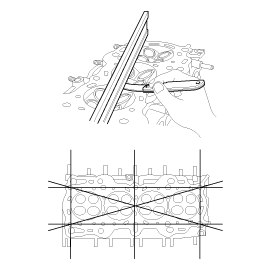
Inspect for flatness.
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surface the contacting the cylinder block and the manifolds for warpage.
Flatness of cylinder head gasket surface
Standard : Less than 0.05mm (0.0020in)
Inspect for flatness.
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surface the contacting the cylinder block and the manifolds for warpage.
Flatness of cylinder head gasket surface
Standard : Less than 0.05mm (0.0020in)

Inspect for cracks.
Check the combustion chamber, intake ports, exhaust ports and cylinder block surface for cracks. If cracked, replace the cylinder head.
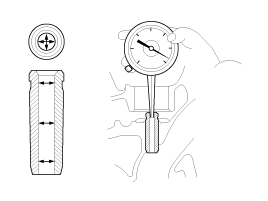
Inspect the valve stems and valve guides.
Using a caliper gauge, measure the inner diameter of valve guide.
Valve guide inner diameter :
5.500 ~ 5.512mm (0.2165 ~ 0.2170in)
Using a micrometer, measure the outer diameter of valve stem.
Valve stem outer diameter
Intake : 5.465 ~ 5.480mm (0.2152 ~ 0.2157in)
Exhaust : 5.458 ~ 5.470mm (0.2149 ~ 0.2154in)
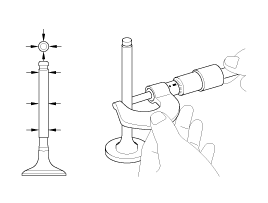
Subtract the valve stem outer diameter measurement from the valve guide inner diameter measurement.
Valve stem- to-guide clearance
Intake : 0.020 ~ 0.047mm (0.0008 ~ 0.0019in)
Exhaust : 0.030 ~ 0.054mm (0.0012 ~ 0.0021in)
If the clearance is greater than specification, replace the valve or the cylinder head.
Inspect the valves.
Check the valve is ground to the correct valve face angle.
Check that the surface of valve for wear.
If the valve face is worn, replace the valve.
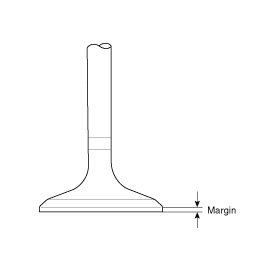
Check the valve head margin thickness.
If the margin thickness is less than minimum, replace the valve.
Margin
Standard
Intake : 1.1mm (0.0433in)
Exhaust : 1.26mm (0.0496in)
Check the length of valve.
Valve length
Standard
Intake : 93.15mm (3.6673 in)
Exhaust : 92.60mm (3.6457 in)
Check the surface of valve stem tip for wear.
If the valve stem tip is worn, replace the valve.
Inspect the valve seats.
Check the valve seat for evidence of overheating and improper contact with the valve face. If the valve seat is worn, replace the cylinder head.
Check the valve guide for wear. If the valve guide is worn, replace the cylinder head.
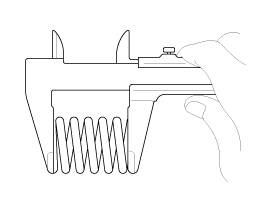
Inspect the valve springs.
Using a steel square, measure the out-of-square of valve spring.
Using a vernier calipers, measure the free length of valve spring.
Valve spring
Standard
Free height : 45.1mm (1.7755in)
Out of square : Less than 1.5˚
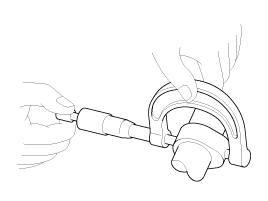
Inspect the cam height.
Using a micrometer, measure the cam height.
Cam height
[1.4L]
Intake : 42.85mm (1.6870in)
Exhaust : 42.85mm (1.6870in)
[1.6L]
Intake : 43.85mm (1.7264in)
Exhaust : 42.85mm (1.6870in)
If the cam lobe height is less than specified, replace the camshaft.
Inspect the camshaft journal clearance.
Clean the bearing caps and camshaft journals.
Place the camshafts on the cylinder head.
Lay a strip of plastigage across each of the camshaft journal.
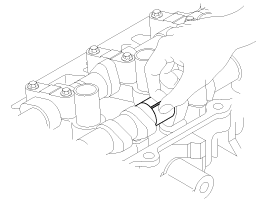
Install the bearing caps and tighten the bolts with specified torque.
Tightening torque :
M6 bolts :
11.8 ~ 13.7Nm (1.2 ~ 1.4kgf.m, 8.7 ~ 10.1lb-ft)
M8 bolts :
18.6 ~ 22.6Nm (1.9 ~ 2.3 kgf.m, 13.7 ~ 16.6lb-ft)
Do not turn the camshaft.
Remove the bearing caps.
Measure the plastigage at its widest point.
Bearing oil clearance
Standard : 0.027 ~ 0.058mm (0.0011 ~ 0.0023in)
Limit : 0.1mm ( 0.0039in)
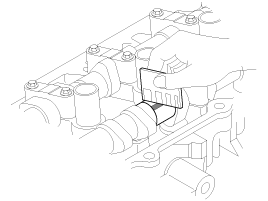
If the oil clearance is greater than specified, replace the camshaft. If necessary, replace the bearing caps and cylinder head as a set.
Inspect the camshaft end play.
Install the camshafts.
Using a dial indicator, measure the end play while moving the camshaft back and forth.
Camshaft end play
Standard : 0.1 ~ 0.2mm (0.0039 ~ 0.0079in)
If the end play is greater than specified, replace the camshaft. If necessary, replace the bearing caps and cylinder head as a set.
Remove the camshafts.
Inspect the CVVT for smooth rotation.
Clamp the camshaft using a vise. Be careful not to damage the cam lobes and journals in the vise.
Check that the CVVT is locked by turning it clockwise or counterclockwise. It must not rotate.
Seal one of the two advance holes in the camshaft journal with tape.
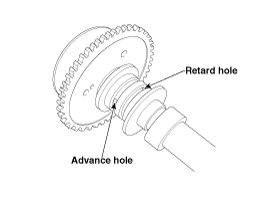
Apply approx. 150 kPa (1.5 kgf/㎠, 21 psi ) of compressed air into the unsealed advance hole to release the lock.
Cover the oil paths with a piece of cloth when applying compressed air to prevent oil from spraying.
With compressed air applied, rotate the CVVT into the advance direction (counterclockwise) within its phasing range and check that the CVVT turns smoothly.
CVVT phasing range
25˚±1˚ (from the most retarded position to the most advanced position)
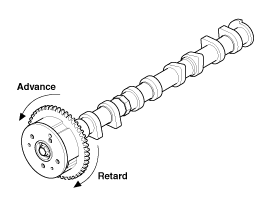
Rotate the CVVT into the most retarded position (clockwise) and then check that the CVVT is locked.