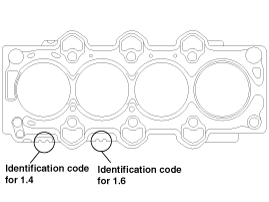
Displacement | 1.4 / 1.6 | ||
Average of piston protrusion | +0.035mm(0.0014in) ≤ ~ < +0.105mm(0.0041in) | +0.105mm(0.0041in) ≤ ~ < +0.175mm(0.0069in) | +0.175mm(0.0069in) ≤ ~ < +0.245mm(0.0096in) |
Uncompressed gasket thickness | 1.00 ~ 1.15mm(0.0394 ~ 0.0453in) | 1.05 ~ 1.20mm(0.0413 ~ 0.0472in) | 1.10 ~ 1.25mm(0.0433 ~ 0.0492in) |
Compressed gasket thickness | 0.90 ~ 1.00mm(0.354 ~ 0.394in) | 0.95 ~ 1.05mm(0.0374 ~ 0.0413in) | 1.00 ~ 1.10mm(0.0394 ~ 0.0433in) |
Range of each rank | ~≤0.14mm(0.0055in) | 0.14mm(0.0055in) ≤ ~ < 0.21mm(0.0083in) | 0.21mm(0.0083in) ≤ ~ |
Identification code | 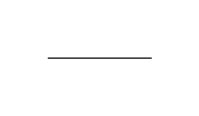 | 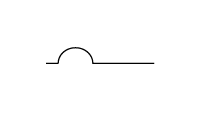 | 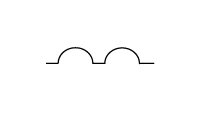 |
Gasket grade | A | B | C |
Install the gasket so that the identification mark faces toward the timing chain side.
Install the cylinder head gasket (A) on the cylinder block.
Install in the correct direction.

Carefully place the cylinder head (A) so as not to damage the gasket.

Install the cylinder head bolts.
Do not apply engine oil on the cylinder head bolts.
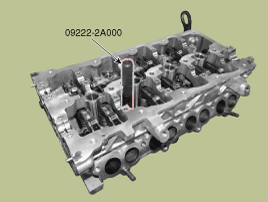
Using the SST (09221-4A000), install and tighten the 10 cylinder head bolts, in several passes, in the sequence shown.
Tightening torque :
47.1~51.0Nm (4.8~5.2 kgf.m, 34.7~37.6 lb-ft) + (88~92°) + (118~122°)
Always use new cylinder head bolts. Cylinder head bolts are torque-to-yield bolts designed to be permanently elongated beyond the state of elasticity when torqued, so if the bolts are removed and reused, it may cause the bolts to break or fail to maintain clamping force.
Install the hydraulic lash adjuster (HLA) (A).

Before installation, the HLA should be held upright so as not to spill diesel oil or attract dust onto HLA.
Carefully insert the HLA into the cylinder head so as not to spill engine oil.
If engine oil has spilled out of the lash adjuster, HLA bleeding should be performed according to the below procedure.
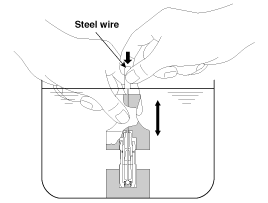
HLA bleeding procedure
Stroke the lash adjuster in engine oil by pushing its cap 4 to 5 times while pushing the ball down slightly using a hard steel wire. Be careful not to give the ball a hard push as the ball weighs only several grams.
Installing with engine oil spilt out of the lash adjuster and air in it may cause an abnormal noise.
Install the cam follower (A).

Install the remaining parts in the reverse order of removal.