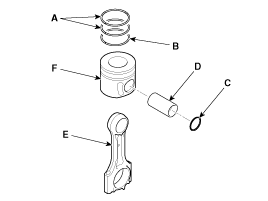
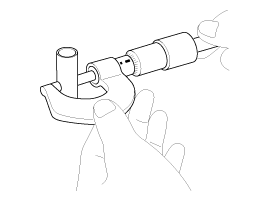
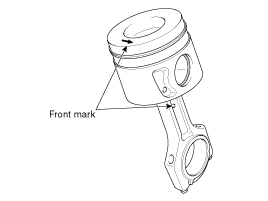
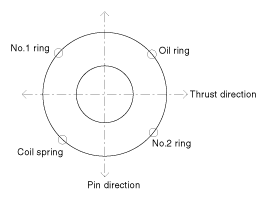
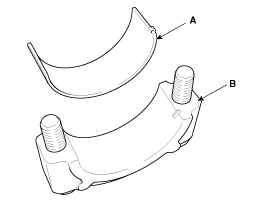
Remove the piston and connecting rod assemblies .
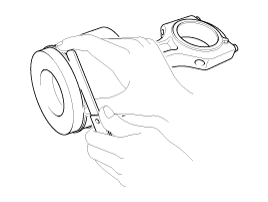
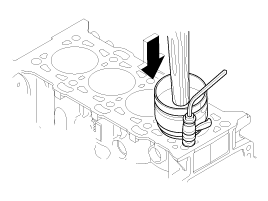
Using a ridge reamer, remove all the carbon from the top of the cylinder.
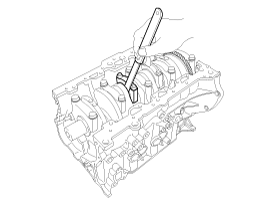
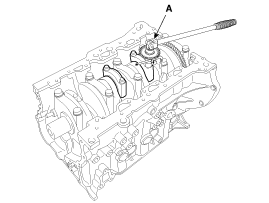
Remove the connecting rod bearing caps (A).
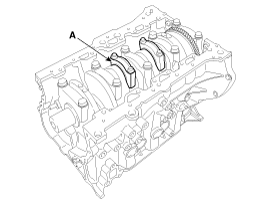
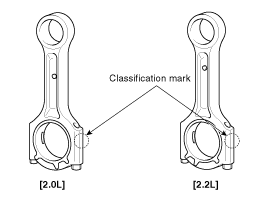
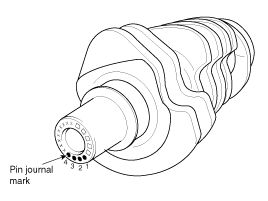
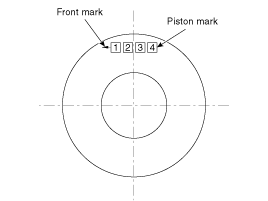
Mark the connecting rod, and caps to be able to reassemble in the original position and direction.
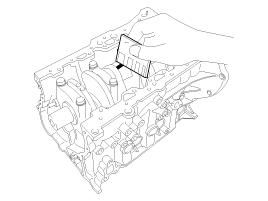
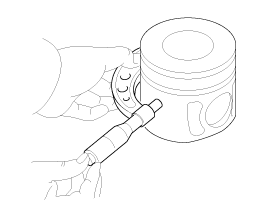
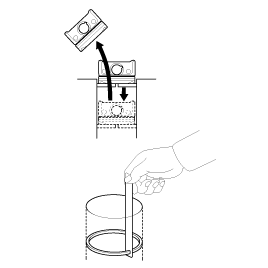
Push the piston and connecting rod assembly with upper bearing through the top of the cylinder block.
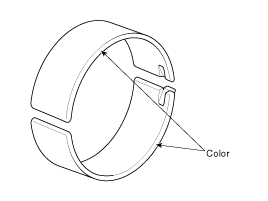
Keep the connecting rod ands cap with their bearings assembled together.
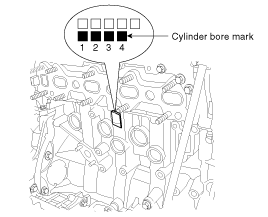
Arrange the piston and connecting rod assemblies in the correct order.
Mark the piston and connecting rod assemblies to be able to reassemble in the original position.