Is sensor contaminated?
 | ▶ Go to "Catalyst converter check" procedure. |
 | ▶ Replace HO2S(S2) and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure. |
Inspect the front HO2S for any silicon contamination. This contamination will be indicated by a white powdery coating and this will result in a bad false voltage signal.
If contamination is evident on the HO2S, replace contaminated sensor with the new one and go to next step.
Is sensor contaminated?
 | ▶ Go to "Catalyst converter check" procedure. |
 | ▶ Replace HO2S(S2) and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure. |
Catalyst converter visual check
▶ Check discoloration by over-heating.
▶ Check deflection or crack(hole).
▶ Check noise.
Check whether the catalyst converter is genuine.
After erase the DTC, drive the vehicle more than 60sec according to "Enable Conditions"(Refer to "DTC Detecting Condition"). And then, confirm DTC.
Is there something wrong?
 | ▶ Go to "Check Catalyst converter performance" procedure. |
 | ▶ Many malfunctions in the electrical system are caused by poor harness(es) and terminals. Faults can also be caused by interference from other electrical systems, and mechanical or chemical damage. So, check poor connections and the related circuit between ECM/PCM and component thoroughly. Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure. |
Connect GDS to DLC(Data Link Cable).
Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature.
Check the "Current Data" about related DTC with GDS.
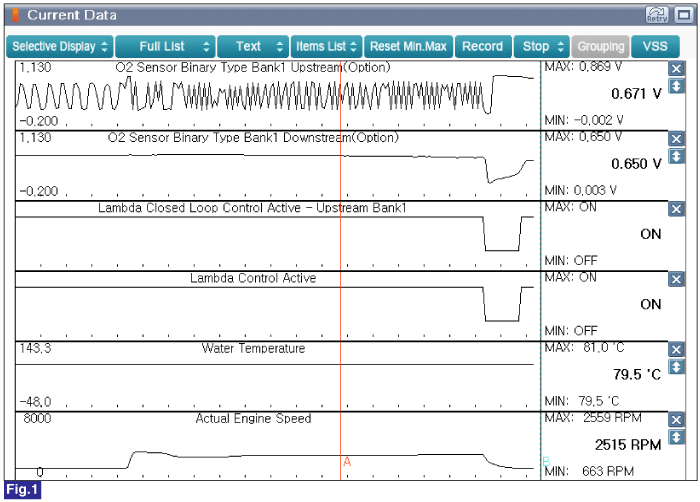
Fig.2) Approx. 2500rpm
To compare the performance of the catalyst oxygen sensor 1 and 2 can be determined.
When HO2S(S1) and HO2S(S2) have the same value, the catalyst convertor is defective.
Does the Catalyst converter operate properly? (Check variation)
 | ▶ Go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure. |
 | ▶ If no problems were found with the circuits or connectors, Replace the Catalyst converter. |